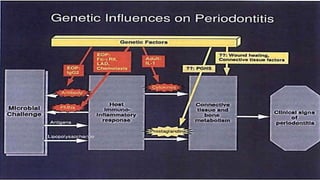
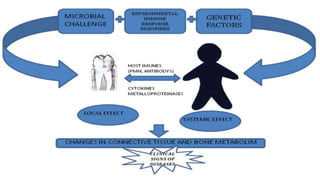
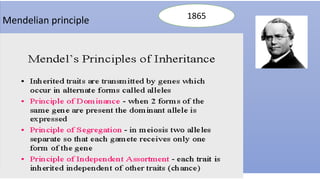
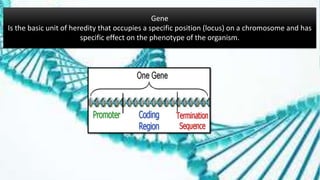
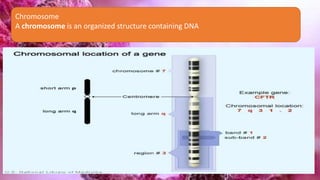
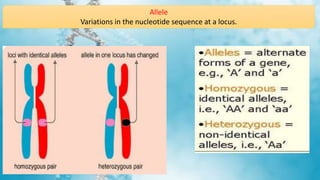
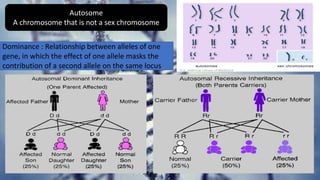
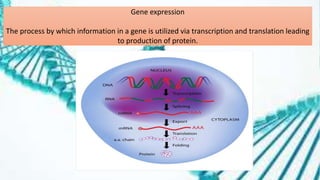
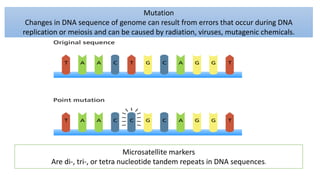
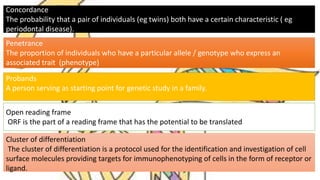
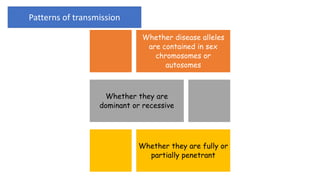
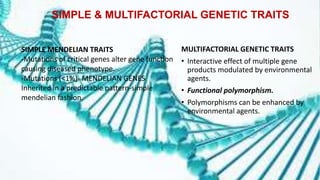
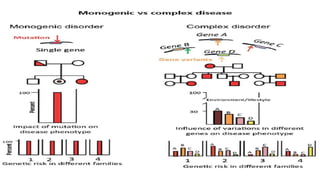
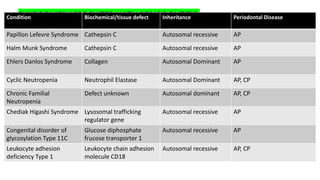
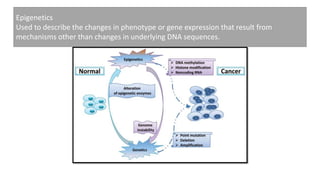
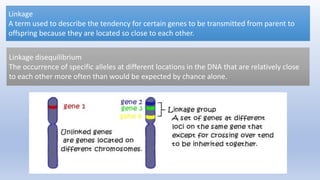
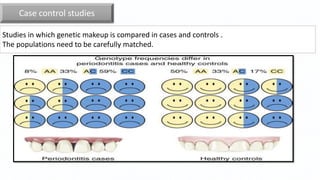
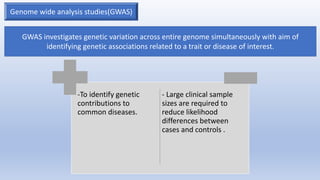
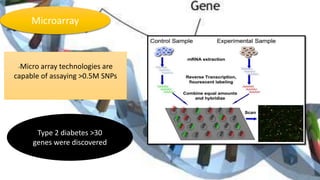
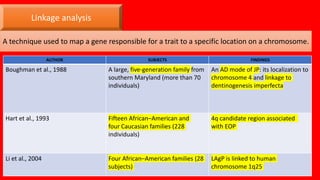
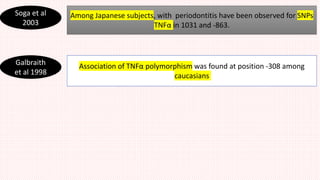
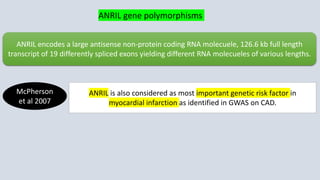
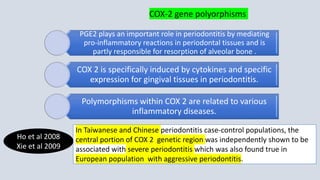
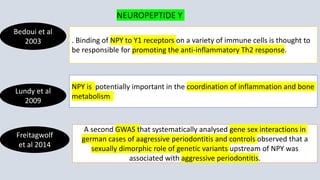
This document summarizes genetic factors associated with periodontitis. It discusses various genetic studies related to chronic and aggressive periodontitis, including studies on gene polymorphisms like IL1, TNF, FCγR, IL10, and others. It also covers genetic terminology, types of genetic studies like twin studies, family studies, case-control studies and genome-wide association studies. Specific gene mutations linked to syndromes associated with periodontitis are mentioned.









![CTSC gene which was observed in 8 families and was found that these mutations
resulted in complete loss of enzyme.[Hart et al 1999].
CTSC mutations have also been identified in families with prepubertal periodontitis .
It has also been found that polymorphic functional variants of CTSC may be involved
in more common type of aggressive periodontitis.
Papillon lefevre syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticfactors-191219153412/85/Genetic-factors-25-320.jpg)











![Decreased expression of ANRIL is correlated with decreased expression levels
of ADIPORI, VAMP3 and C11ORF10. [Bochenek et al 2013]
Protein VAMP3 belongs to VAMP/synaptobrevin family and plays a role in
phagocytosis wherein VAMP3 mediates the transfer of TNF to cell surface
[Murray et al 2005]
VAMP3 gene polymorphisms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticfactors-191219153412/85/Genetic-factors-51-320.jpg)

![Risk gene of aggressive periodontitis GLT6D1 mapped to
chromosome 9 at 9q34.3 [ Schafer et al 2010].
It encodes for an unknown protein belonging to family of
proteins that is characterized by a glycosyl transferase domain 1 .
Mainly expressed in gingiva and T cells.
GLT6D1 gene polymorphisms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticfactors-191219153412/85/Genetic-factors-53-320.jpg)
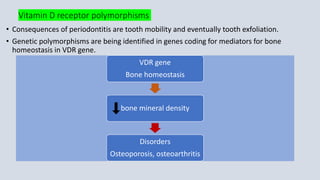



![Late failures in implant dentistry
Rogers et al
2002 laine et
al 2006
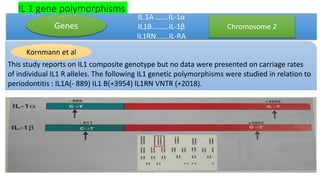
Studies reported on IL1A -889, IL1B -511, IL1B +3954 and IL1RN VNTR
polymorphisms separately in association with late implant failures.
Feloutzis et al
2003
-In a study of 90 Caucasian patients were investigated for peri-implant
bone loss at time of re-examination [mean 5.6 years]
-28 patients carrying IL1 composite genotype were stratified in to non-
smokers , former smokers and heavy smokers
-Heavy smokers were found to have more annual bone loss.
Gruica et al
2004
IL1 composite genotype and smoking were significantly associated with
peri-implant bone loss after 8 years in function among Caucasians.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticfactors-191219153412/85/Genetic-factors-60-320.jpg)
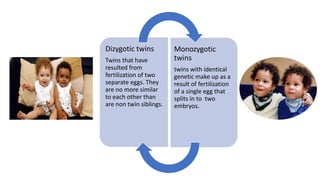
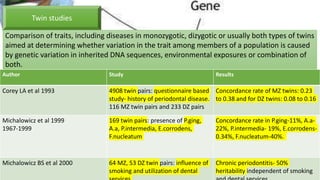
![Evidence for the role of genetics in periodontitis
A study was done on 77 siblings of 39 probands with LJP and GJP and it was found that 50 %
of siblings suffered from JP. 11 families a co-occurrence of LJP and GJP was present.
[Boughman et al 1992].
A family with 527 subjects: 60 with LJP,72 with GJP ,254 unaffected subjects and 141 with
unknown periodontal condition in Caucasians and African American families. The authors
concluded that the most likely mode of inheritance was autosomal dominant in both
American and Caucasian with penetrance of 70% in African americans and 73 % in
Caucasians.[Marizata et al 1994]
Aggressive periodontitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticfactors-191219153412/85/Genetic-factors-61-320.jpg)
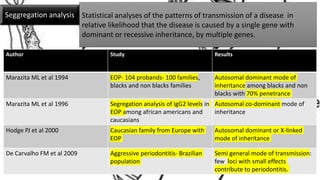
![Chronic periodontitis
A study was done in 75 families consisting of 178 subjects to determine familial aggregation
.The results showed both gingival index and attachment loss showed a stronger correlation
between mothers and offspring compared with fathers and offspring.[Beaty et al 1993]
A study analysed periodontal condition in an untreated population in Guatemala consisting of
109 siblings from 40 nuclear families with an age range of 35-60 years. They failed to show
familial clustering for periodontal disease.[Dowsett et al 2002]
A study was done in 78 subjects and was found that significant sibling relationship effect on
plaque, calculus and loss of attachment but not for pocket depth.[van der Velden et al 1993]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geneticfactors-191219153412/85/Genetic-factors-62-320.jpg)