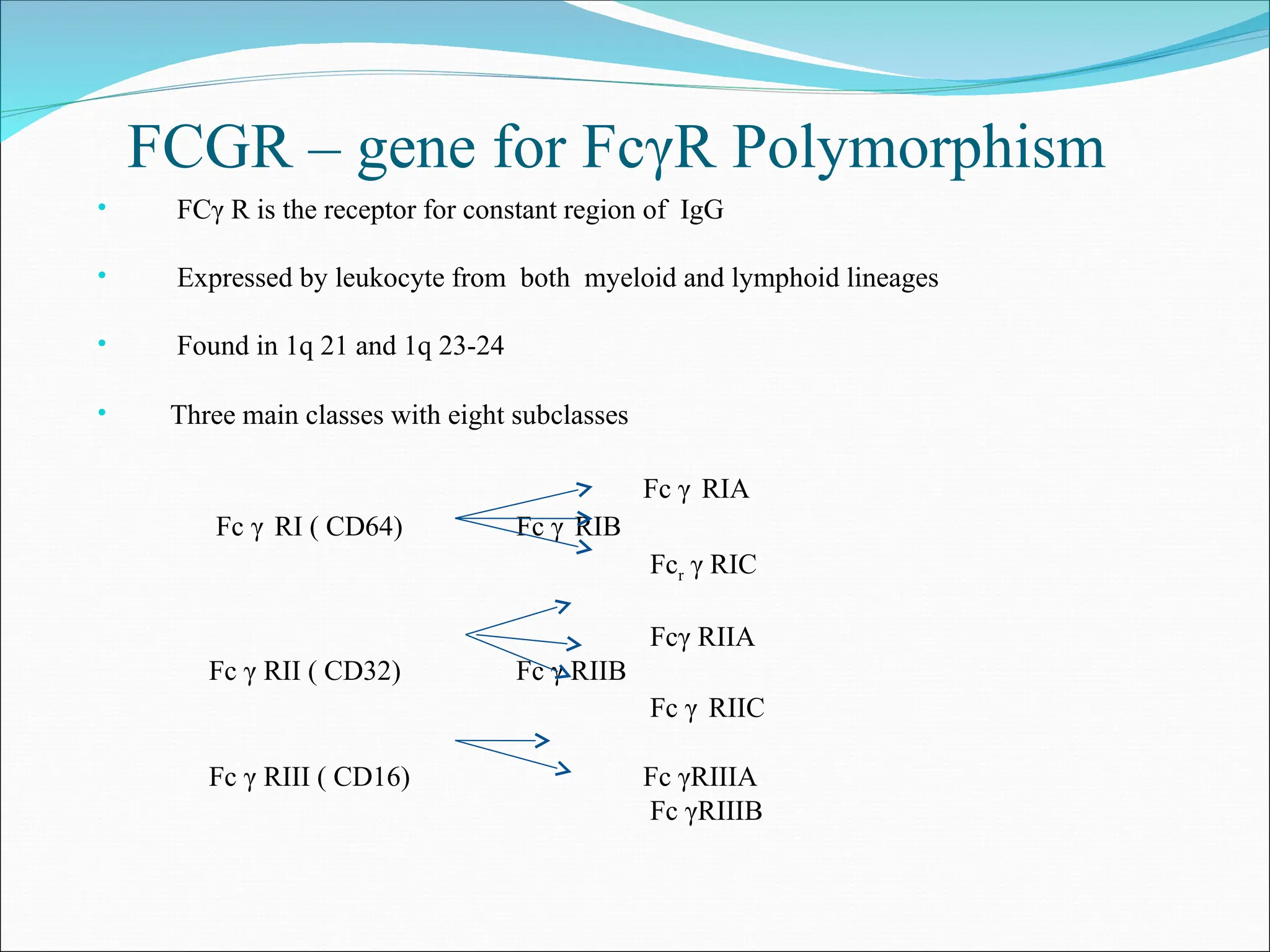
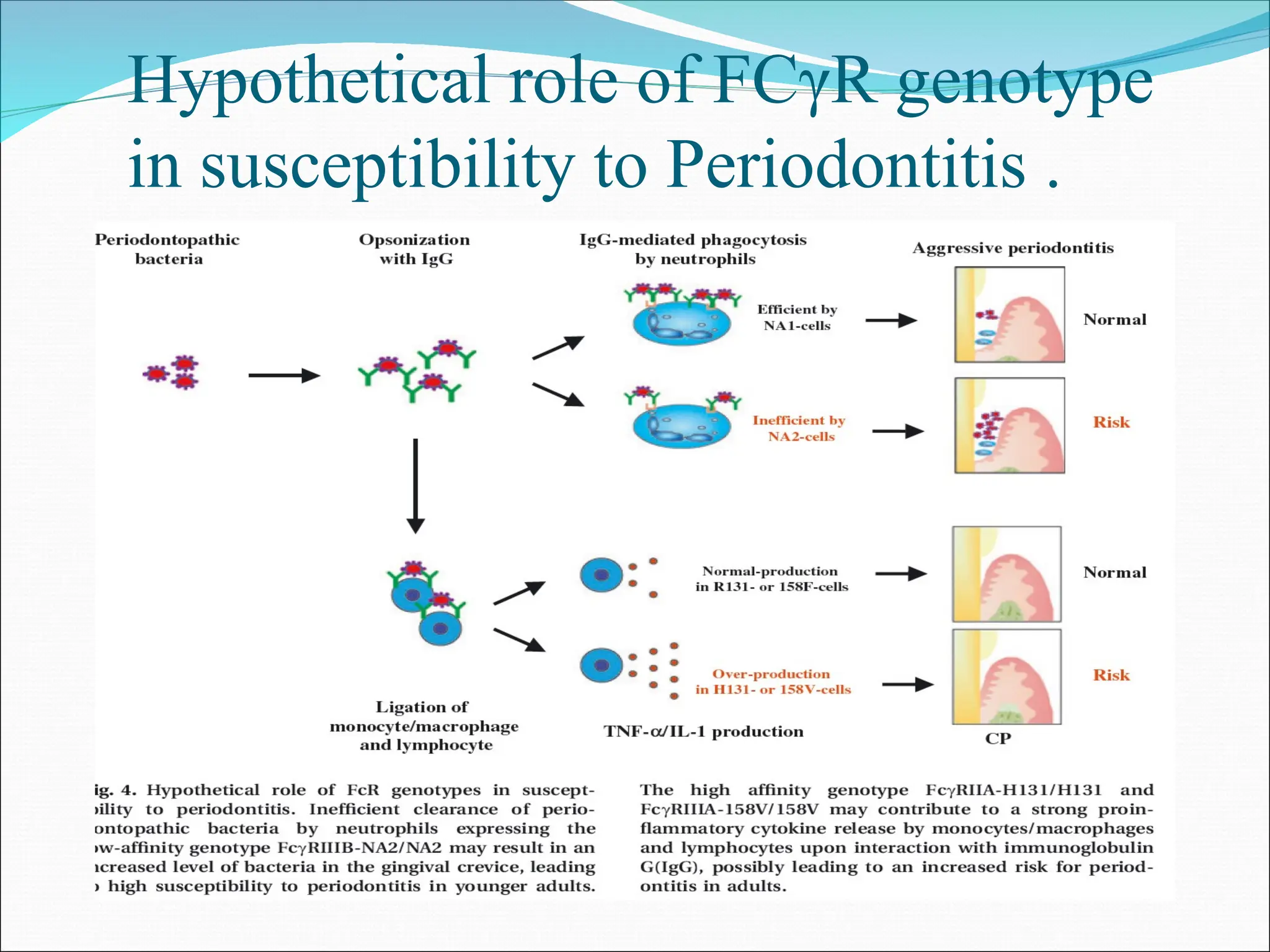
The document discusses the role of genetics as a risk factor for periodontal disease, highlighting various genetic polymorphisms and their associations with chronic and aggressive periodontitis. It details different methodologies for genetic studies, such as segregation analysis, linkage analysis, and association studies, and emphasizes the significance of specific cytokine gene polymorphisms in the disease's progression. The document also presents numerous examples of genetic factors that contribute to periodontal disease susceptibility and the complexities of genetic versus environmental influences.