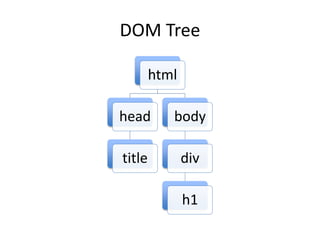
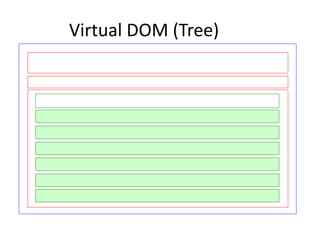
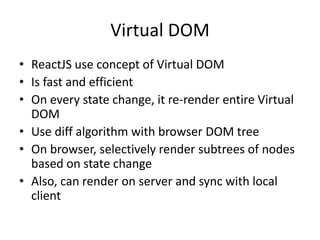
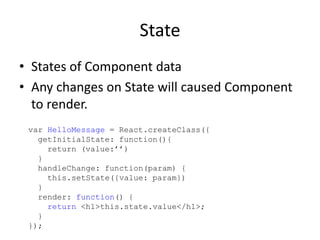
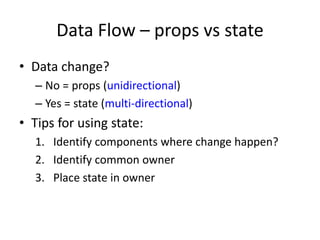
ReactJS is a library for UI development, emphasizing a component-based architecture rather than being a framework. It utilizes a virtual DOM for efficient rendering and supports unidirectional data flow through props and state management. Essential concepts include handling events, controlled components, and organizing UI into a component hierarchy.