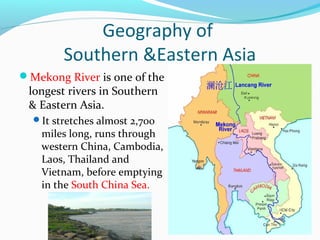
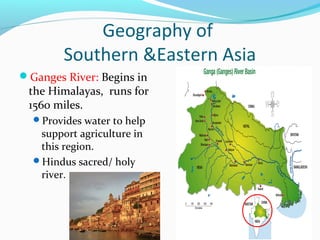
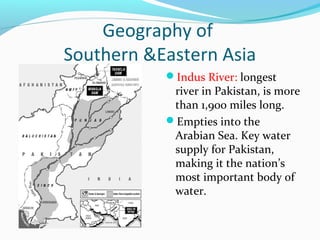
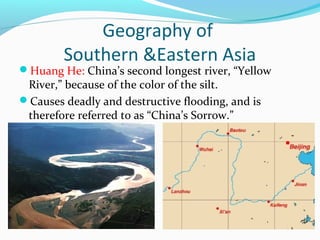
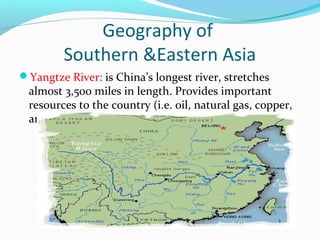
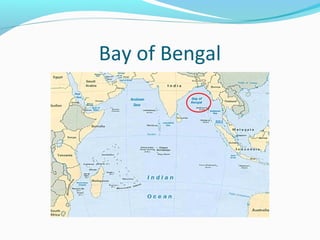
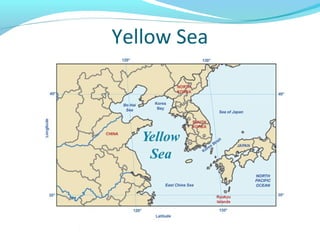
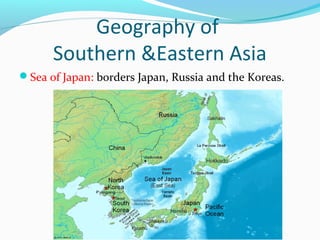
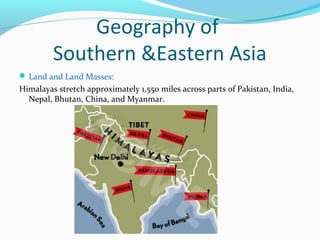
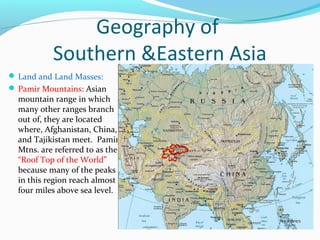
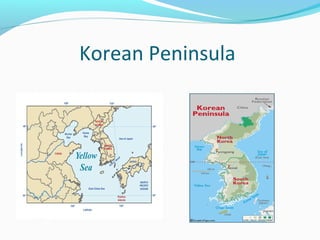
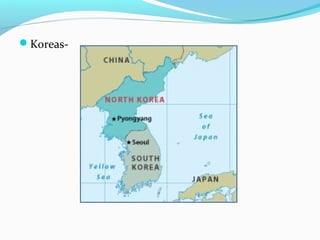
The document discusses the geography of Southern and Eastern Asia. It describes several major rivers that run through the region like the Mekong River and Ganges River. It also discusses large deserts like the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert. Mountains ranges are also covered, such as the Himalayas. Bodies of water including the South China Sea, Yellow Sea, and Bay of Bengal are identified. The population distribution is impacted by geography, with many people living near coasts, rivers, and in cities for resources and trade. Pollution is a rising issue from increased development.