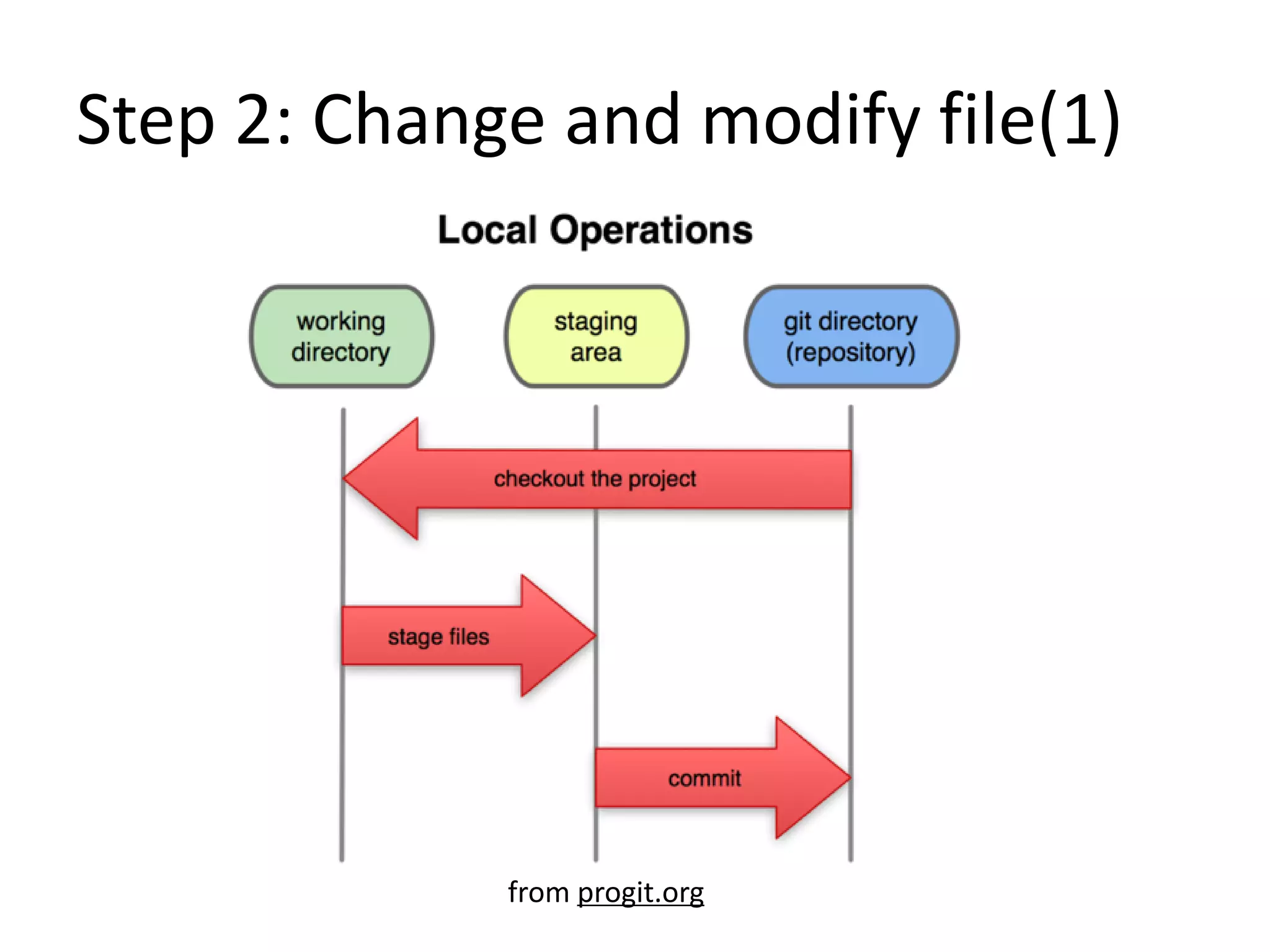
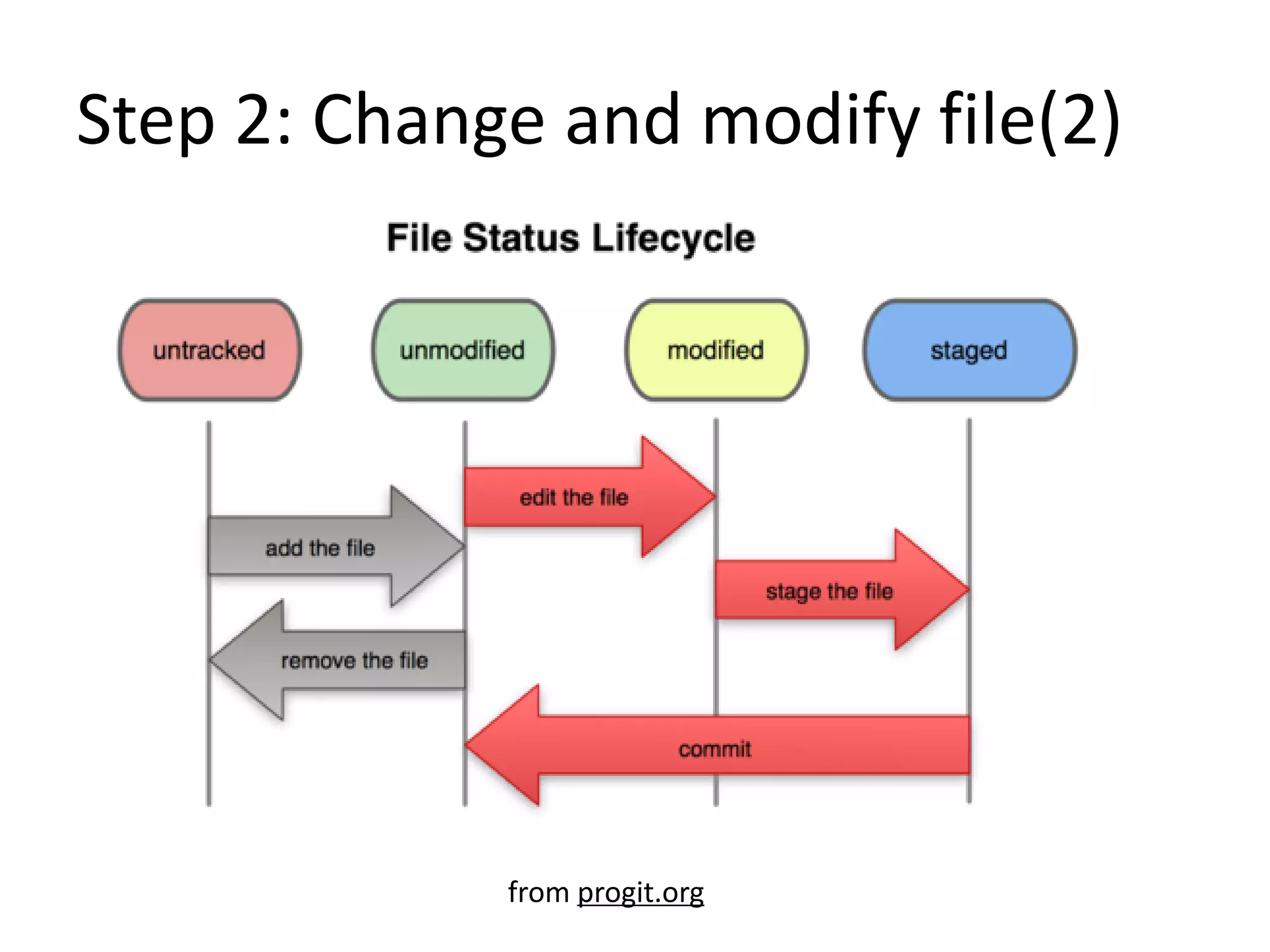
Git is a distributed version control system that focuses on speed, efficiency, and usability for large projects. It allows for distributed development, non-linear development, efficient handling of large projects, and cryptographic authentication of history. The document provides an overview of Git and outlines 8 steps for a Git study guide, including setting up the environment, initializing and committing projects, viewing logs and history, tagging, branching, and working with remote repositories. Resources for further learning about Git are also listed.