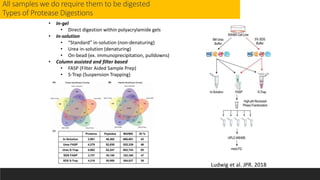
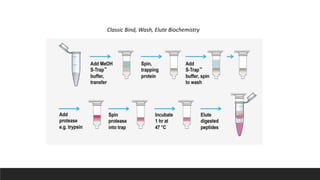
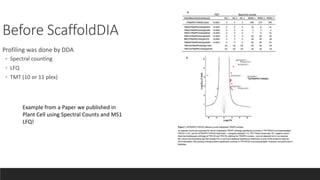
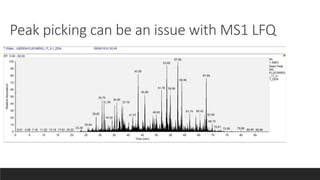
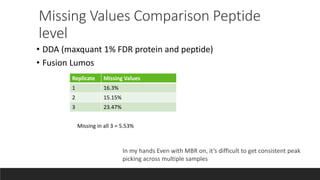
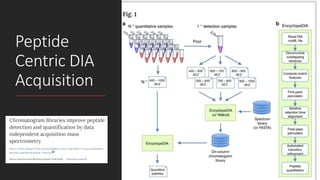
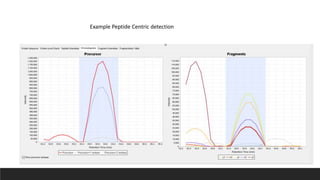
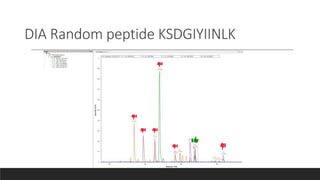
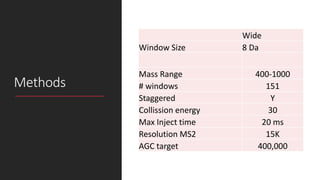
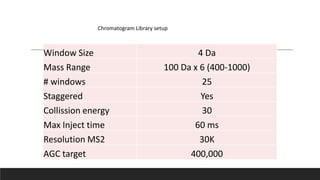
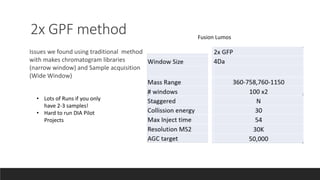
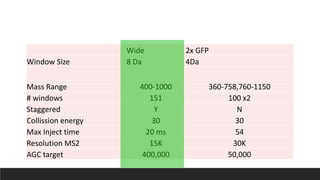
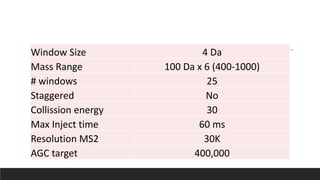
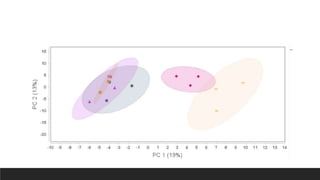
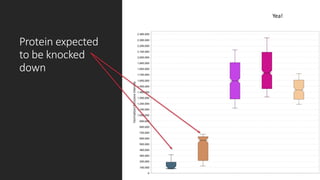
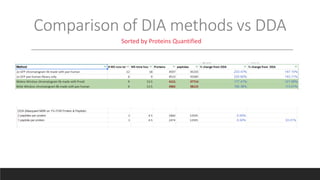
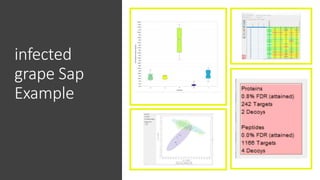
This document describes the work done at the UC Davis Proteomics Core Facility, which uses suspension trapping and peptide-centric DIA with deep learning to develop more universal proteomics methods. The core analyzes diverse sample types from various species using techniques like AP-MS, TMT, DIA, and PTM analysis. Peptide-centric DIA with ScaffoldDIA software provides better quantification than DDA, especially for human samples. Using Prosit deep learning to generate in silico libraries improves pathogen and protein identification from samples like infected grape sap. The core finds that DIA with gas phase fractionation works well for smaller sample sets and provides advantages over DDA for applications like undepleted serum proteomics.