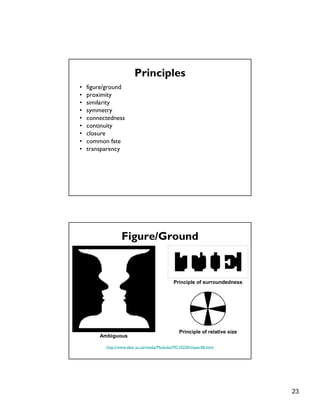
1. Graphic design principles like simplicity, elegance, and minimalism help ensure effective communication through a design. Gestalt principles also inform how human vision organizes visual elements.
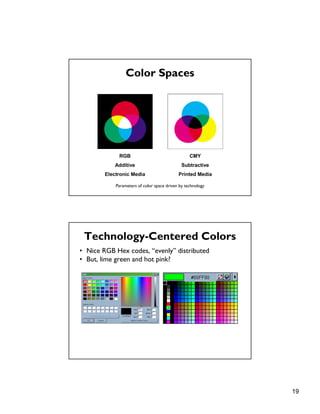
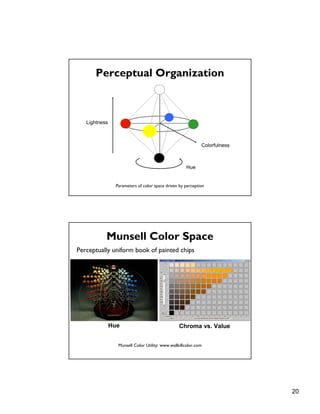
2. Color selection should consider perceptual factors like hue, lightness and chroma, and use a restricted palette. Tools like ColorBrewer can assist in picking appropriate colors.
3. Grid-based design reinforces structure through repetition of elements and alignment. Common layout mistakes around arbitrary positioning and sizing can be avoided through grid techniques.
![1
Graphic Design and Gestalt
Principles
CS160: User Interfaces
Maneesh Agrawala
Keepin' it Real: Pushing the Desktop Metaphor with Physics, Piles and the Pen [Agarawala 06]
VIDEO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-1-320.jpg)


![5
Design is about Communication
Design is about Communication
Principal organs & vasculature
[Leonardo da Vinci ca. 1490]
Strange immersion of torus in 3-space
[Curtis 92]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-5-320.jpg)







![14
Unity
One path to simplicity & elegance is through unifying themes:
– Forms, colors, components with like qualities
Refinement
London Underground [Beck 33] Geographic version of map
Draw viewers’ attention to essential information
– Straighten subway lines to emphasize sequence of stops](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-14-320.jpg)





![24
Figure/Ground
Ambiguous Unambiguous
http://www.aber.ac.uk/media/Modules/MC10220/visper06.html
Proximity
[from Ware 00]
Dots that are near one another are grouped
Dots that are concentrated are grouped](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-24-320.jpg)


![27
Similarity
Rows dominate due to similarity [from Ware 04]
Symmetry
Bilateral symmetry gives strong sense of figure [from Ware 04]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-27-320.jpg)
![28
Connectedness
Connectedness overrules proximity, size, color shape [from Ware 04]
Continuity
We prefer smooth not abrupt changes [from Ware 04]
Connections are clearer with smooth contours [from Ware 04]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-28-320.jpg)
![29
Continuity: Vector Fields
Prefer field that shows smooth continuous contours [from Ware 04]
Closure
We see a circle behind a rectangle, not a broken circle [from Ware 04]
Illusory contours [from Durand 02]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-29-320.jpg)
![30
Common Fate
http://coe.sdsu.edu/eet/articles/visualperc1/start.htm
Dots moving together are grouped
Transparency
Requires continuity and proper color
correspondence [from Ware 04]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gestalt-150308050849-conversion-gate01/85/Gestalt-30-320.jpg)