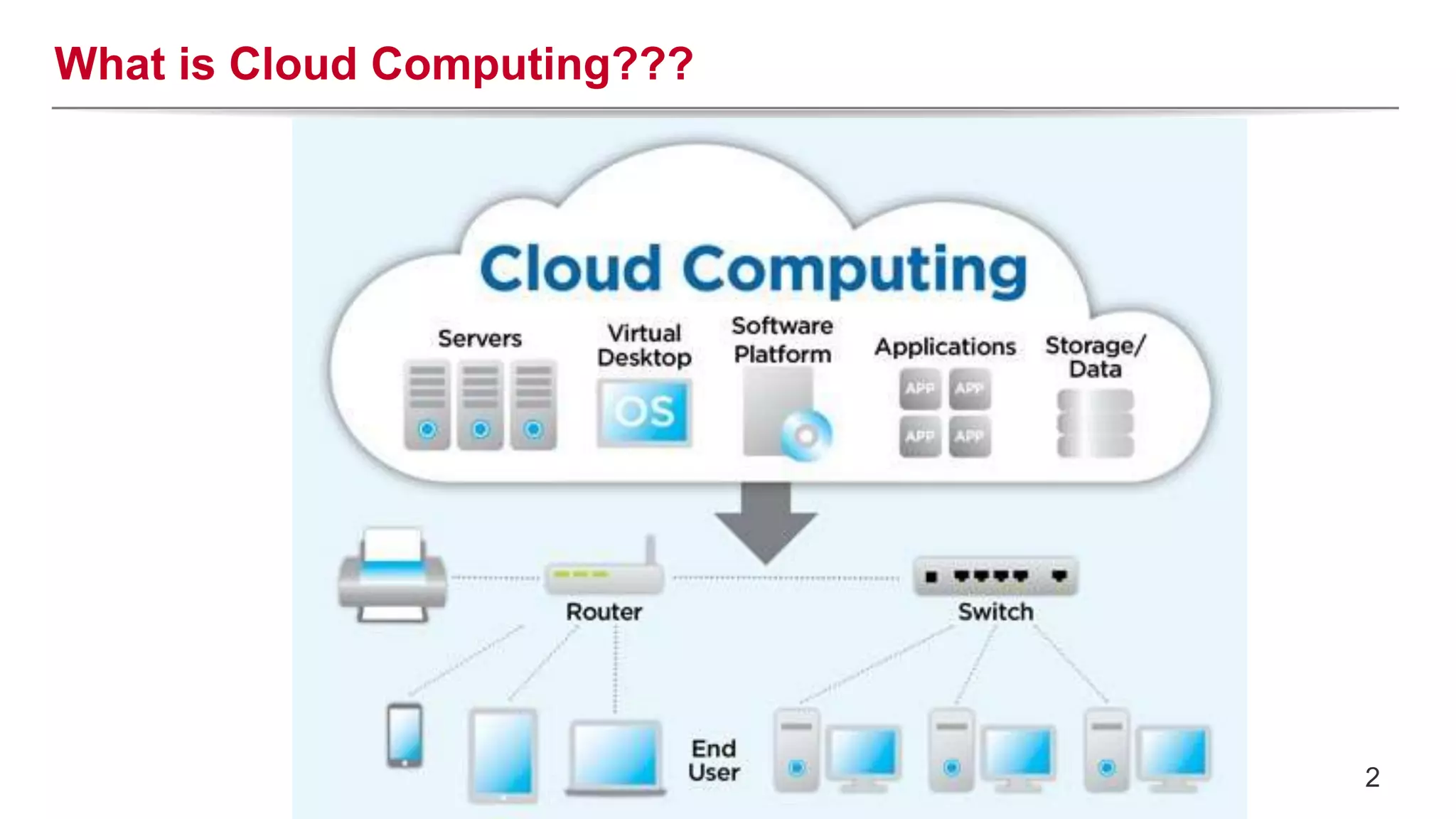
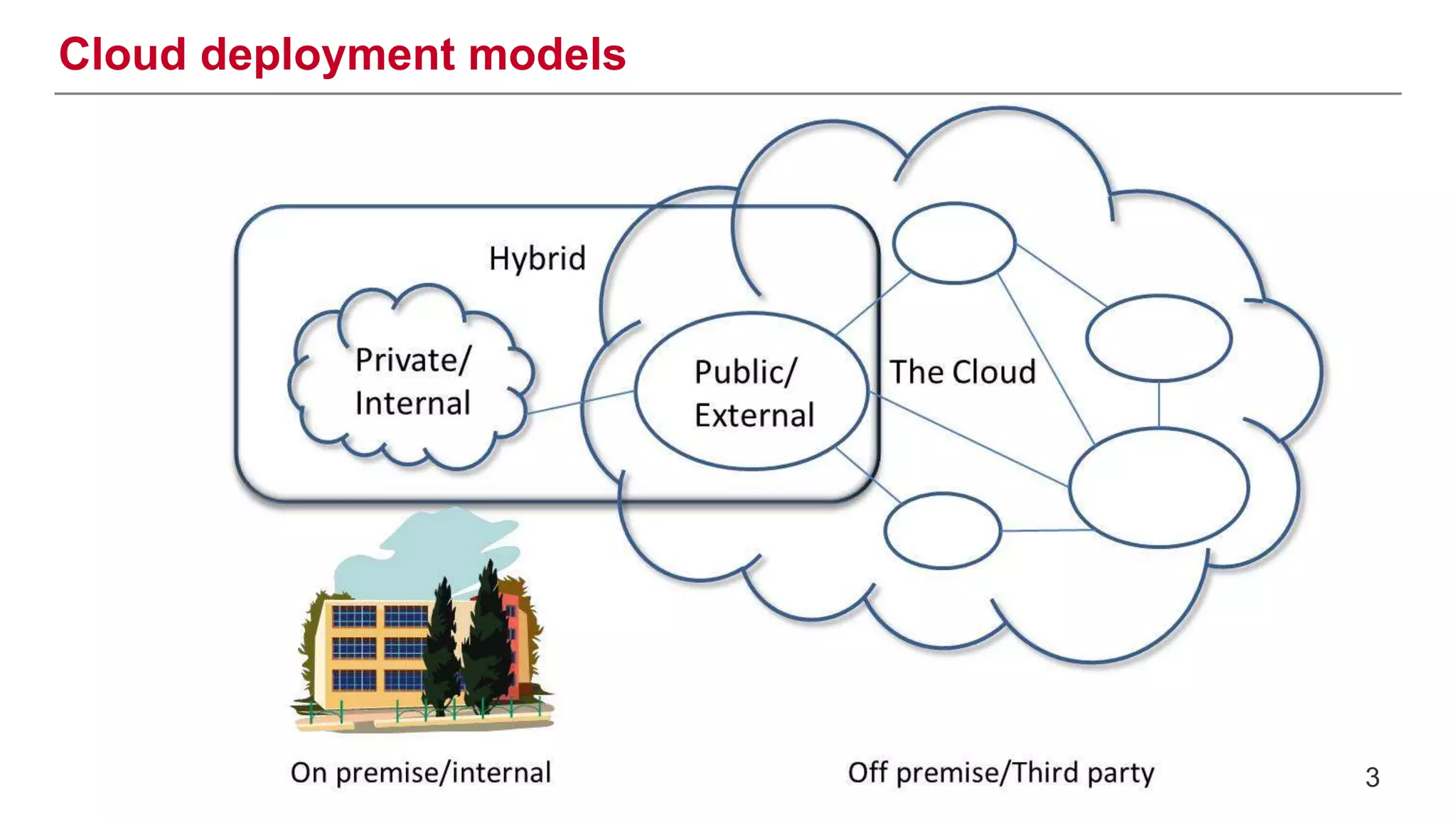
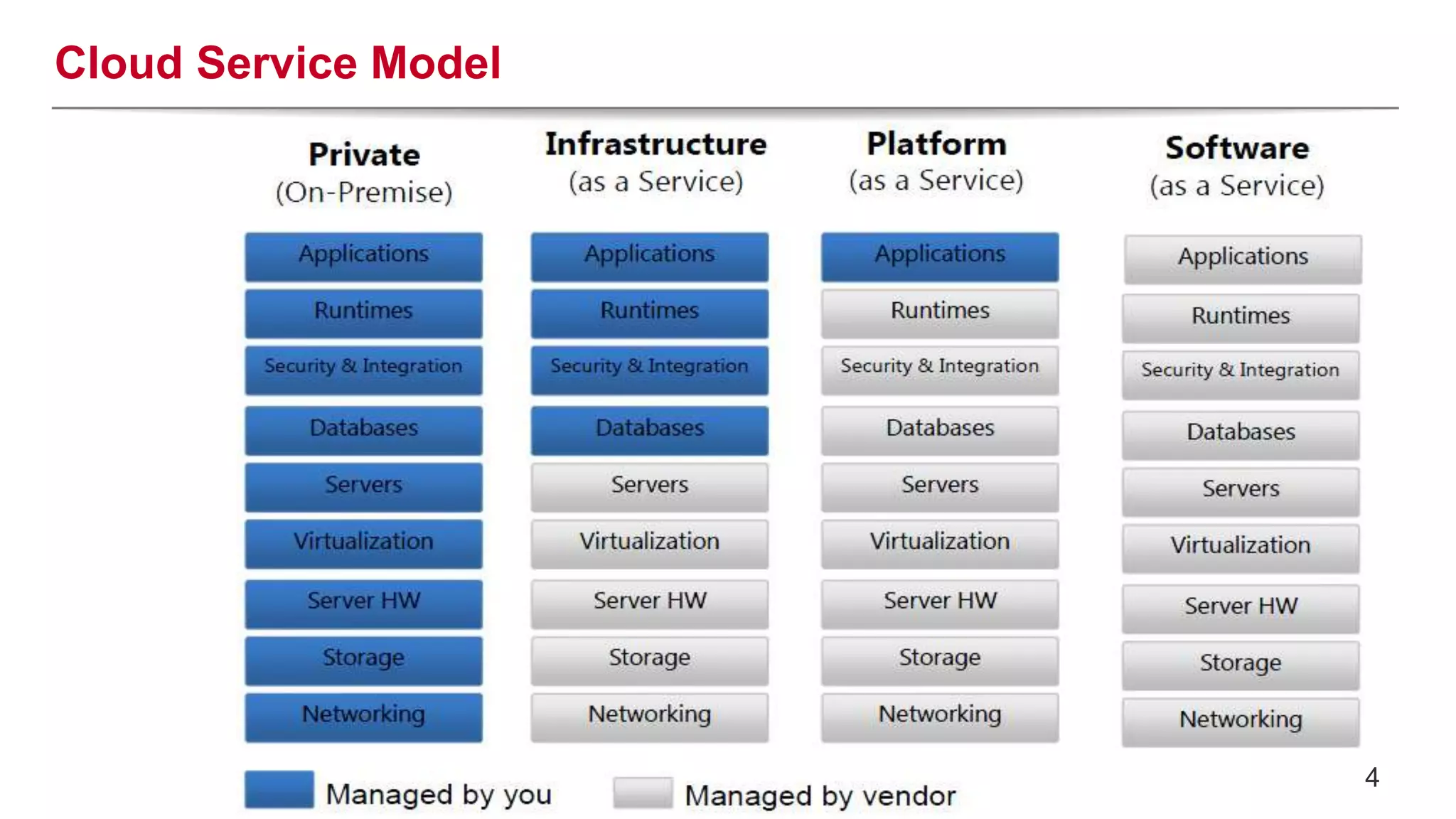
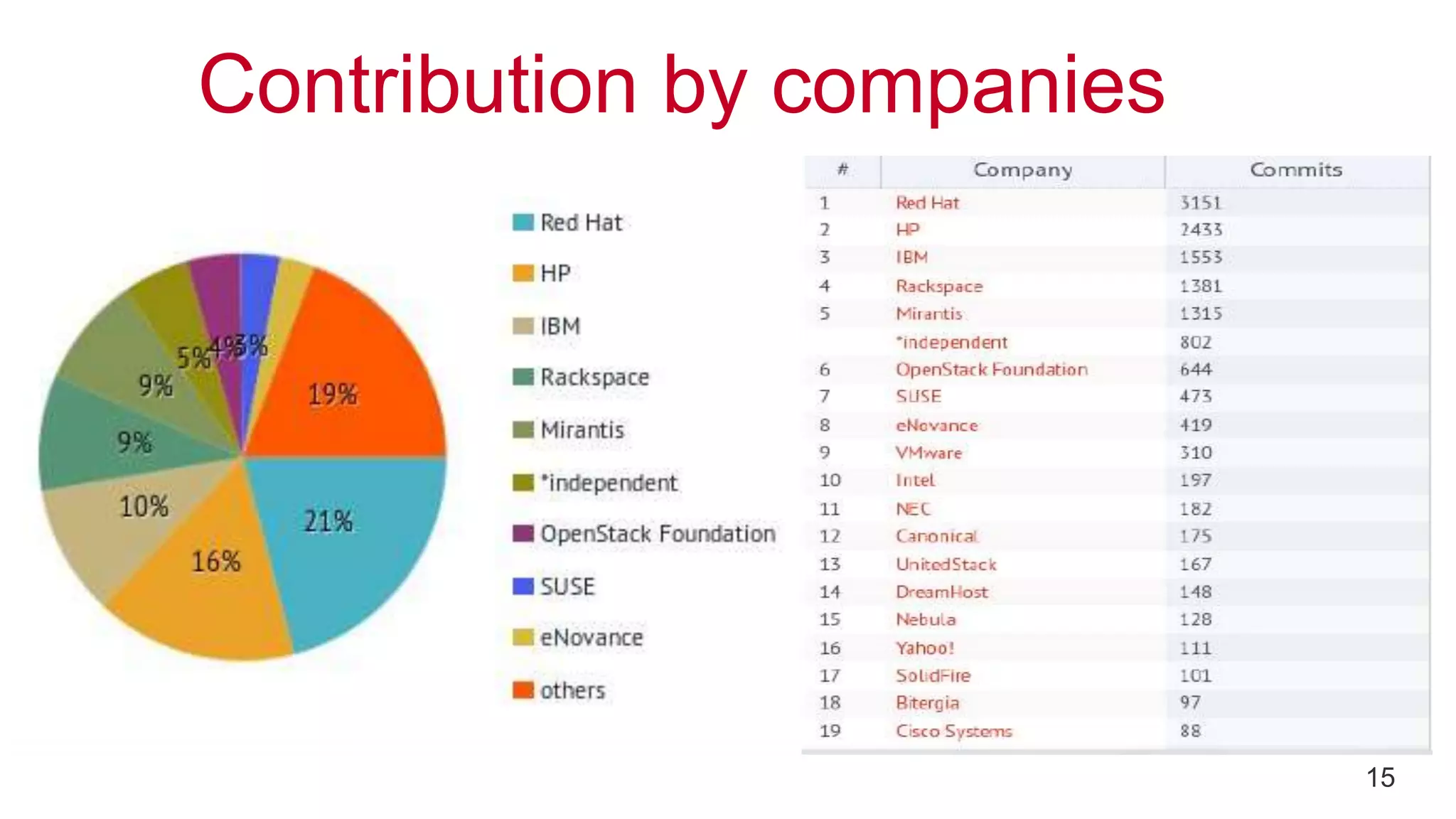
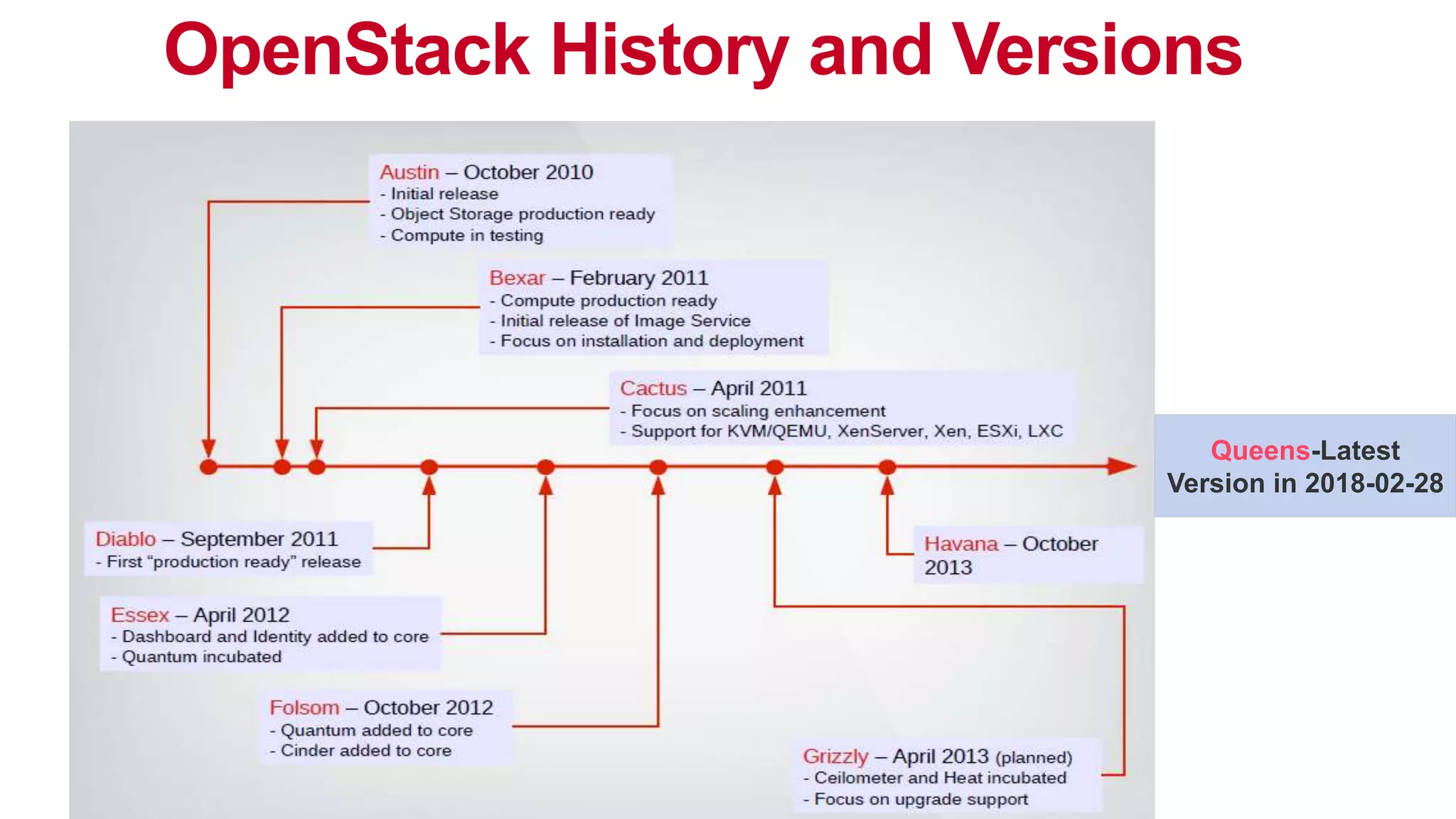
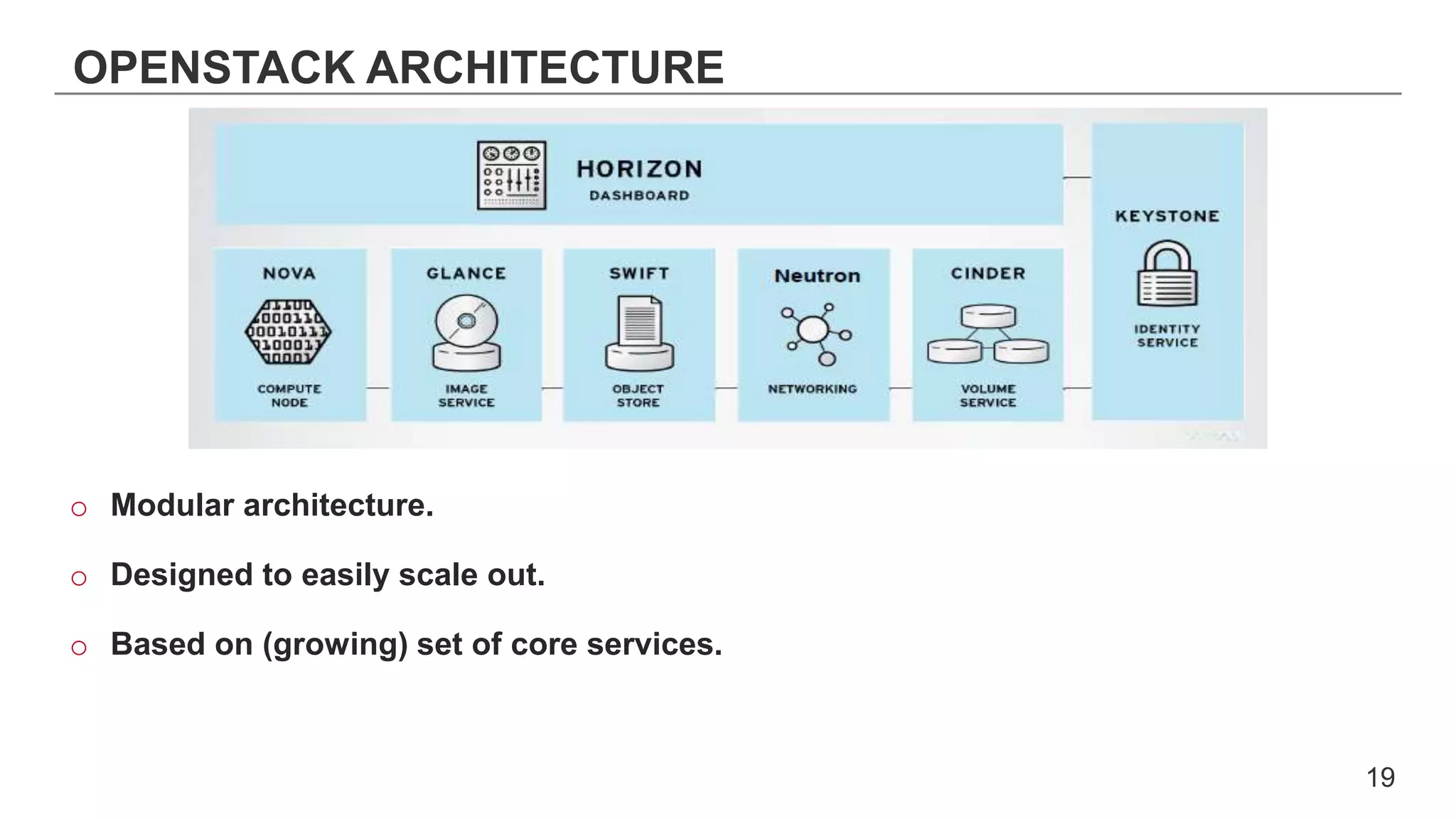
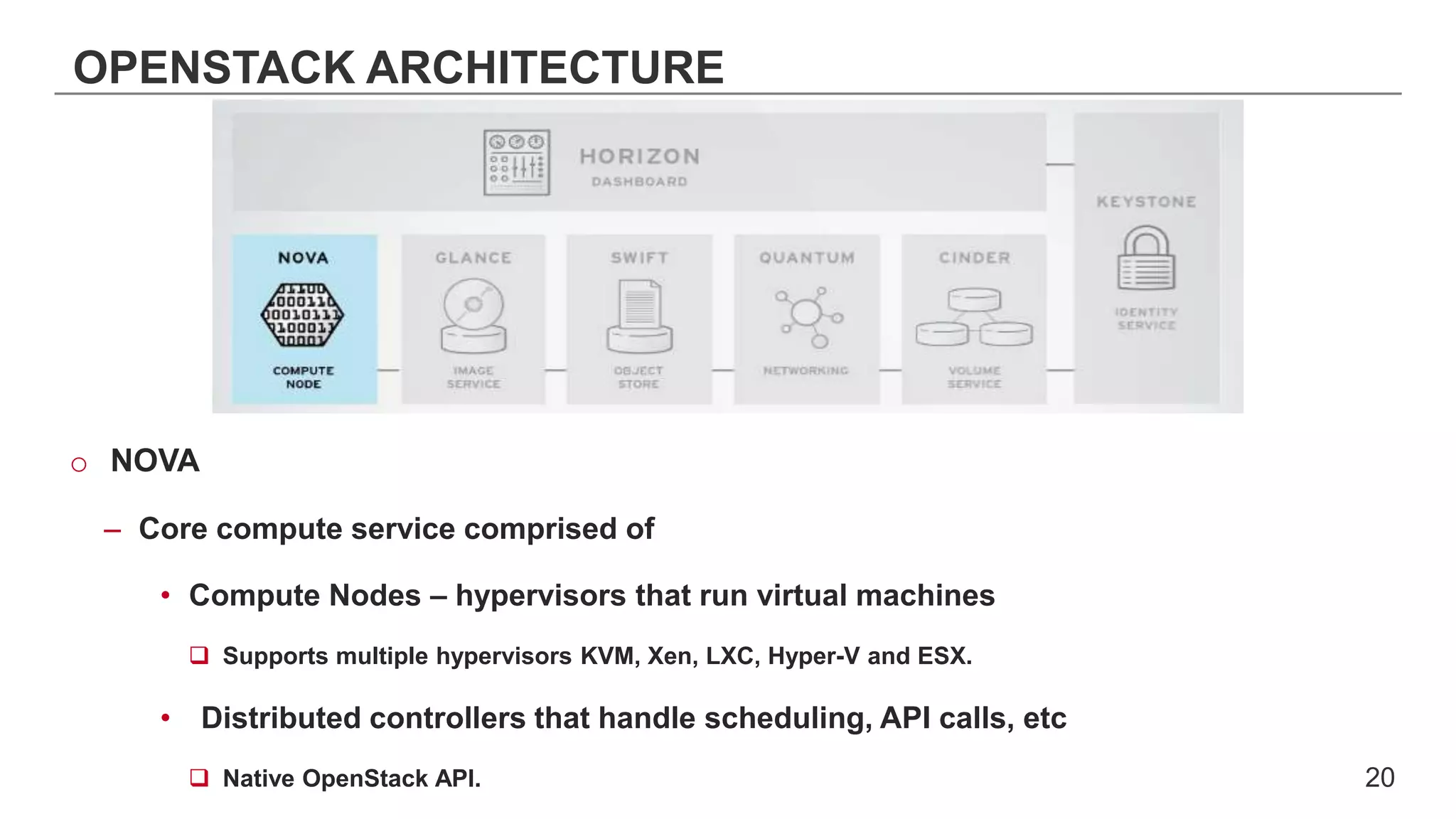
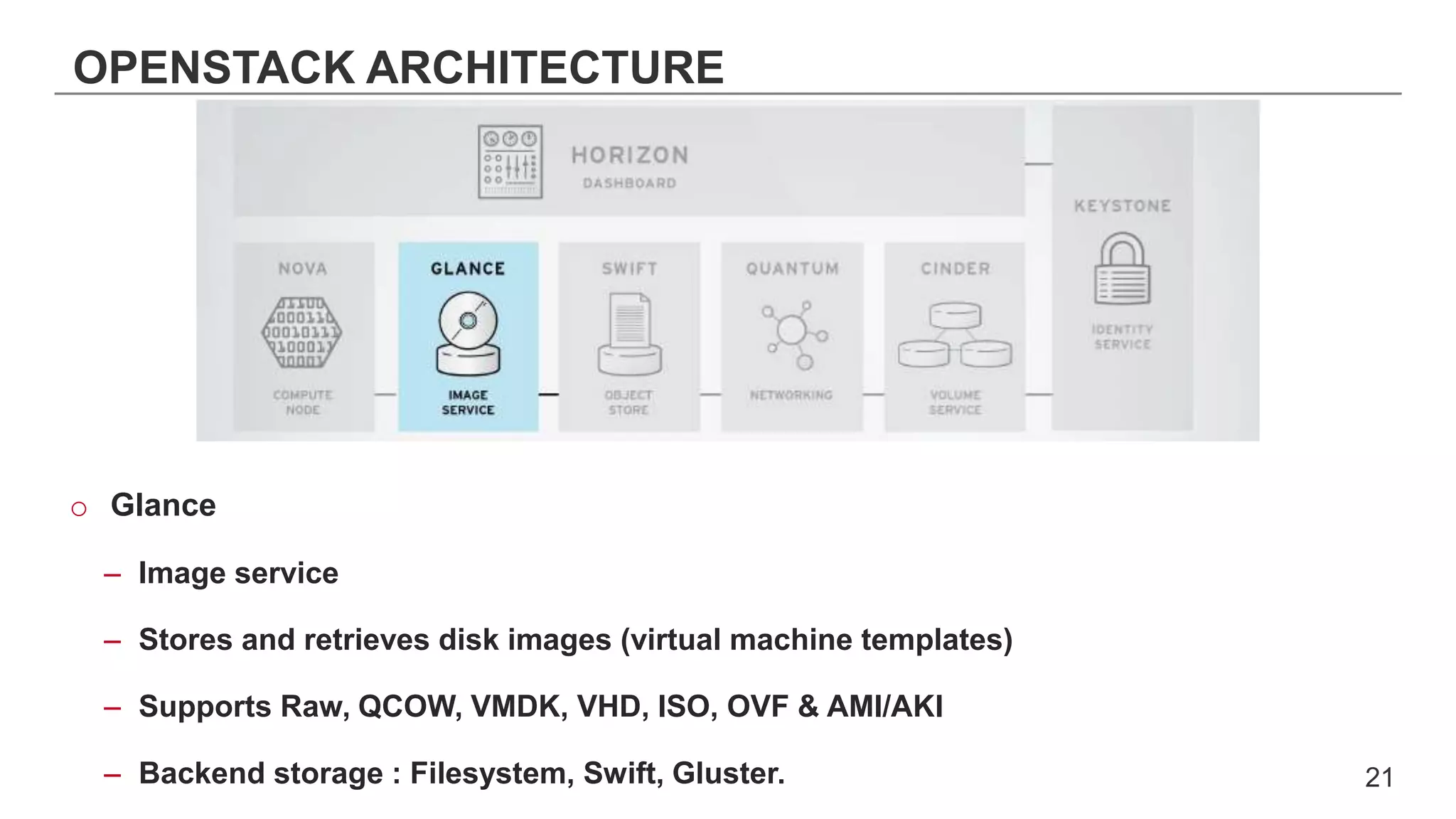
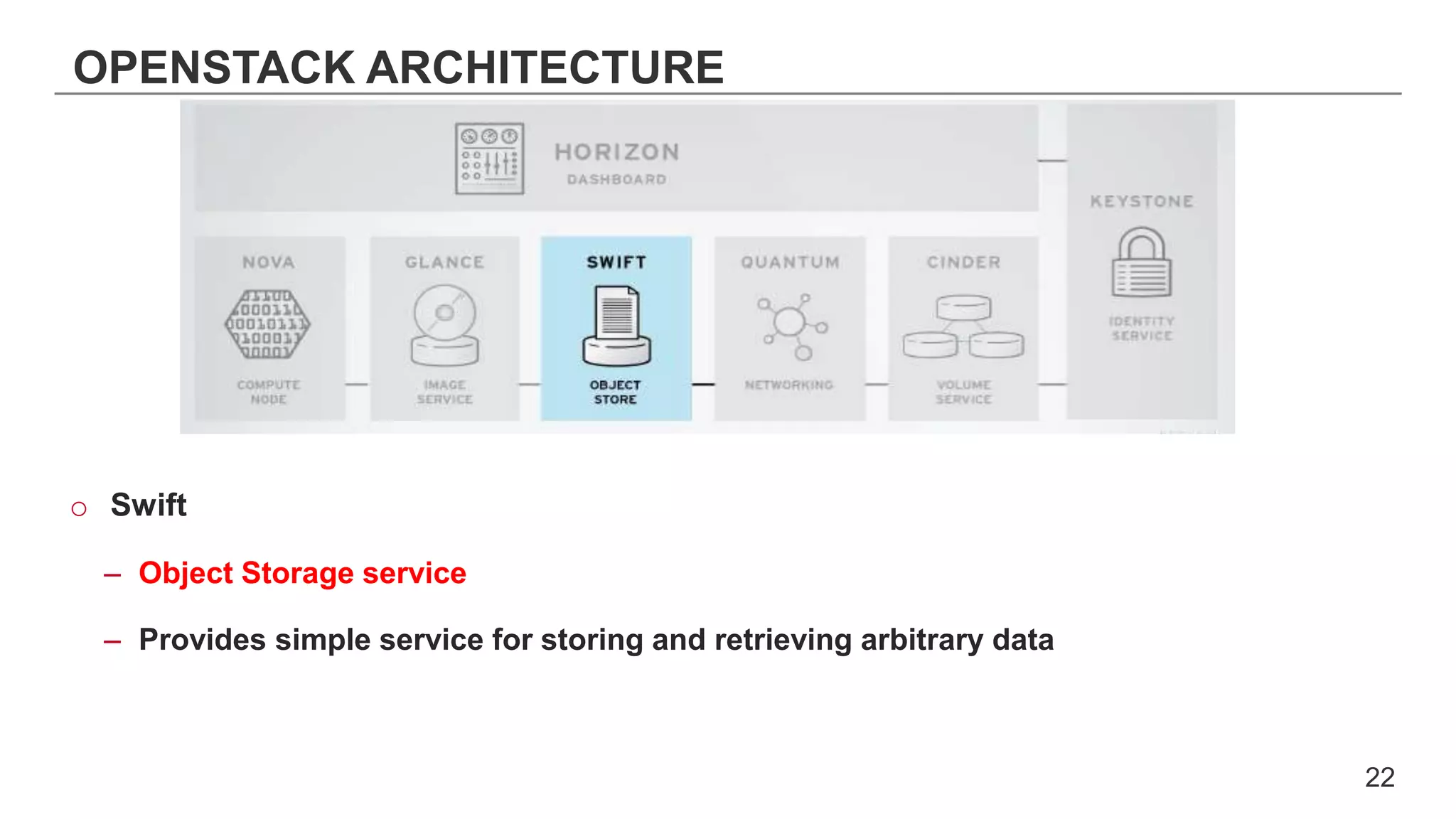
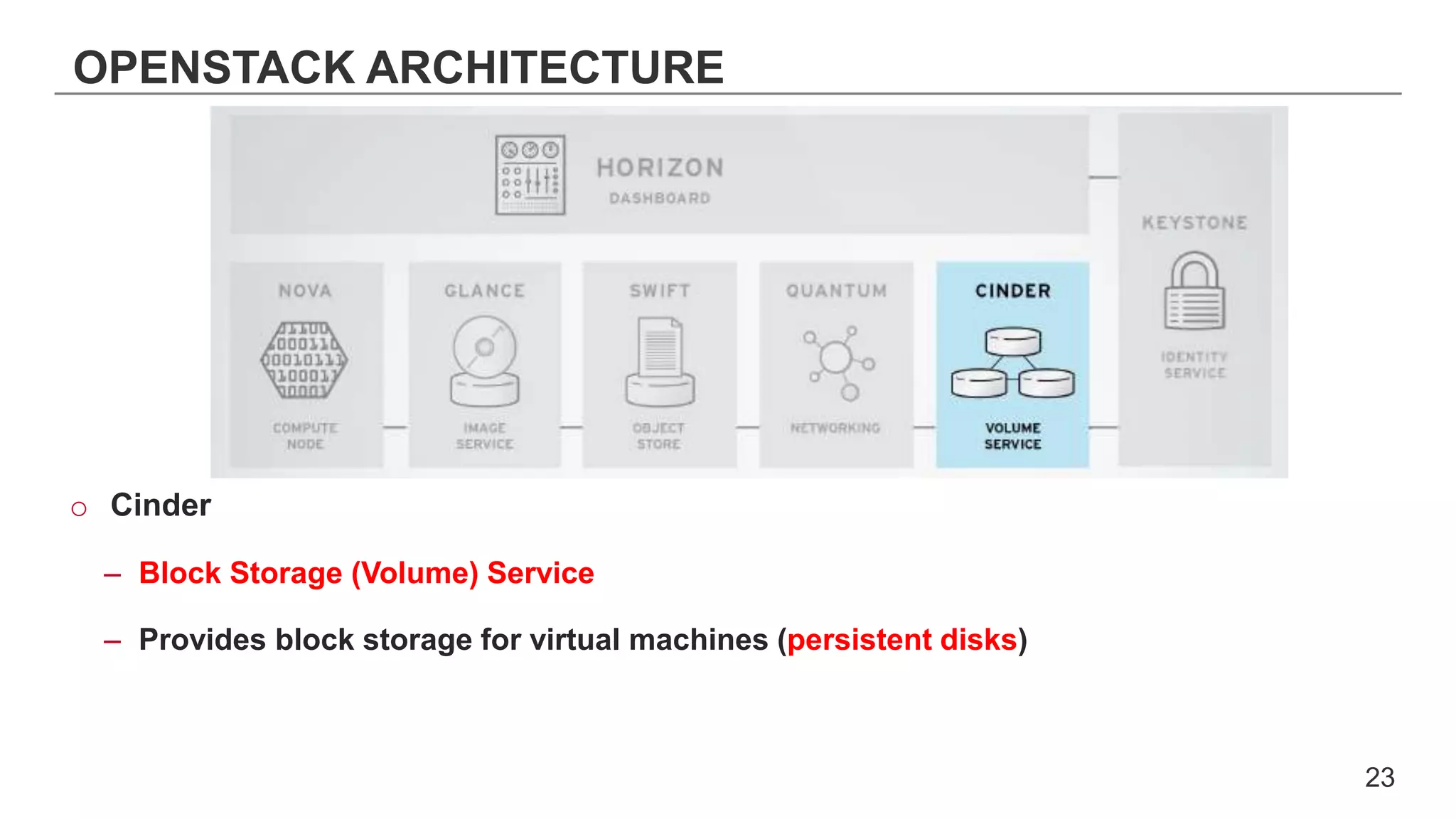
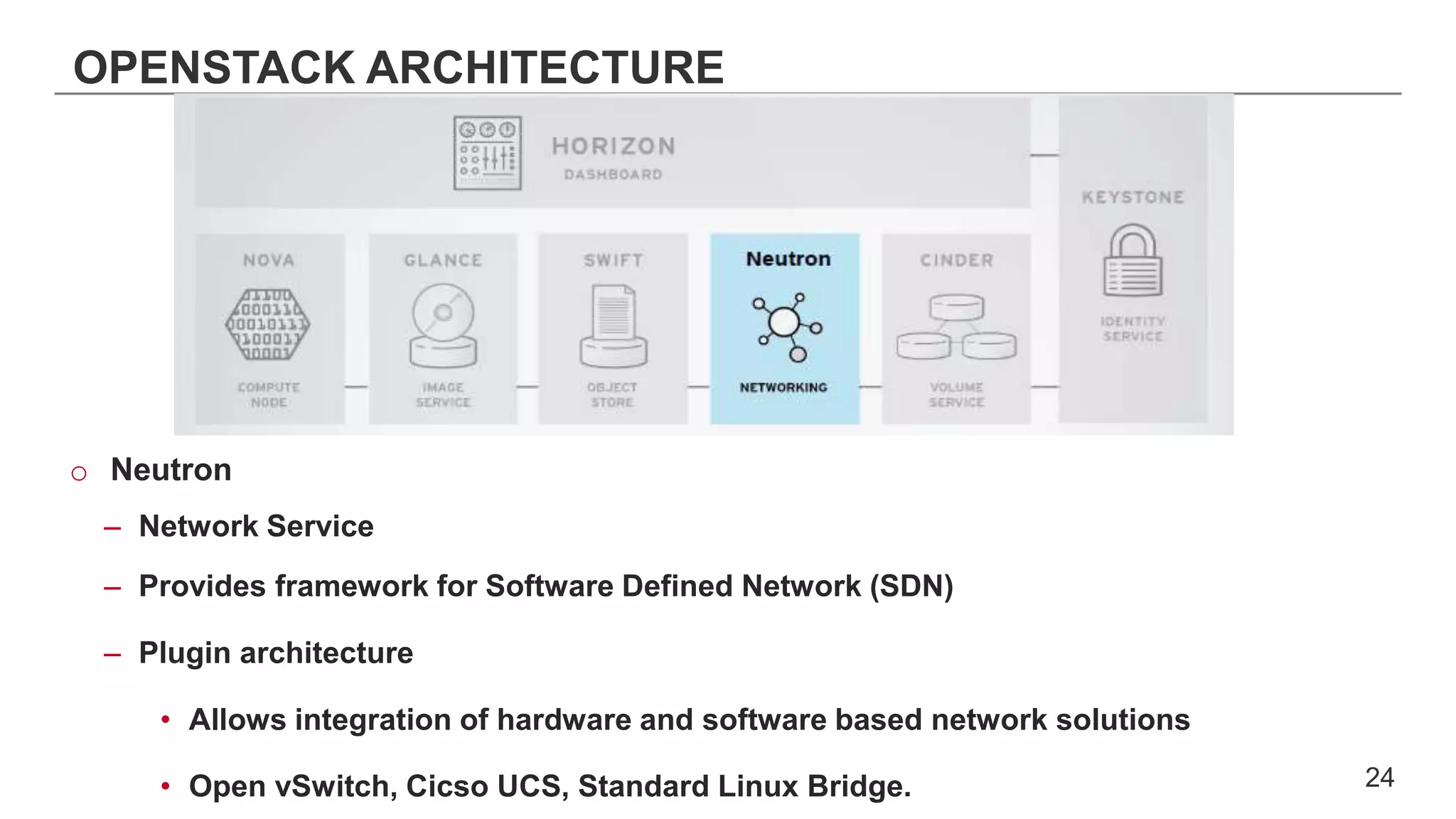
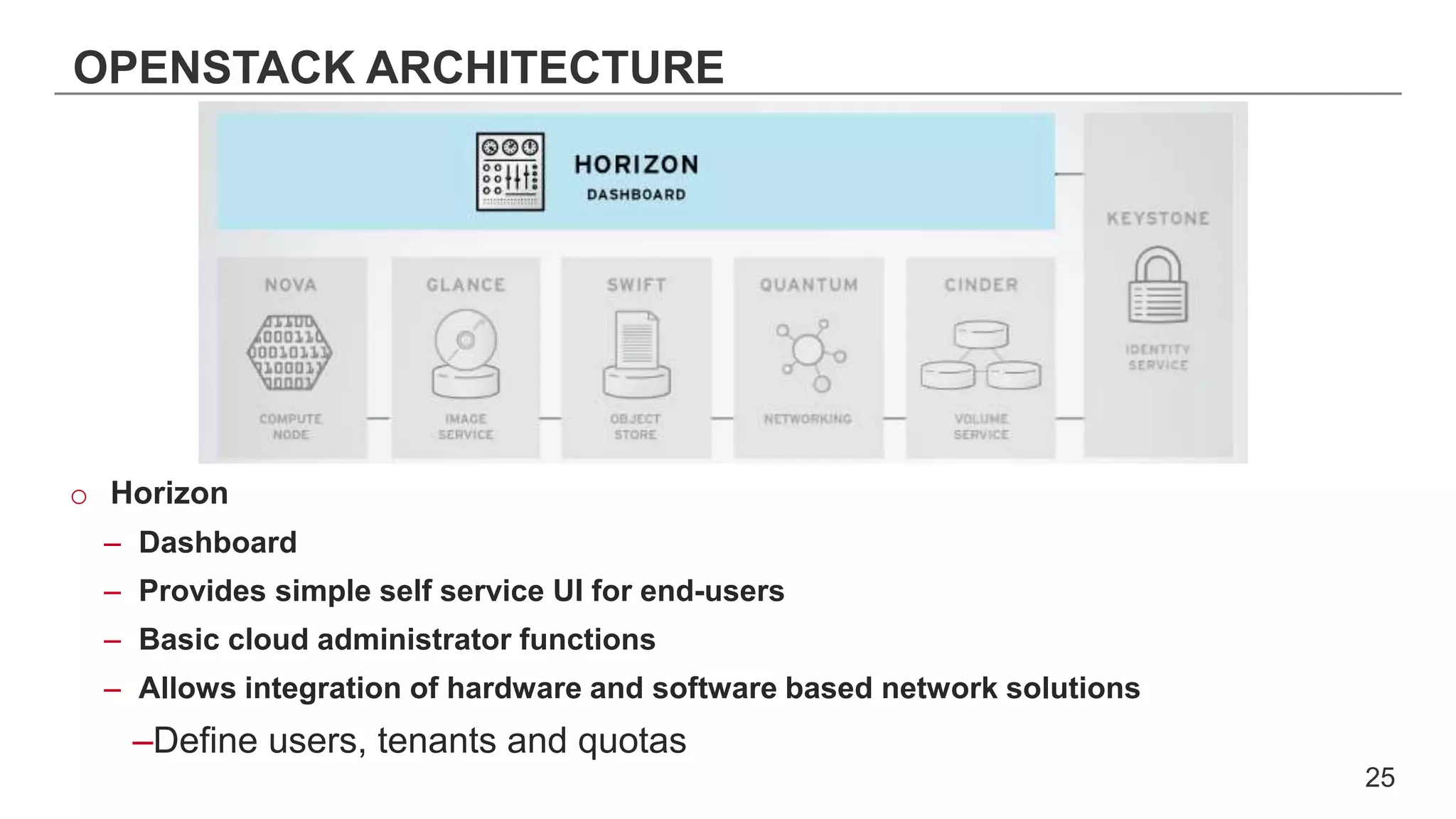
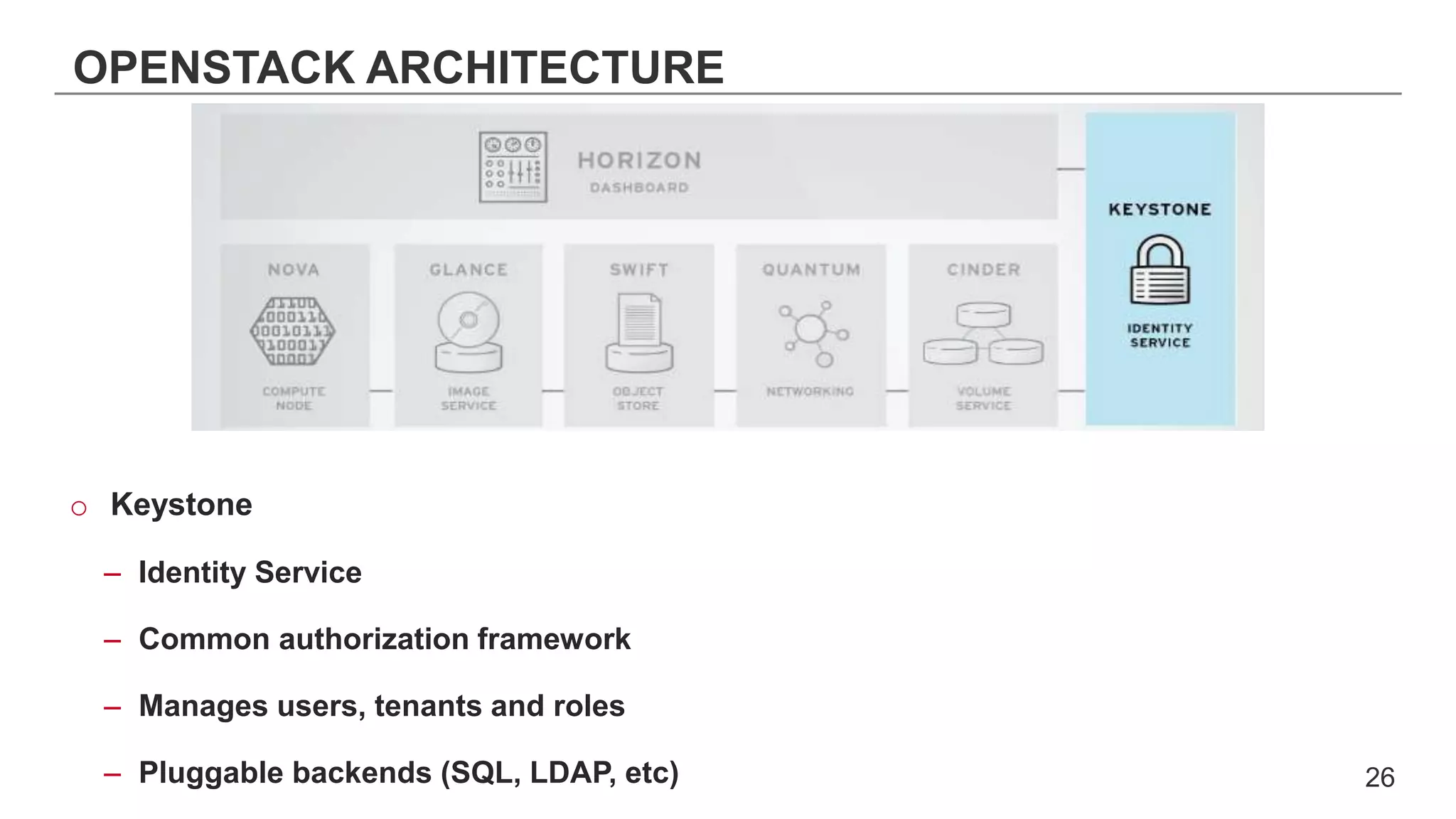
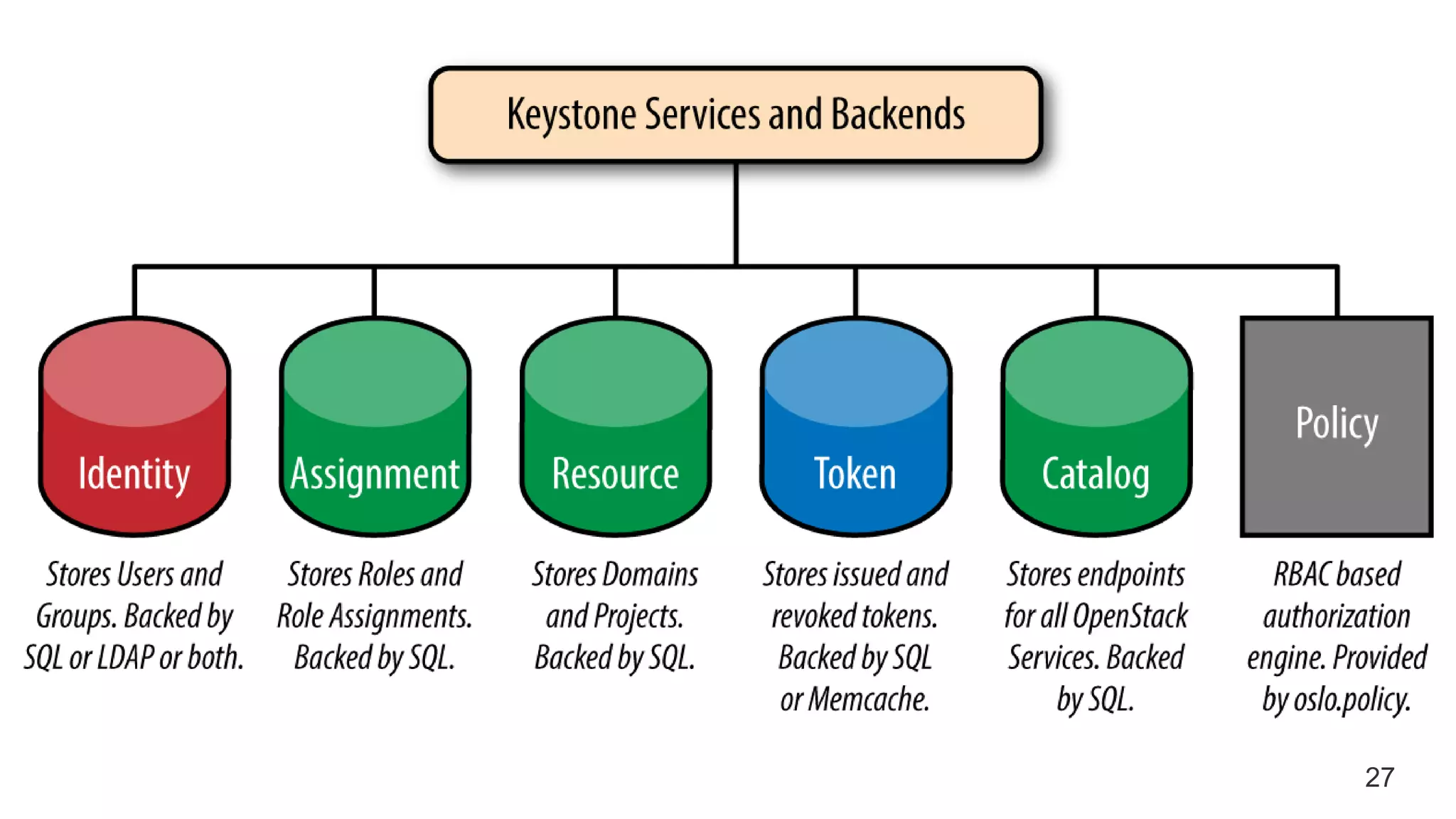
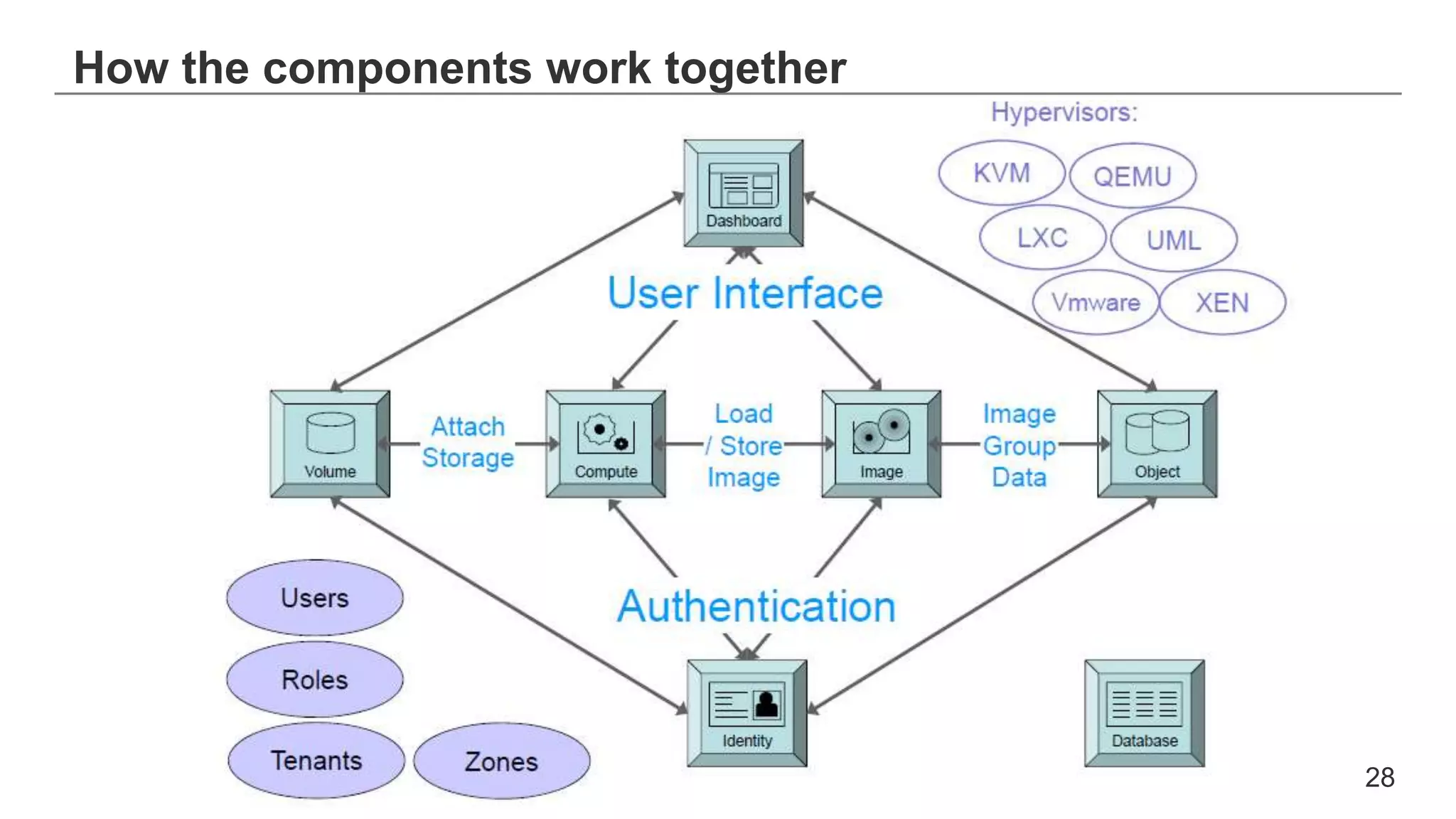
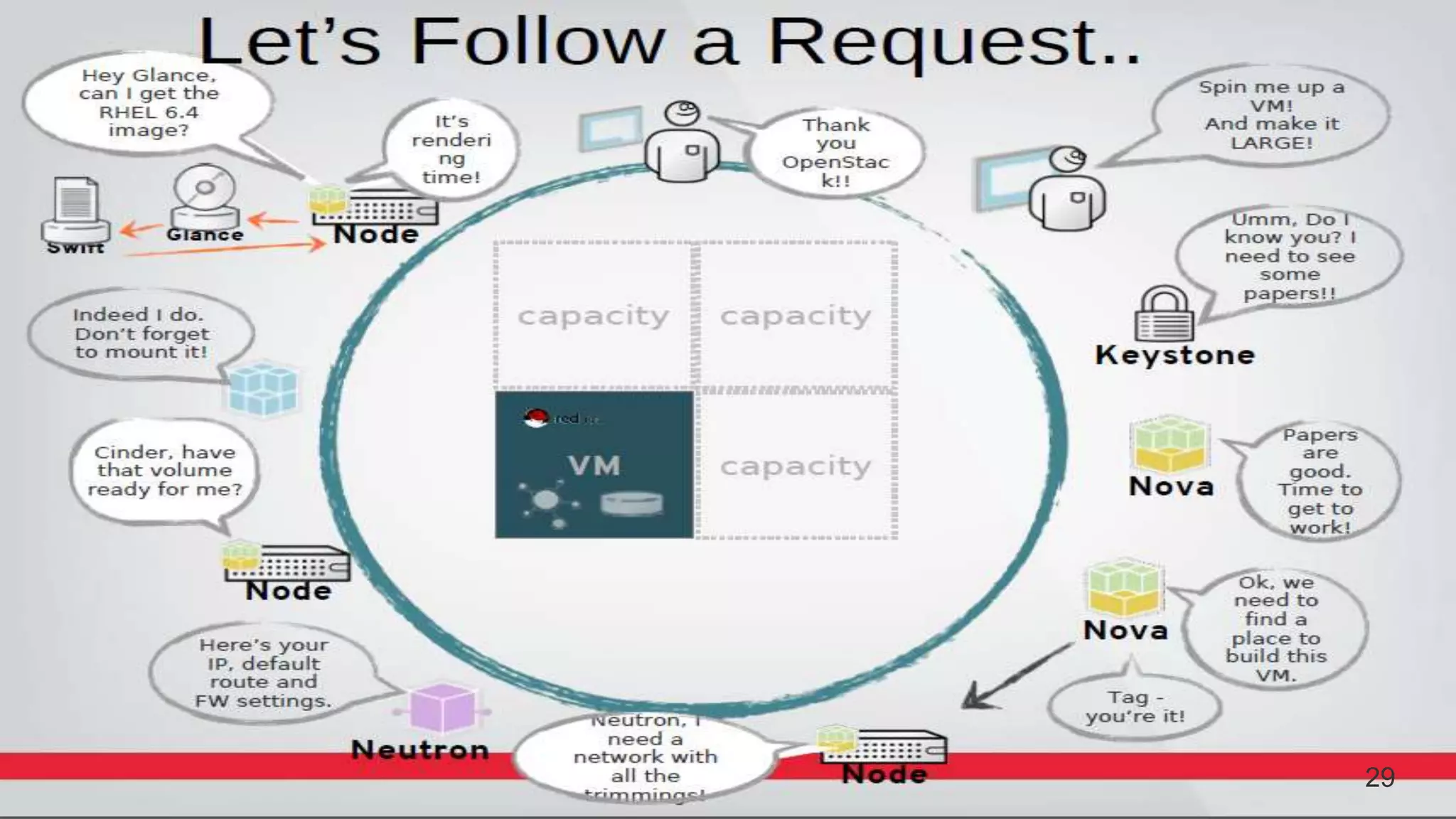
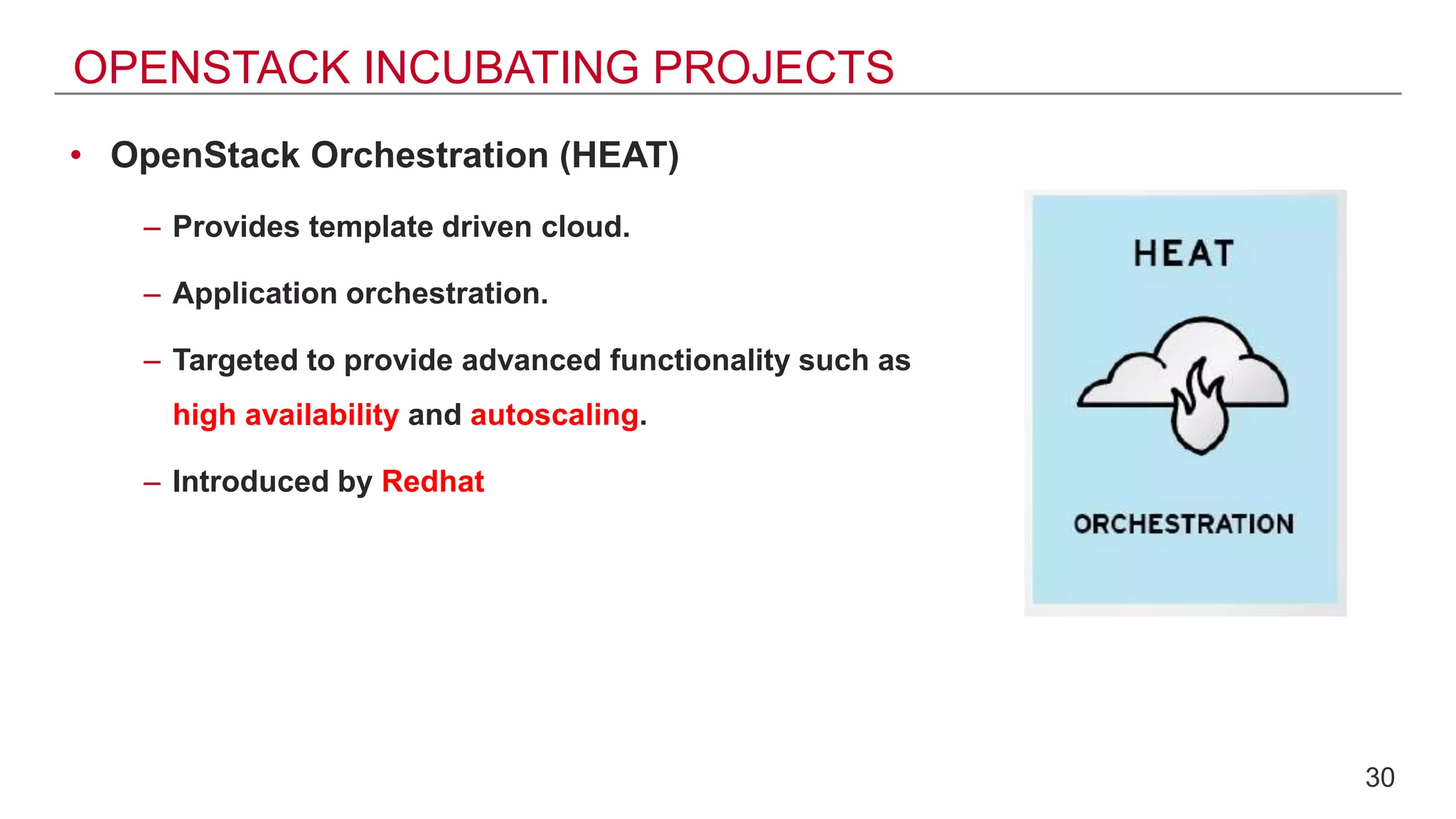
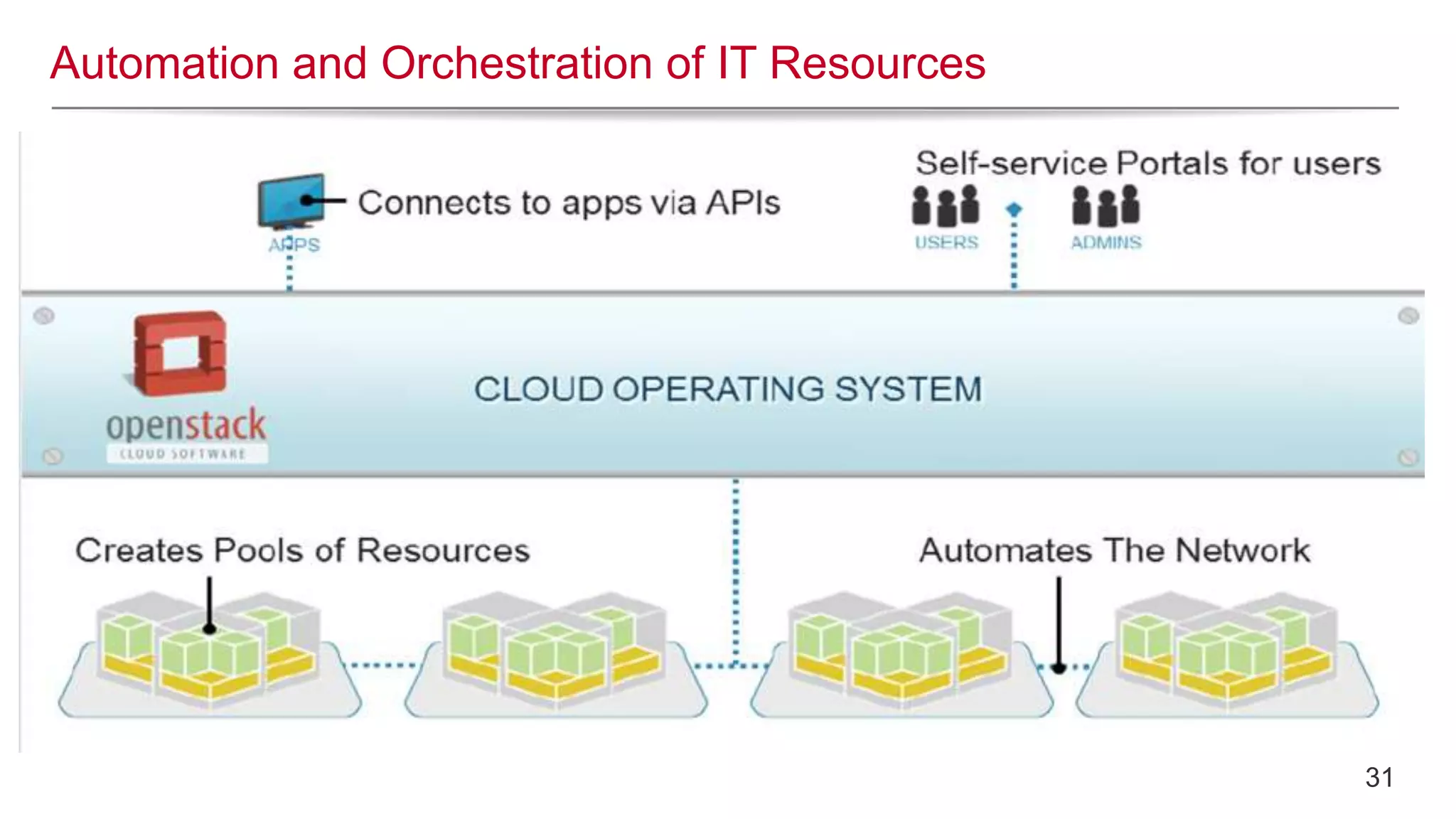
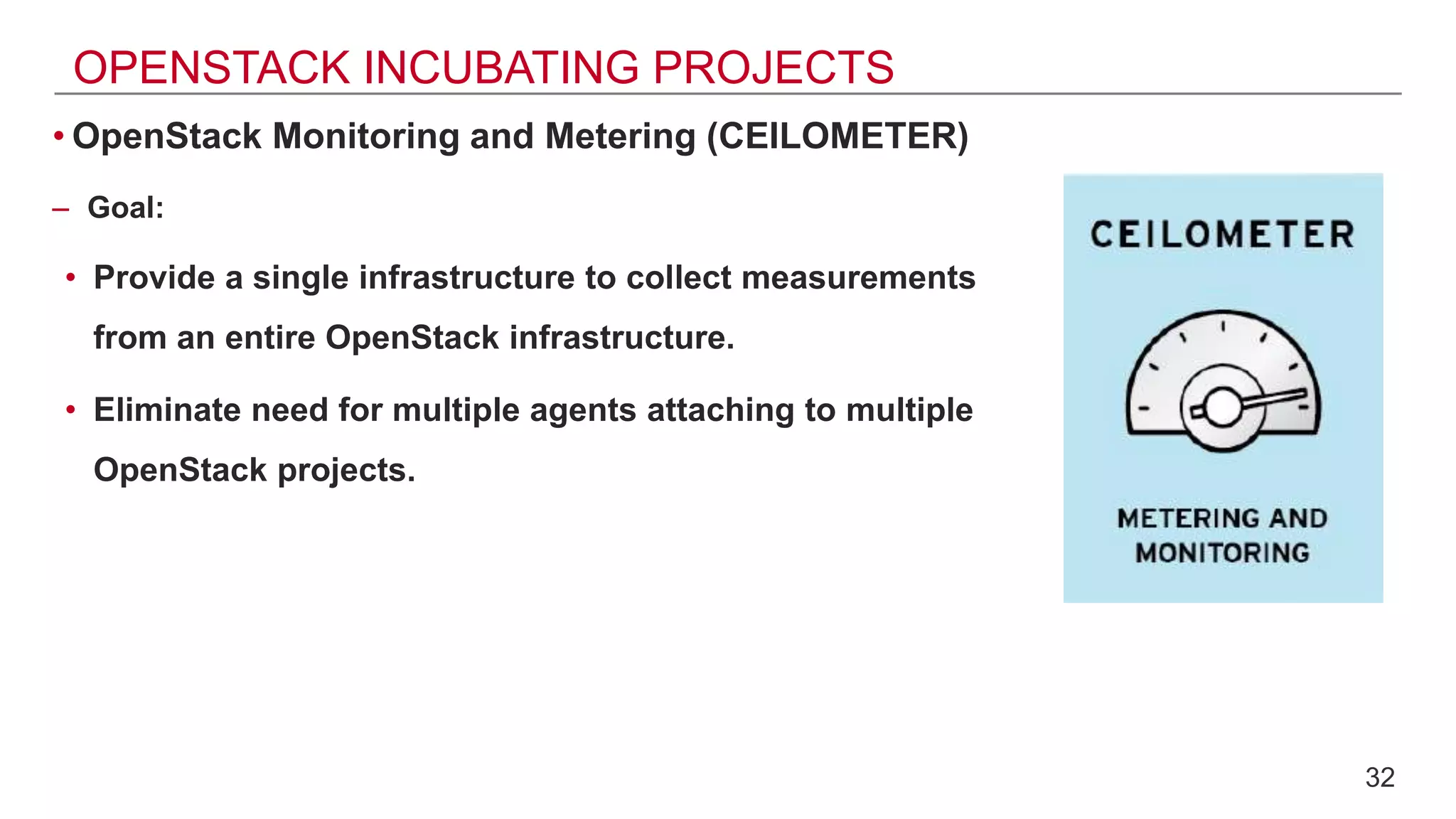
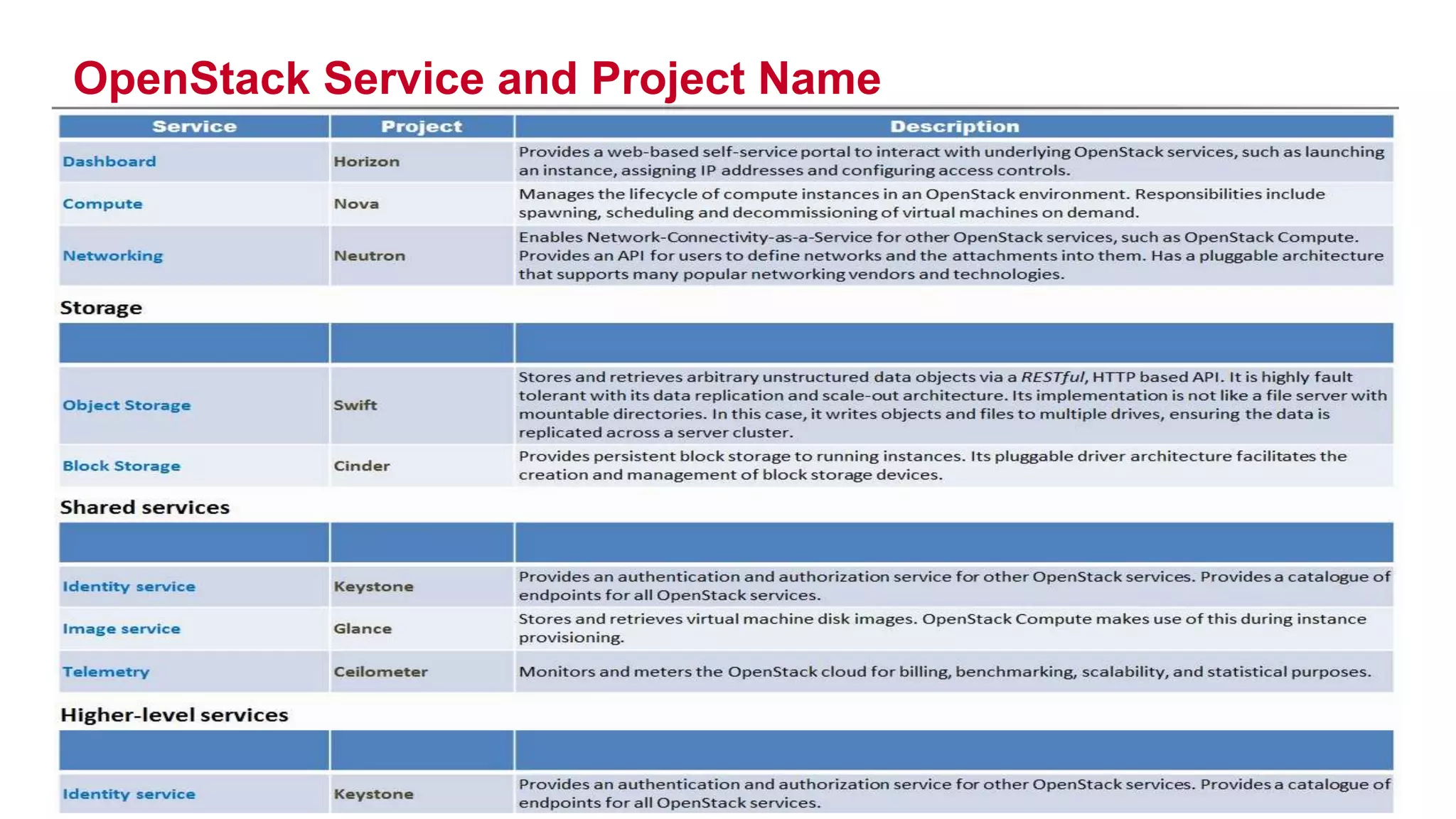
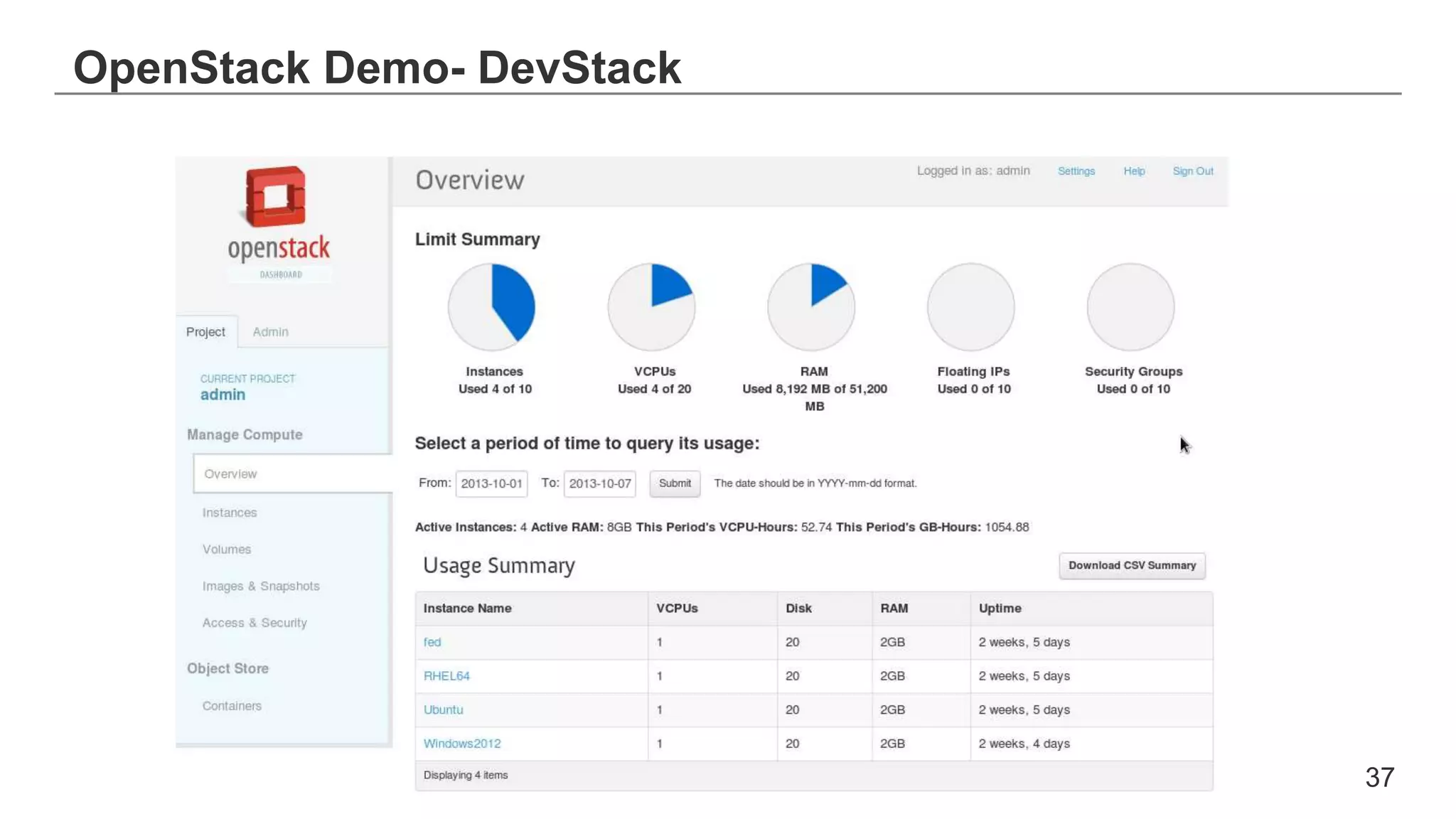
This document provides an introduction to OpenStack, an open source cloud computing platform. It begins with definitions of cloud computing and cloud deployment models. It then explains that OpenStack is an open source software platform for building private and public clouds with components that provide compute, storage, and networking services. The document outlines the core OpenStack components, describes how they work together through a modular architecture, and lists some incubating projects. It provides resources for learning more about OpenStack, trying it out, and deploying it through various options like distributions, packaged deploys, and configuration tools.