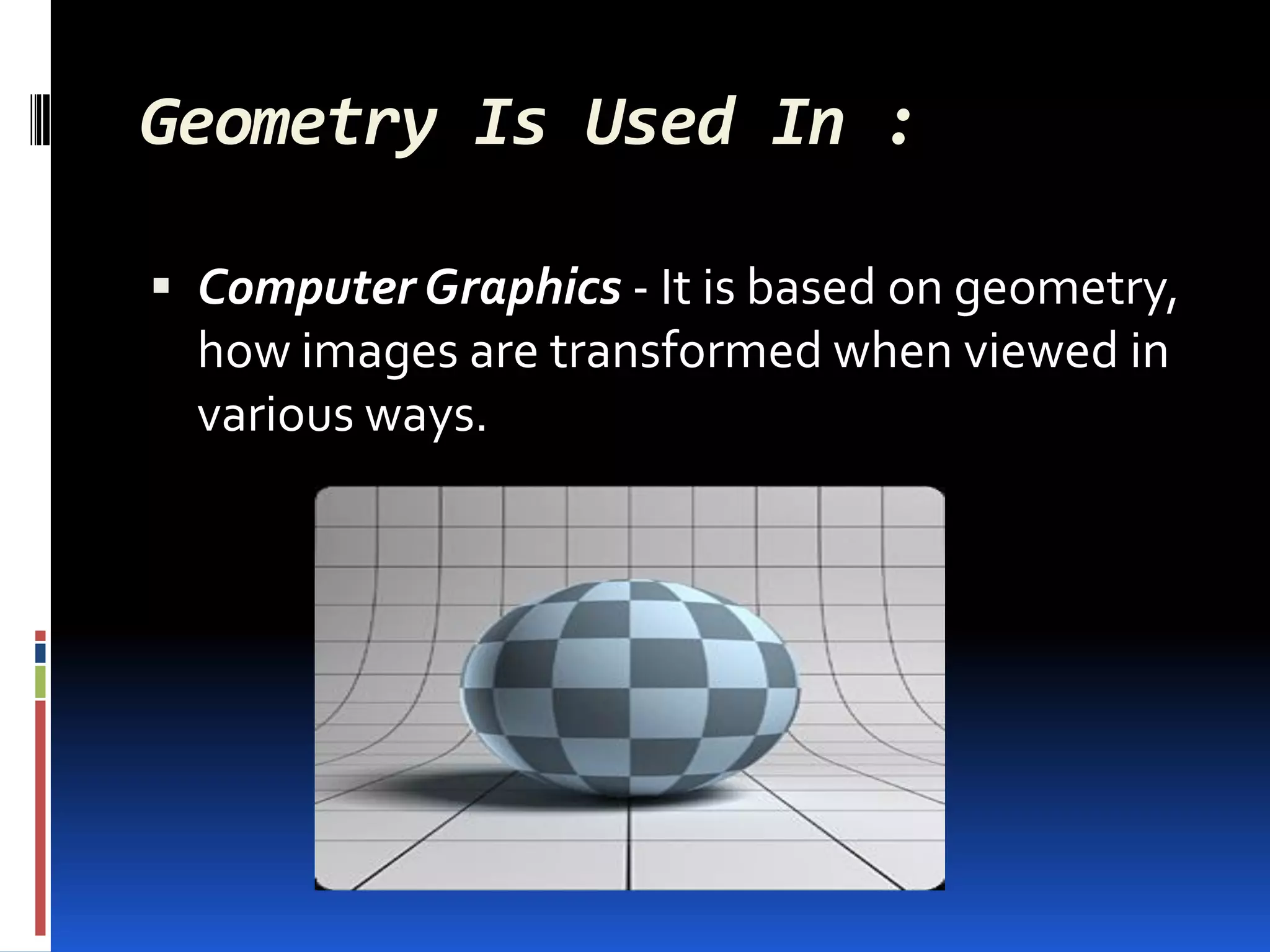
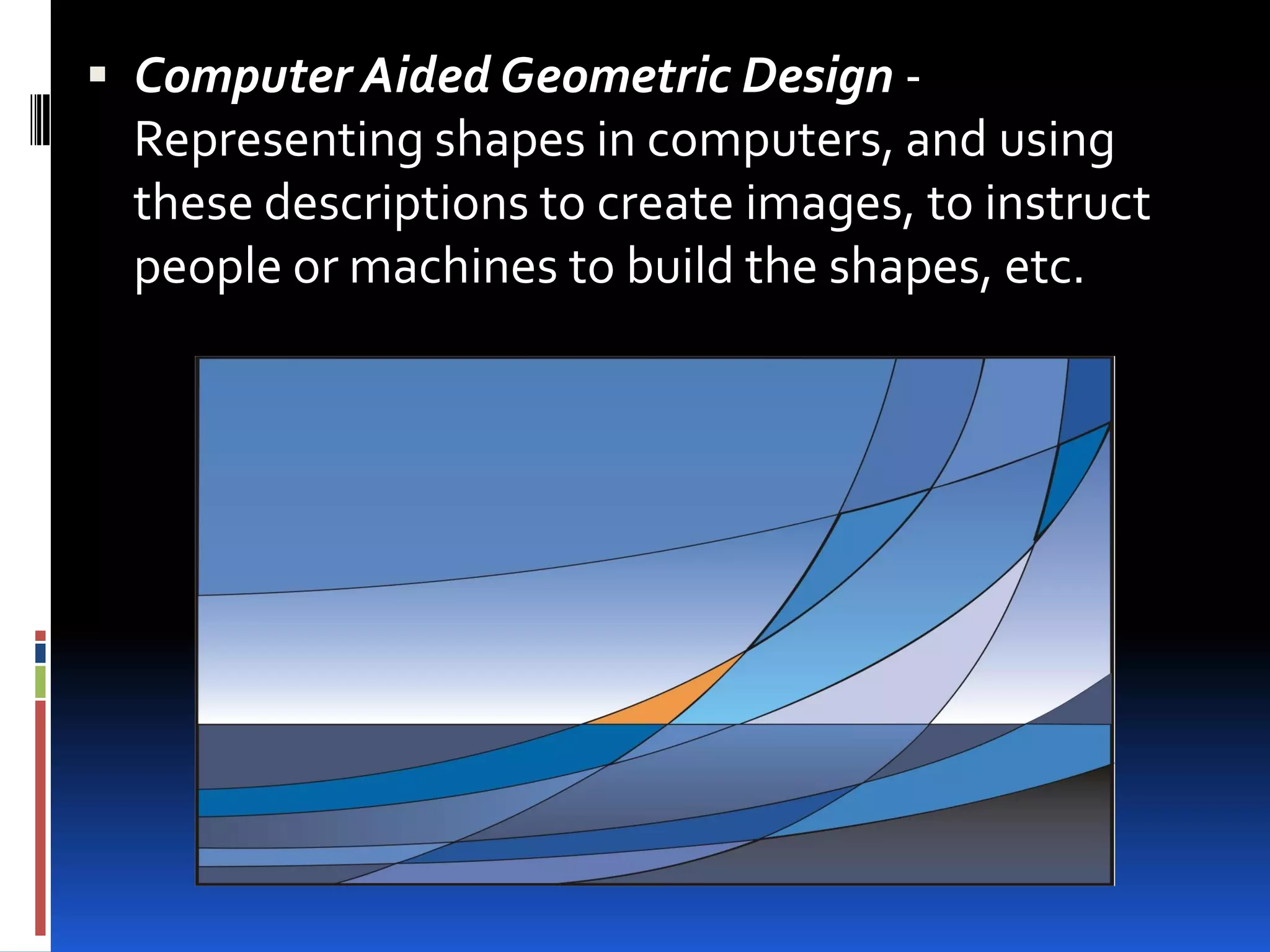
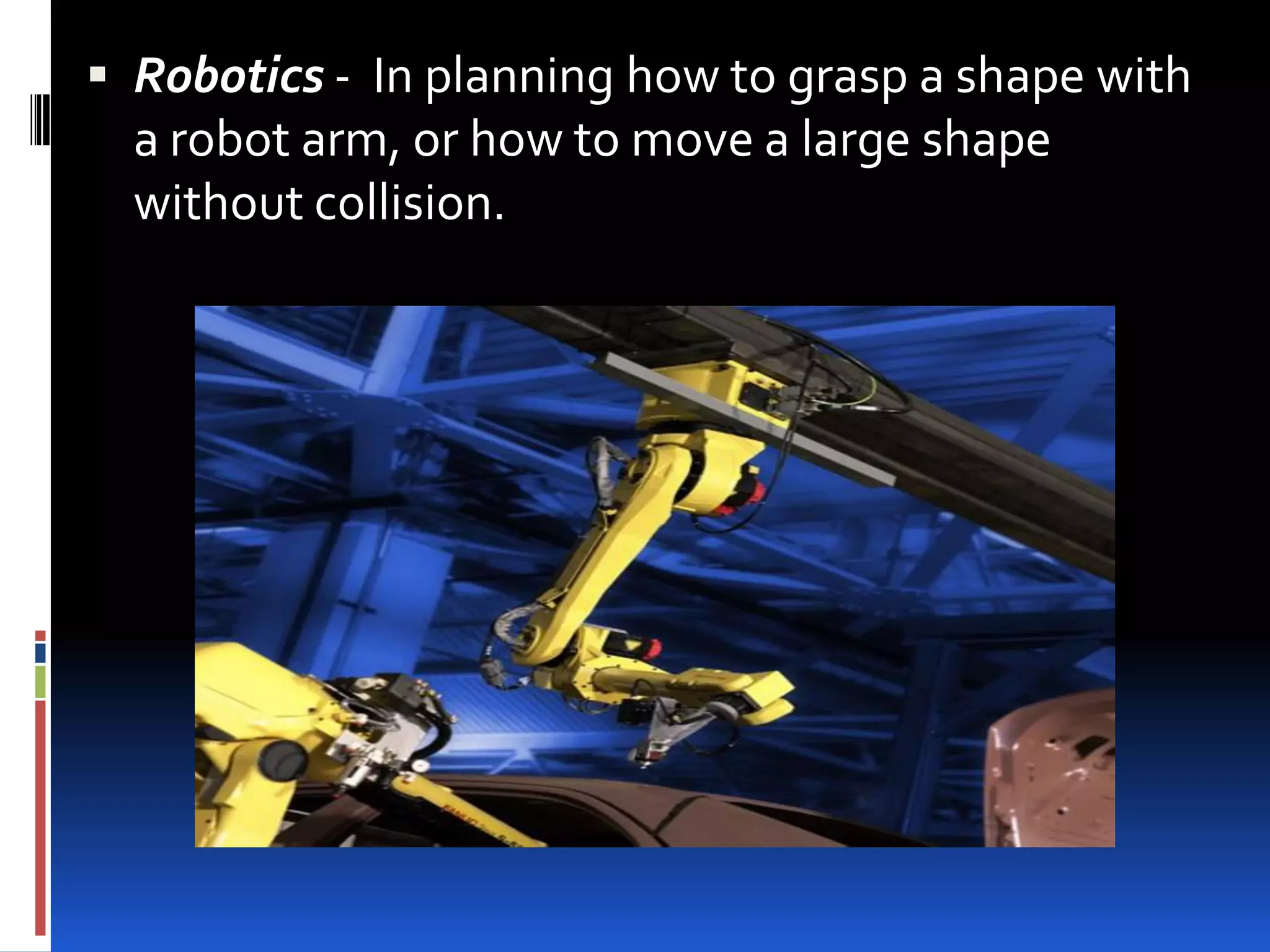
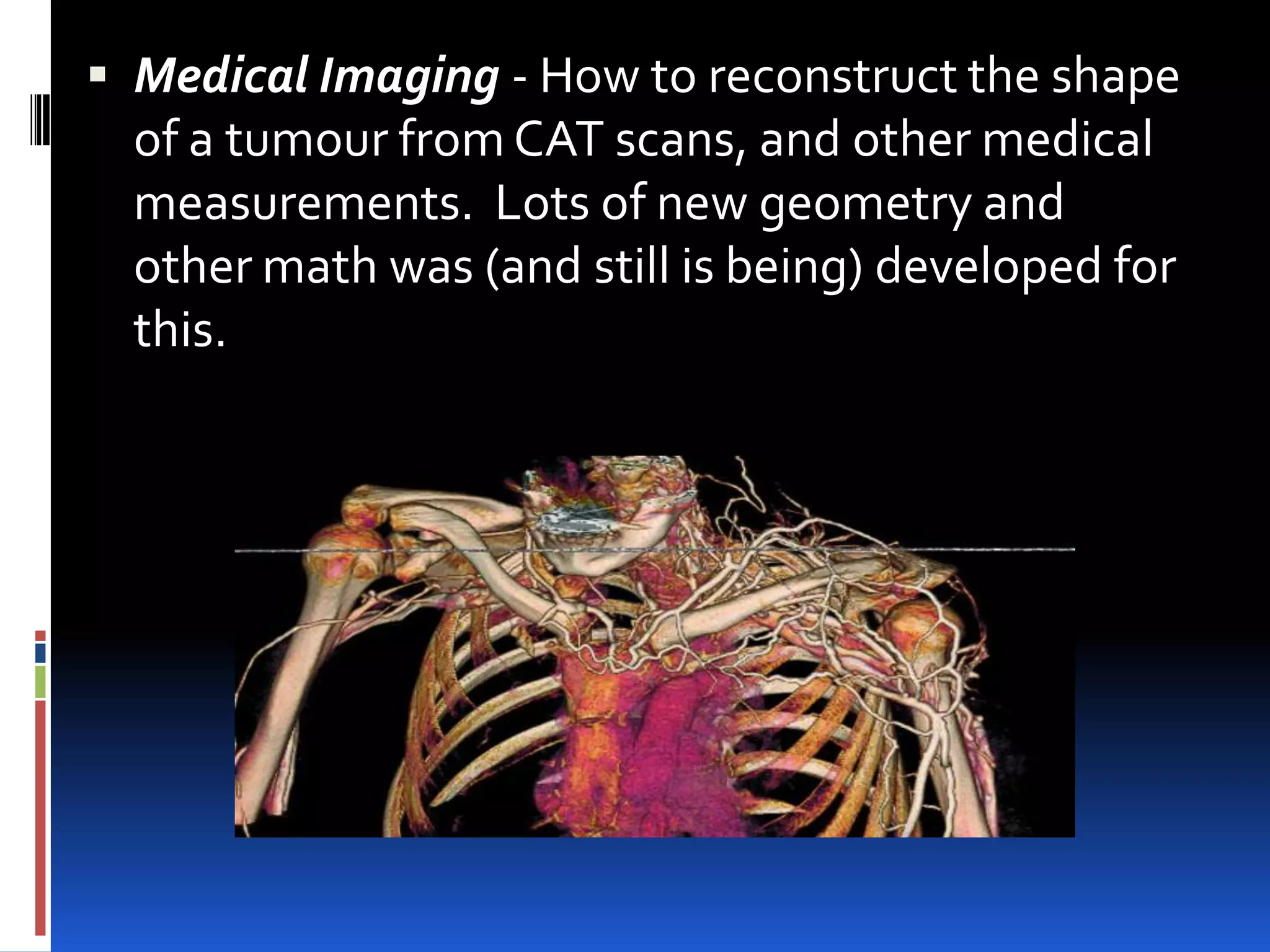
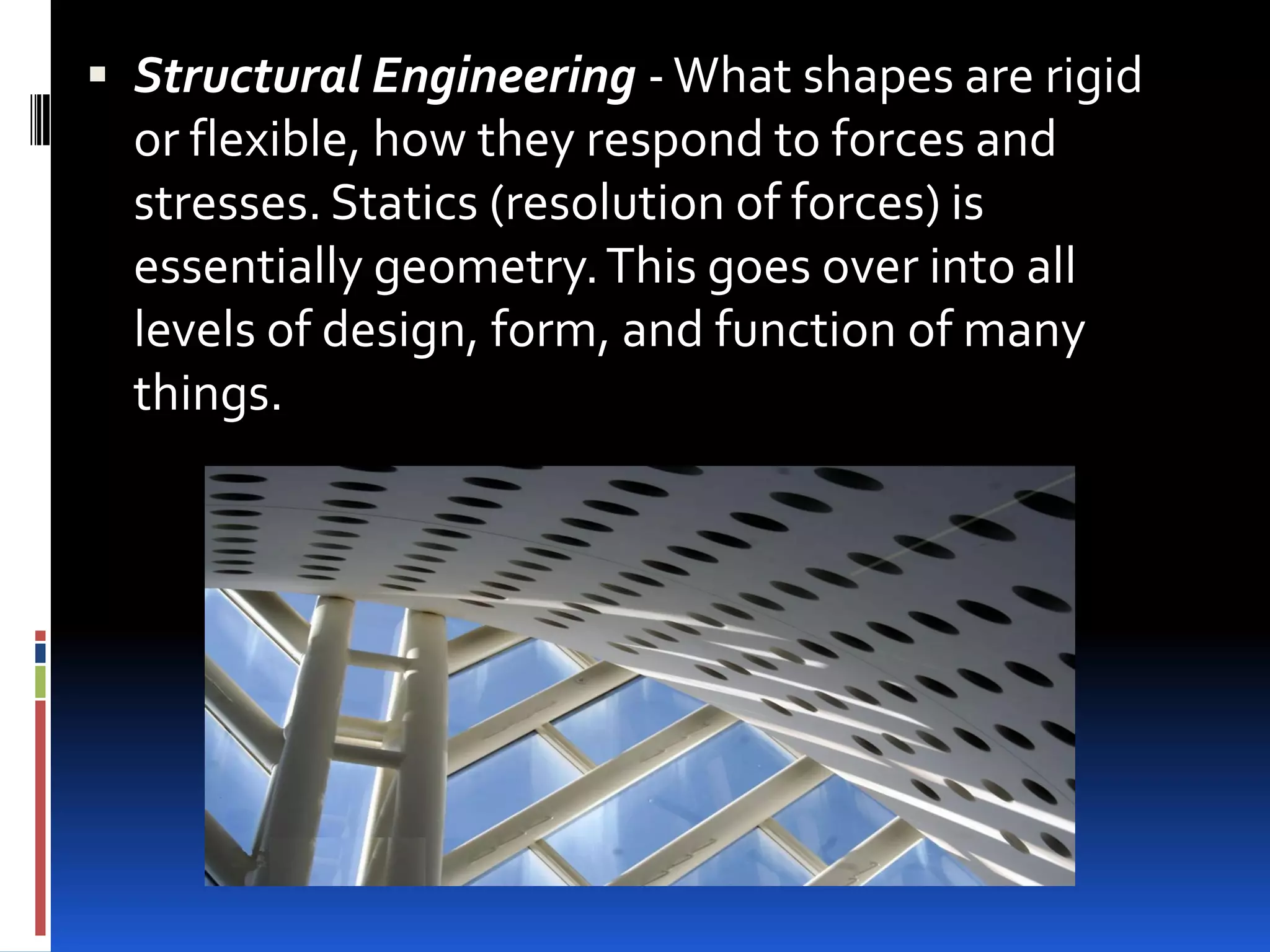
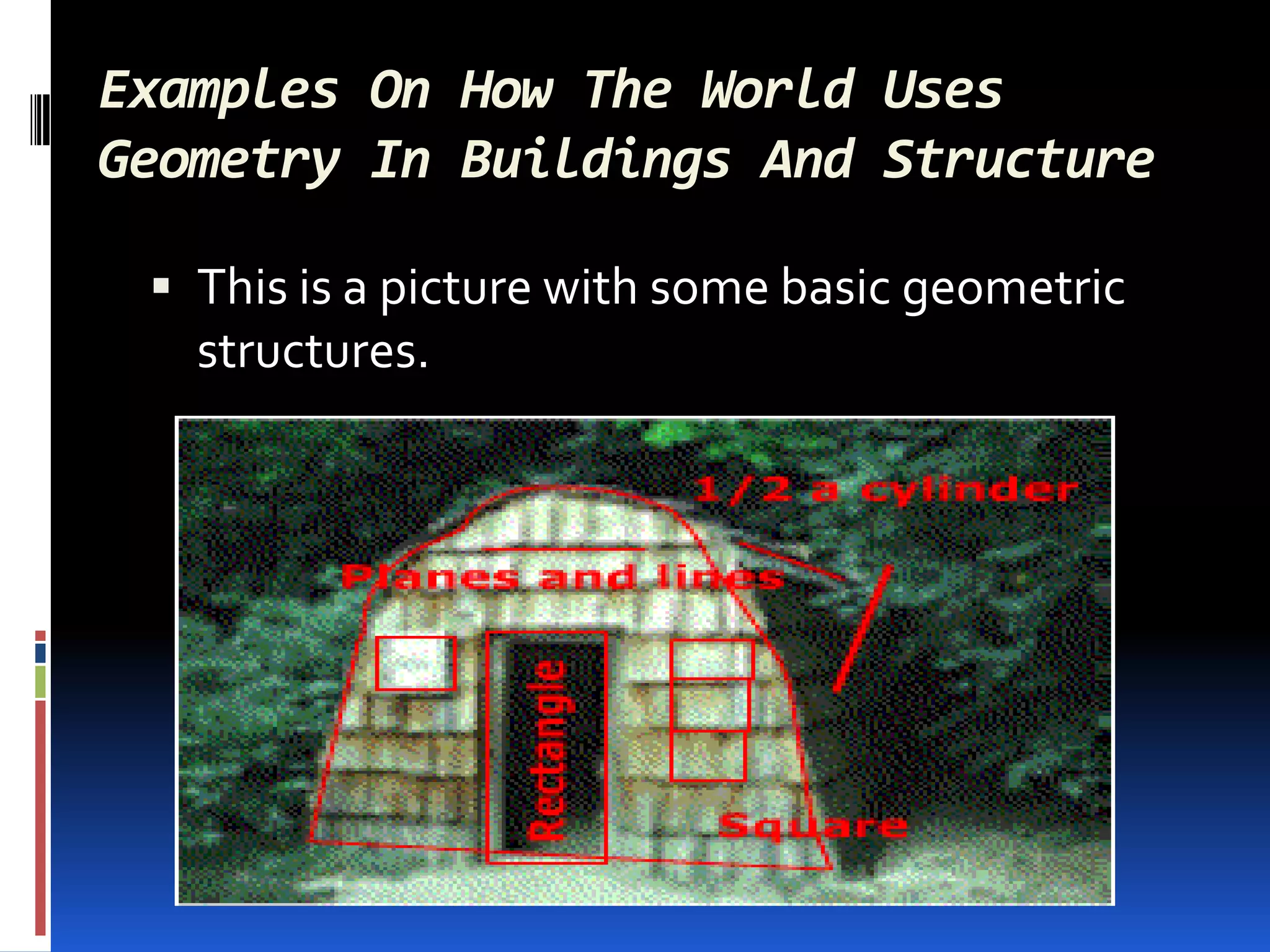
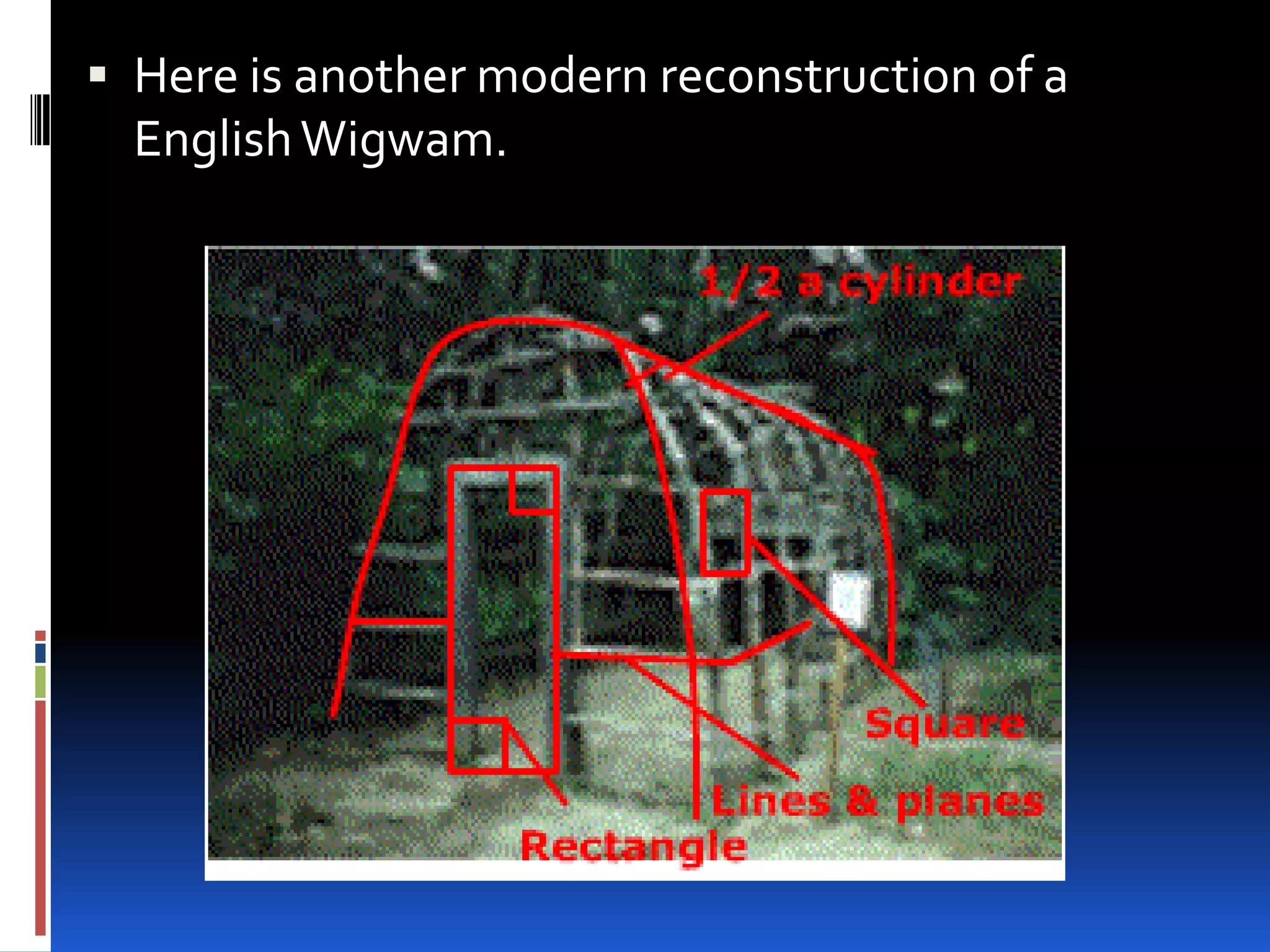
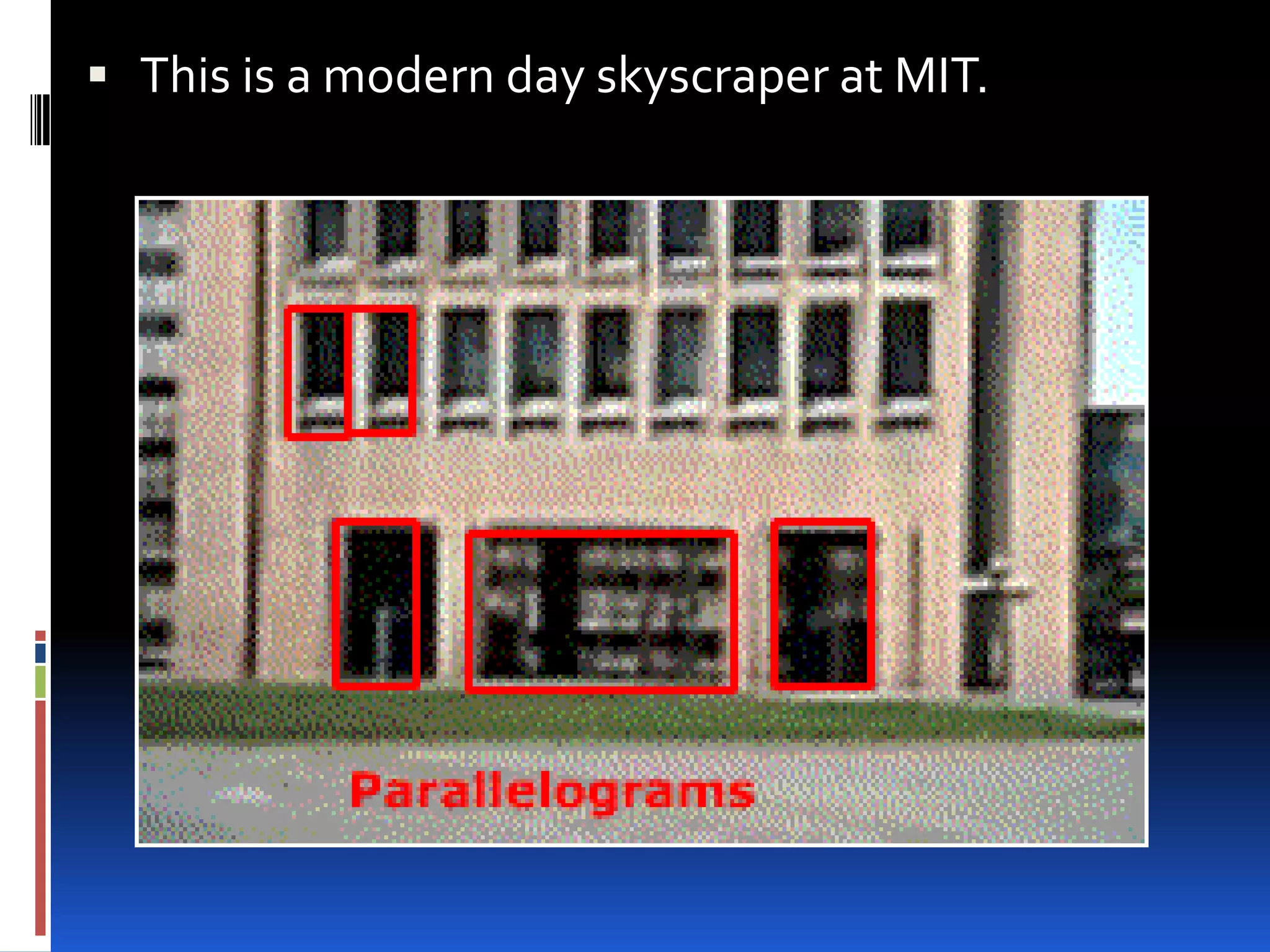
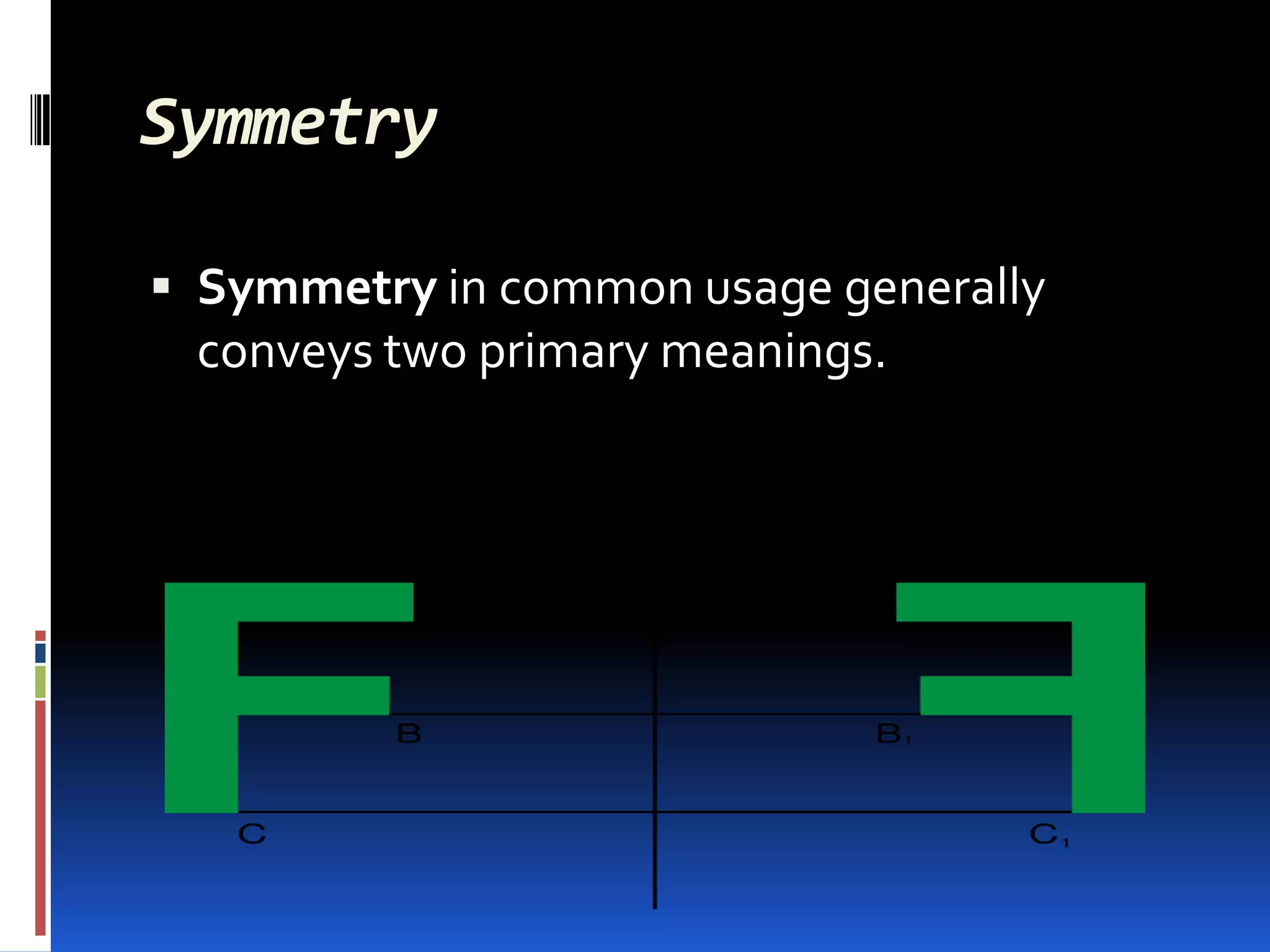
This document provides an overview of geometry and how it is used. It acknowledges sources and indicates this presentation is for student benefit only. Geometry studies size, shape, and spatial relationships. It is used in computer graphics, engineering, robotics, medical imaging, and other fields. Examples of geometric structures in buildings like wigwams, skyscrapers, and cars are presented. Symmetry is also discussed as an important geometric concept seen in nature and science.