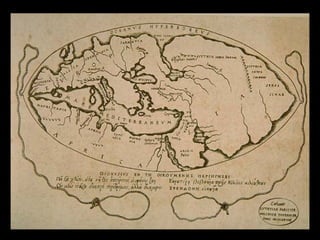
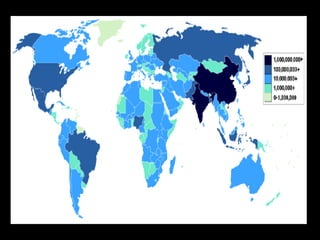
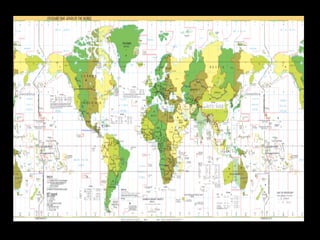
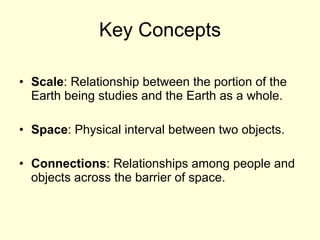
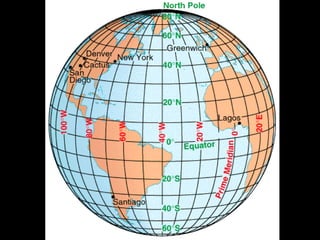
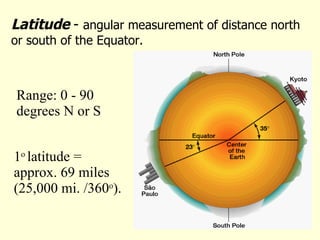
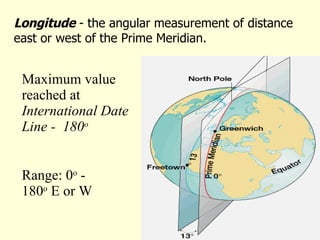
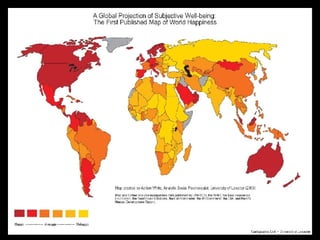
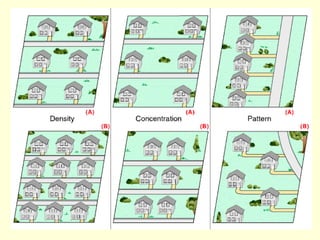
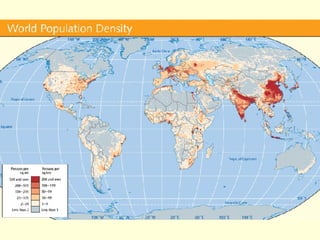
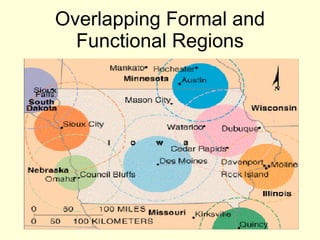
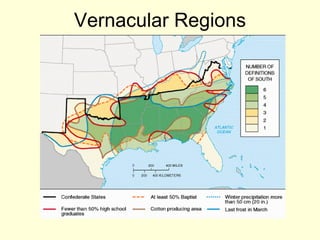
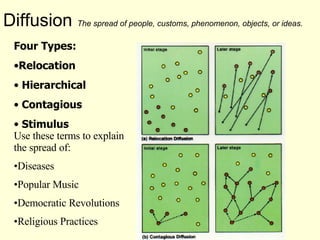
This document provides an overview of key concepts in human geography, including definitions of geography, place, space, scale, region, spatial distribution, diffusion, sense of place, and human-environment interaction. It discusses fundamental geographic concepts such as latitude and longitude, map projections, and core-periphery relationships. Examples are given to illustrate cultural regions, types of diffusion, and how places take on meaning for individuals.