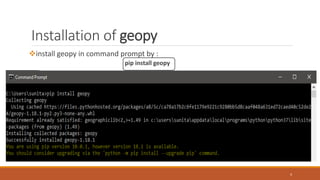
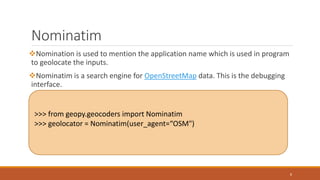
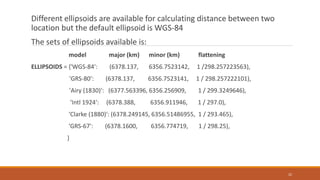
The document discusses the geopy module in Python, which is used for geocoding and geolocation. It allows users to geolocate addresses, cities, countries and landmarks into geographic coordinates and vice versa. The geopy module utilizes third party geocoders like Google Maps, Bing Maps and Nominatim. It discusses how to install, import and use the module to geocode and reverse geocode locations. Various methods like geocode(), reverse() and functions to convert between distance and angle units are also covered.