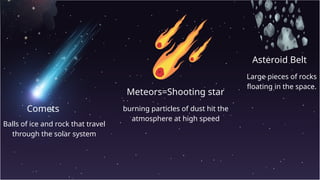
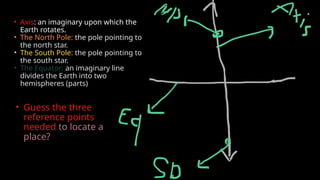
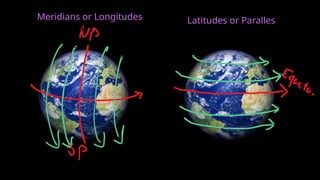
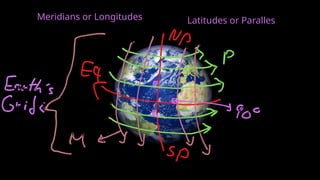
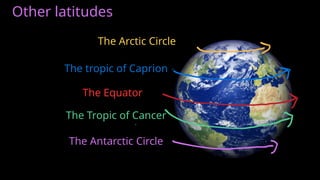
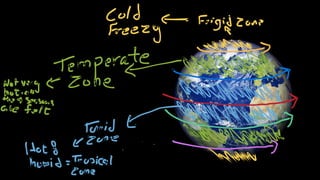
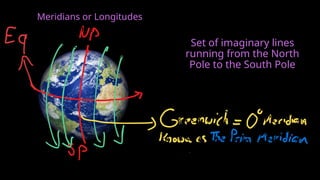
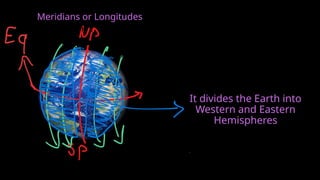
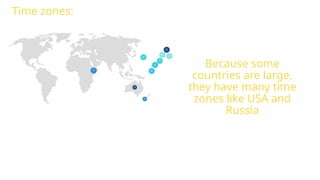
The document provides an educational overview of Earth and the solar system, discussing topics like the characteristics of planets, their orbits, and the definition of celestial bodies such as moons and asteroids. It explains key concepts such as latitude, longitude, and time zones, as well as the Earth's rotation and its impact on day and night as well as the seasons. Additionally, it highlights various planets' features, including their sizes, positions, and unique attributes.