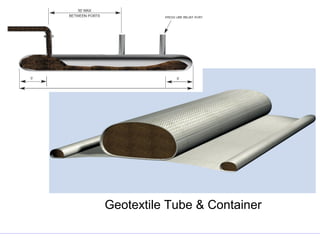
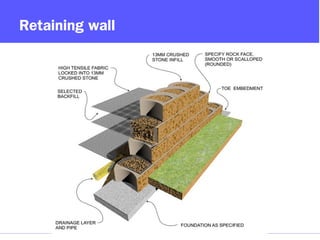
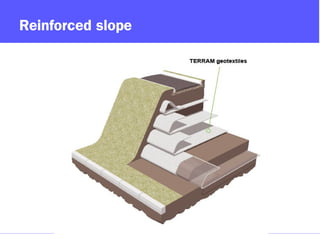
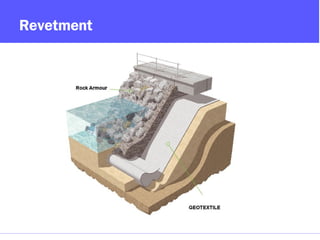
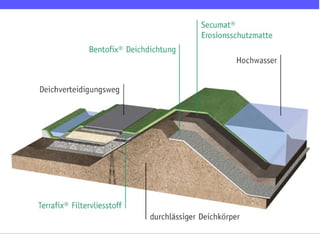
Geosynthetics are man-made materials used with soil, rock, and earth in construction and engineering projects. They are made from polymeric materials and include geotextiles, geogrids, geomembranes, geonets, and more. Geosynthetics serve functions like separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and as barriers. They have been used since the 1920s and have various applications like retaining walls, reinforced slopes, drainage systems, vertical drains, canals, and waste landfills.