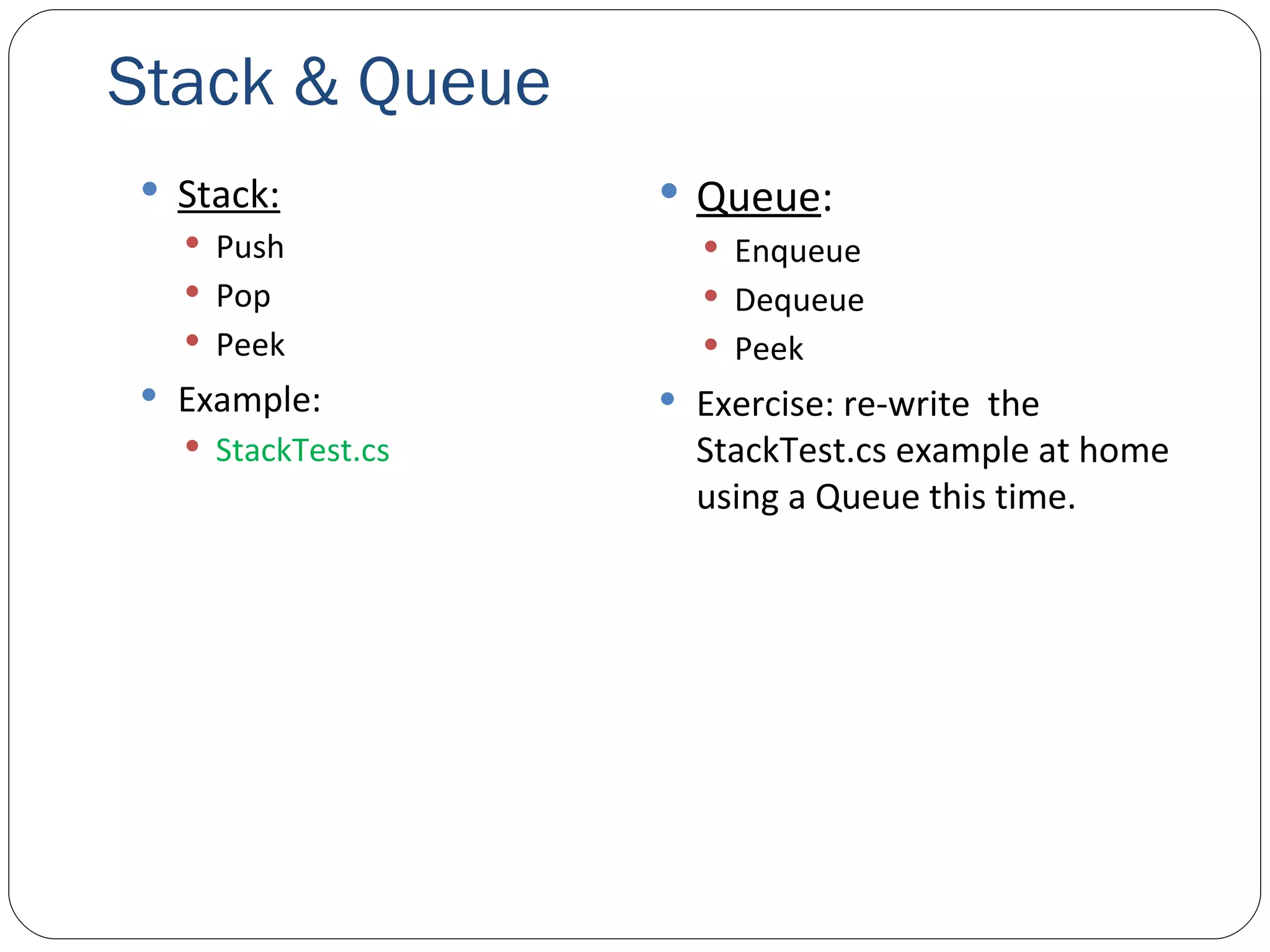
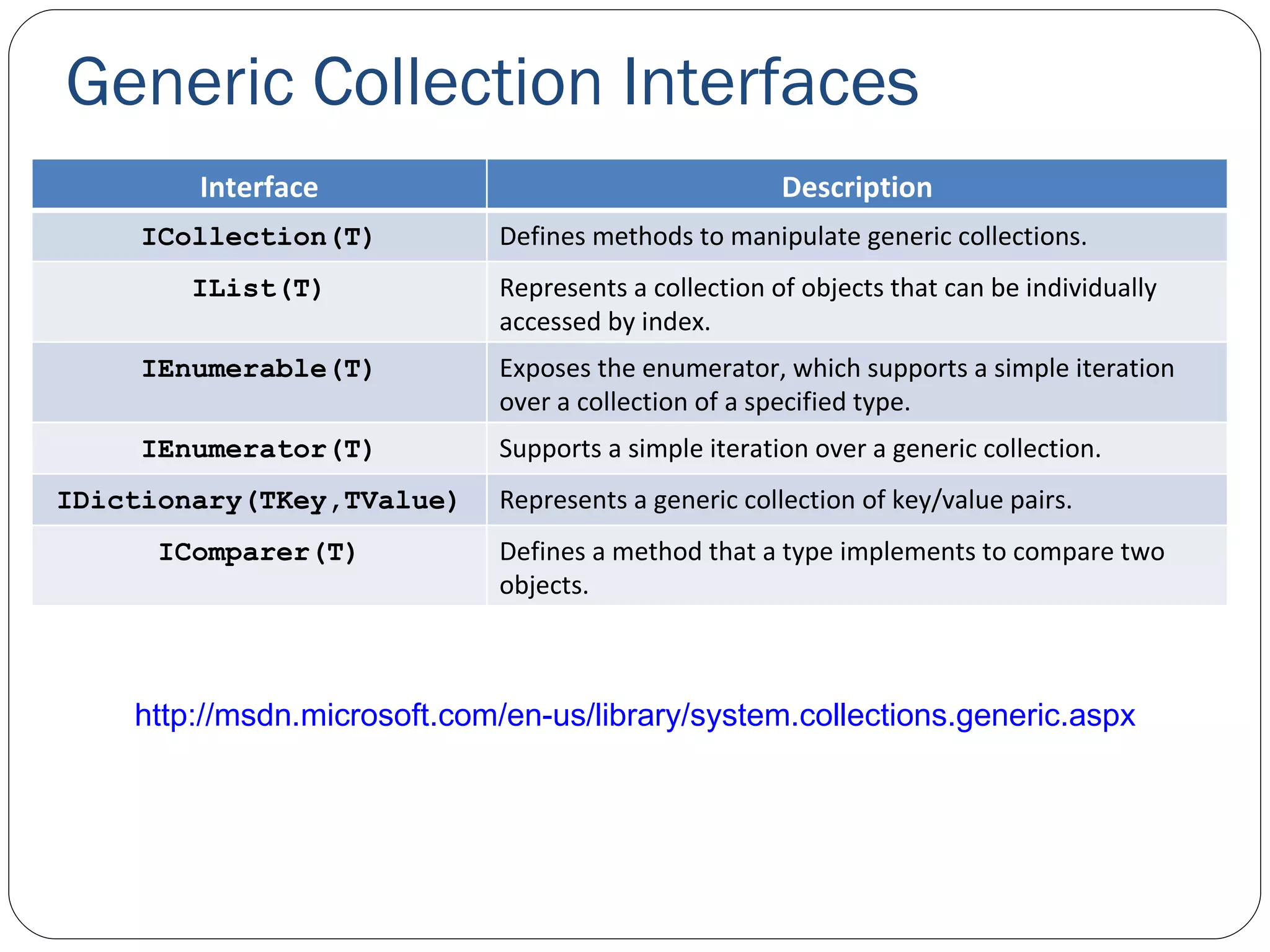
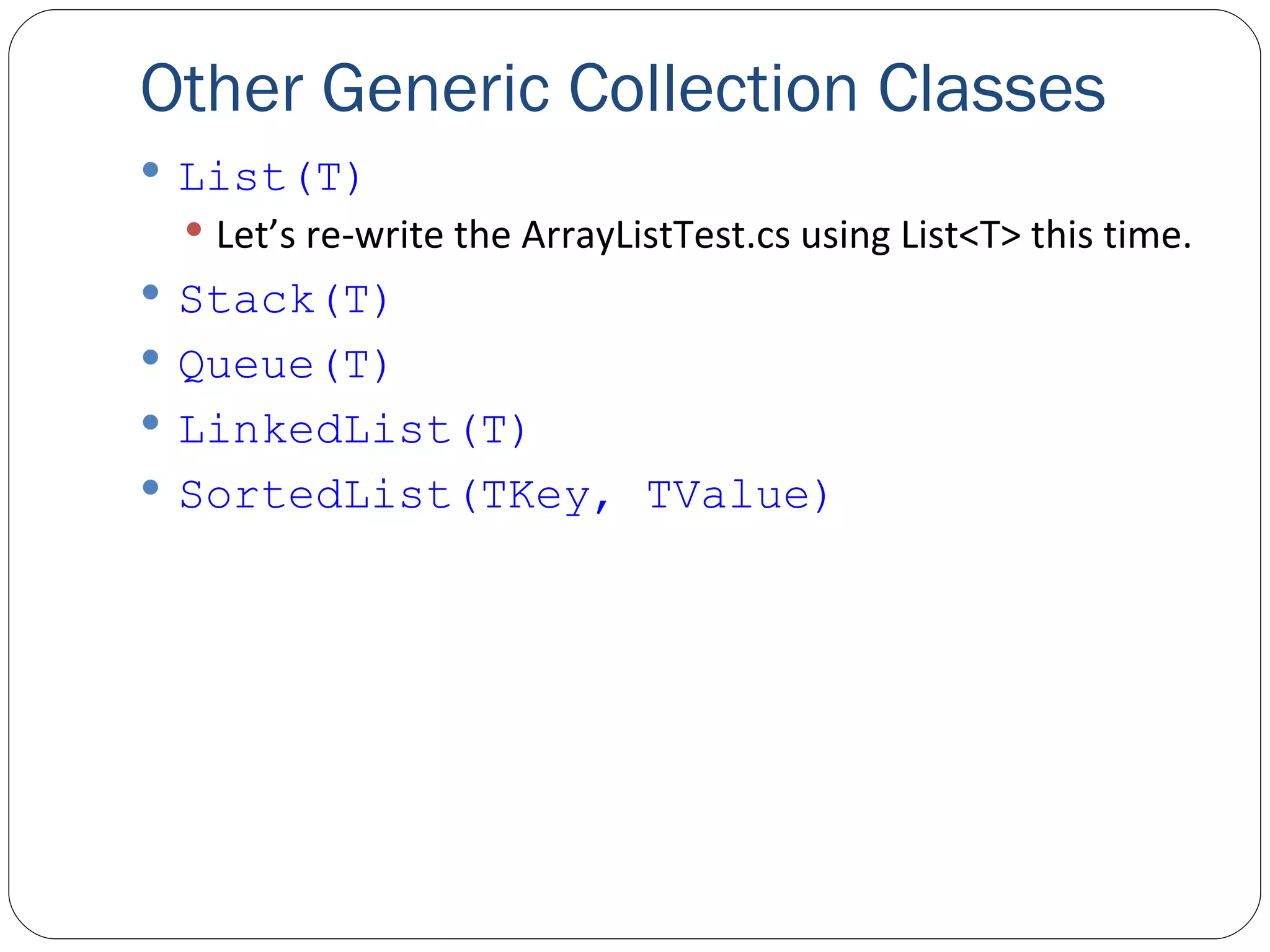
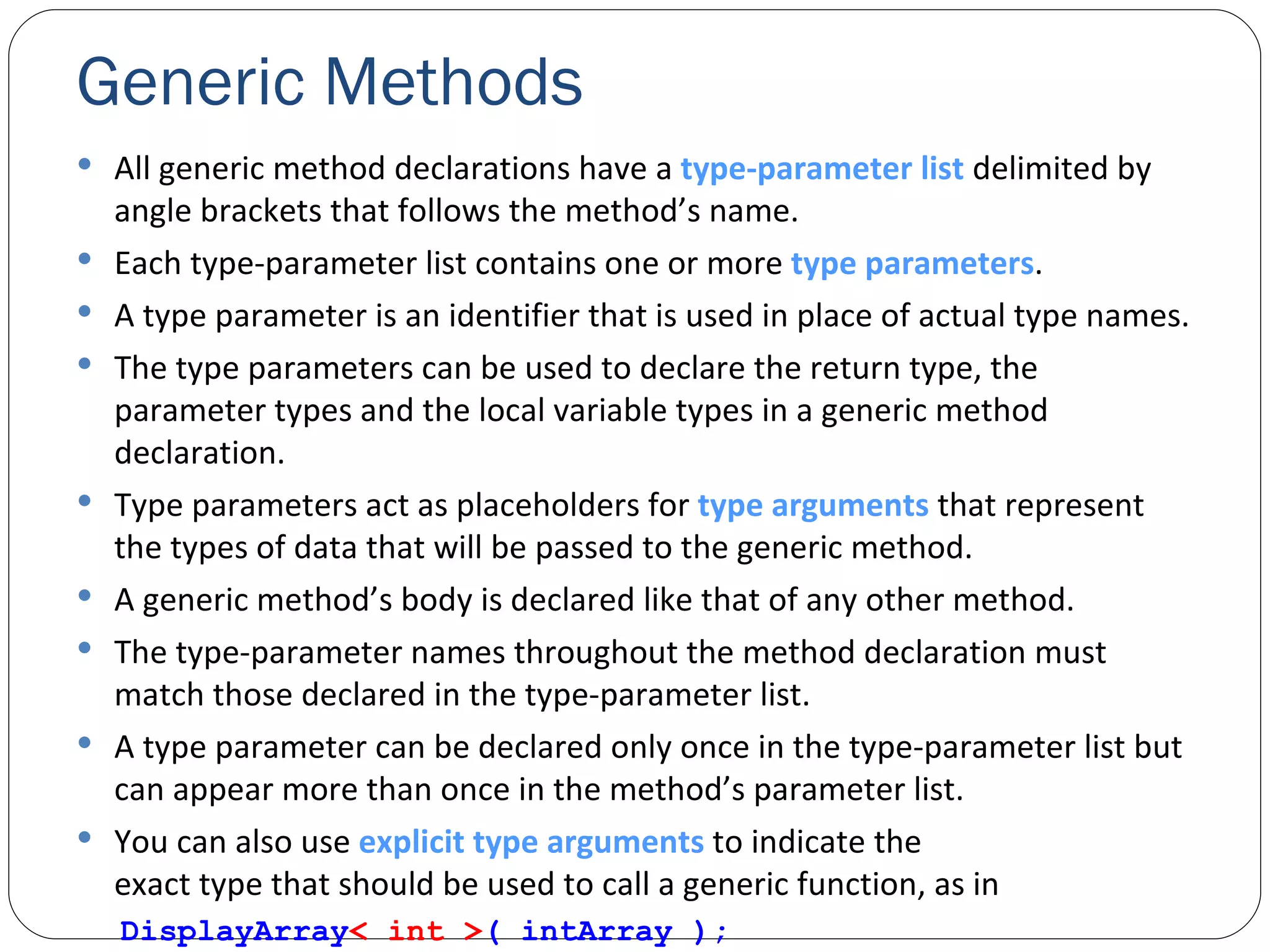
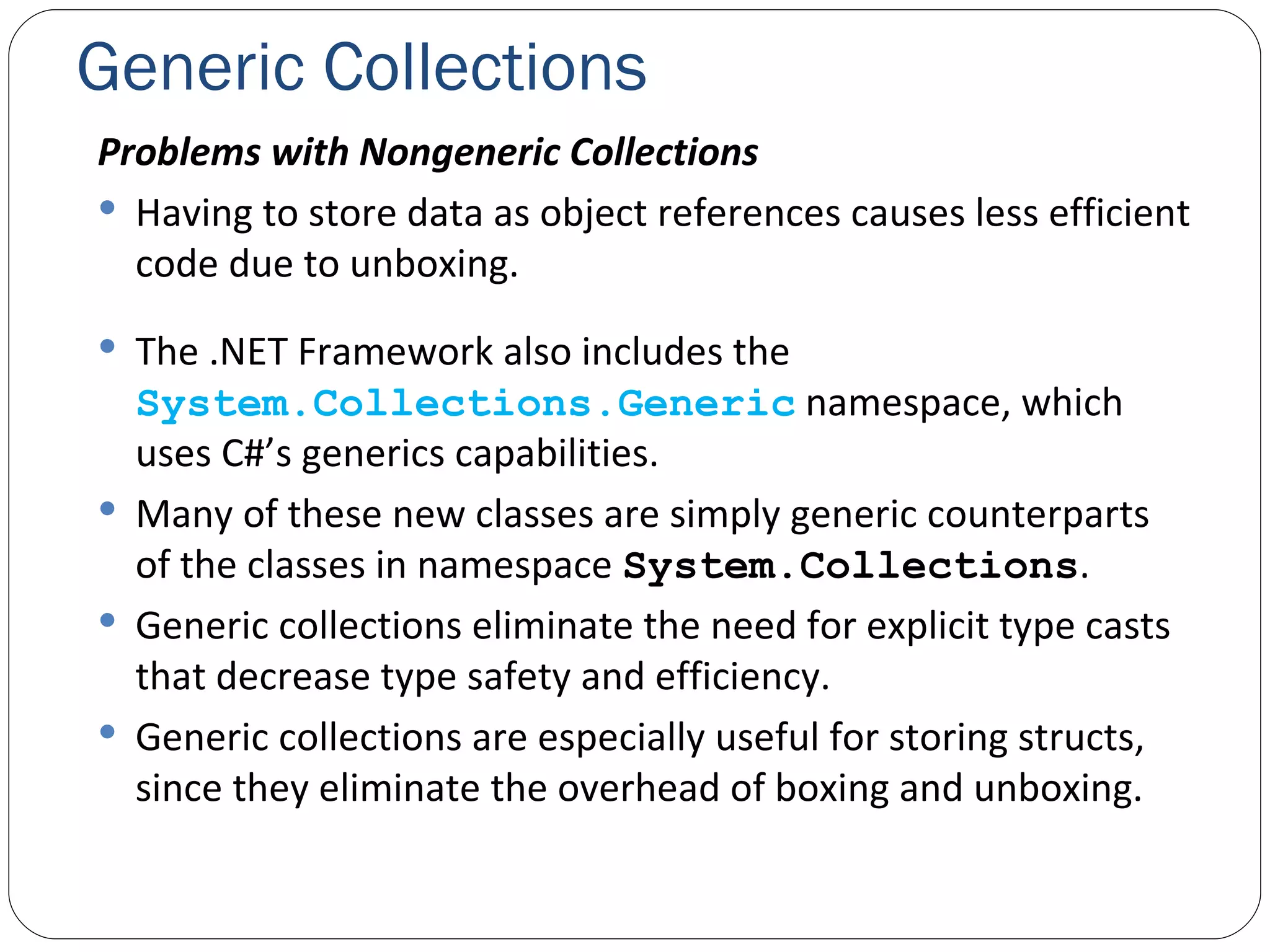
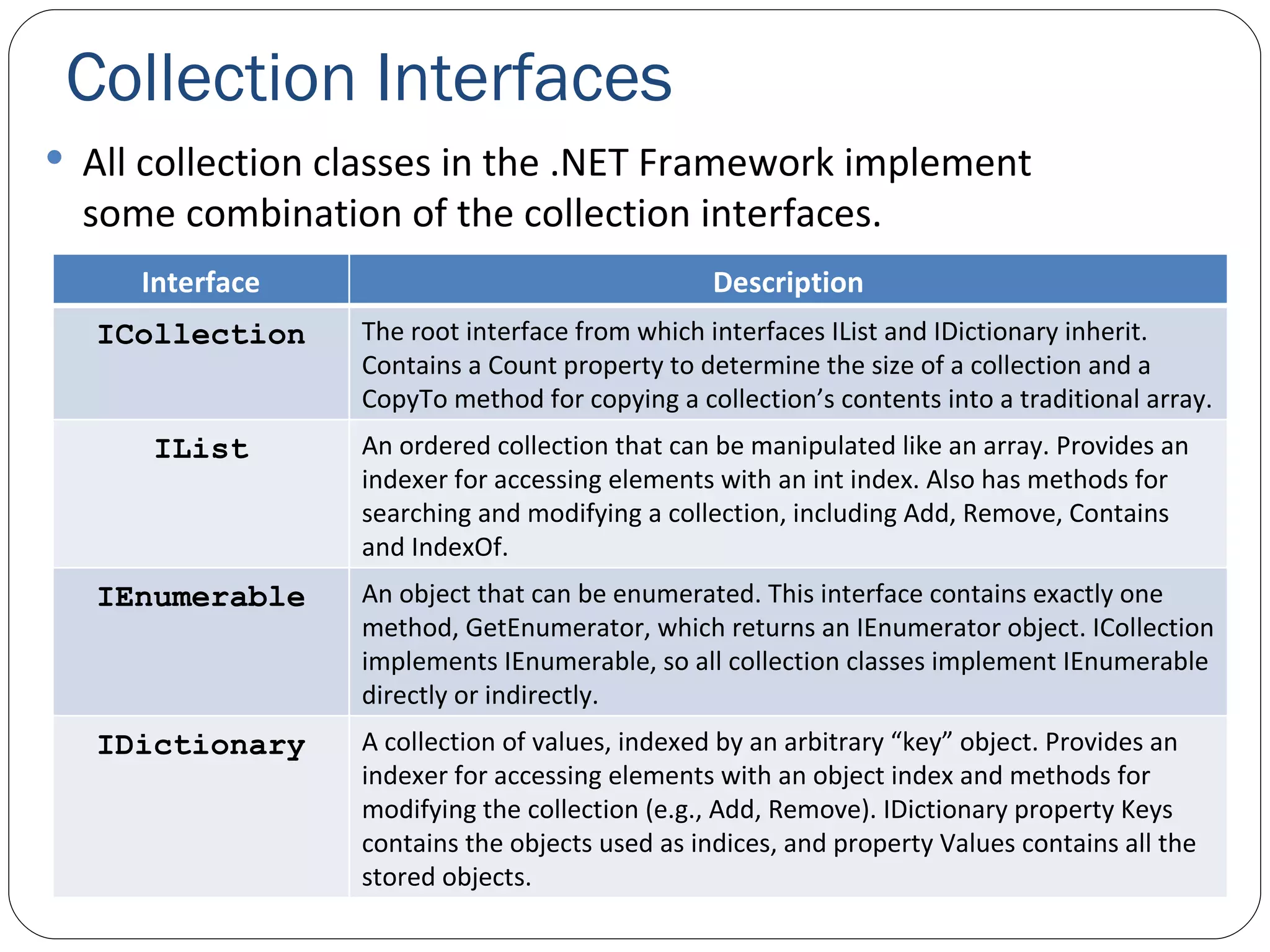
The document discusses generics in .NET and how they provide type safety and code reuse. It explains that generics allow defining methods and classes that can work with different data types. This is done by specifying type parameters that act as placeholders for the actual types. Some key generic concepts covered include generic methods, classes, interfaces, and common collection classes like List, Stack, Queue and how they allow storing and manipulating different types of data.

![Generic Methods Generic methods enable you to specify, with a single method declaration, a set of related methods. Example: OverloadedMethods.cs Note that the array element type (int, double or char) appears only once in each method—in the method header. If we replace the element types in each method with a generic name then all three methods would look like follows: private static void DisplayArray( T [] inputArray ) { foreach ( T element in inputArray ) Console.Write( element + " " ); Console.WriteLine( "\n" ); } However, it will not compile, because its syntax is not correct. GenericMethods.cs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericscollections-091108061446-phpapp02/75/Generics-Collections-3-2048.jpg)



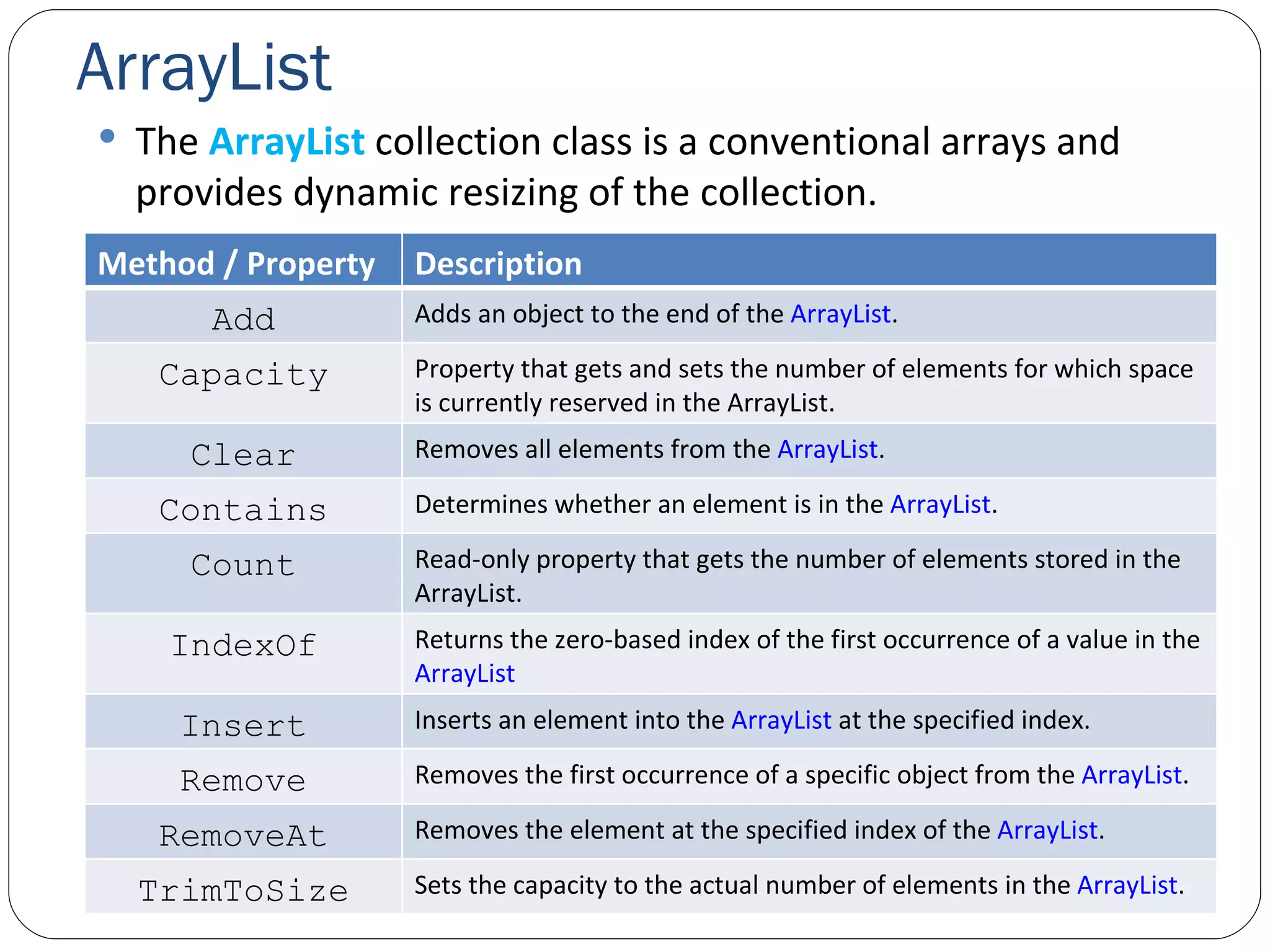
![ArrayList Let’s write code to use ArrayList . Suppose we have two color string arrays as follows: private static readonly string[] colors = { "MAGENTA", "RED", "WHITE", "BLUE", "CYAN" }; private static readonly string[] removeColors = { "RED", "WHITE", "BLUE" }; Let’s create an arrayList and add items in colors into it. Let’s display the size and capacity of arrayList . Let’s find the index of the item “BLUE”. Let’s write a method that removes the items in one ArrayList from another. And then call that method to remove removeColors array from our first arrayList . ArrayListTest.cs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericscollections-091108061446-phpapp02/75/Generics-Collections-10-2048.jpg)
![SortedDictionary<TKey, TValue> A dictionary is the general term for a collection of key/value pairs. A hash table is one way to implement a dictionary. Example: Let’s write a program that counts the number of occurrences of each word in a string read from console using SortedDictionary . To split the sentence into words, we will use this: // split input text into tokens string[] words = Regex.Split( input, @"\s+" ); http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/xfhwa508.aspx Members: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/3eayzh46.aspx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericscollections-091108061446-phpapp02/75/Generics-Collections-12-2048.jpg)
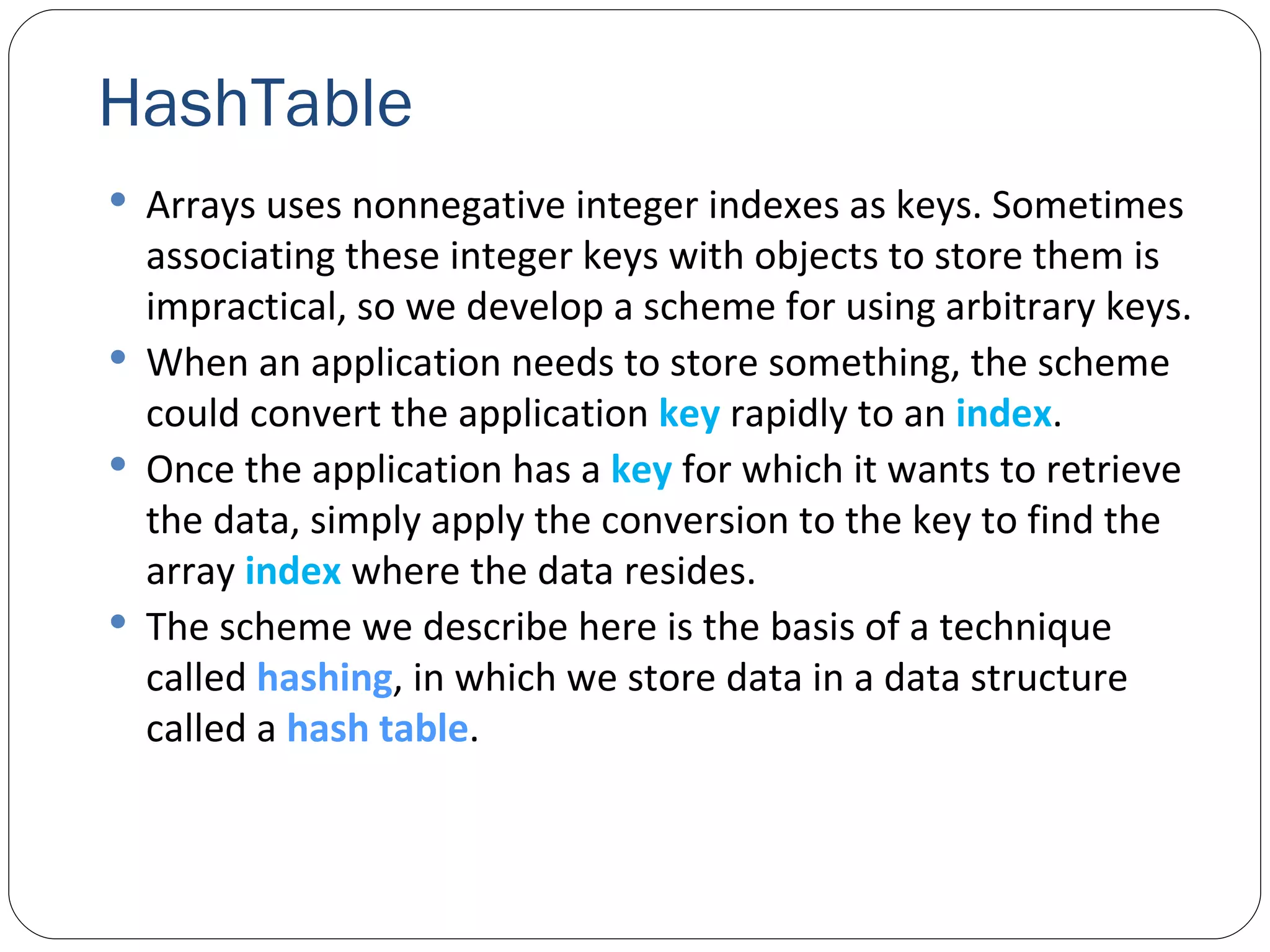
![HashTable A hash function performs a calculation that determines where to place data in the hash table. The hash function is applied to the key in a key/value pair of objects. Class Hashtable can accept any object as a key. For this reason, class object defines method GetHashCode , which all objects inherit. Example: Let’s write a program that counts the number of occurrences of each word in a string read from console. To split the sentence into words, we will use this: // split input text into tokens string[] words = Regex.Split( input, @"\s+" ); HashTable solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericscollections-091108061446-phpapp02/75/Generics-Collections-15-2048.jpg)