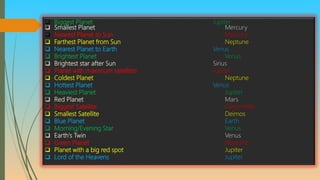
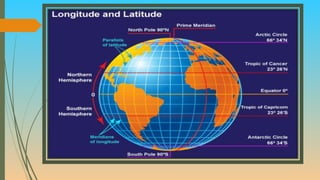
The document provides information about celestial bodies in the universe, galaxy, and solar system. It discusses key components of the solar system including the sun, planets, asteroids, and meteoroids. It also lists interesting facts about various planets and satellites. Furthermore, it defines latitude and longitude, describing how they are measured and important lines such as the equator, tropics, and poles. The document concludes with brief descriptions of time zones and the International Date Line.