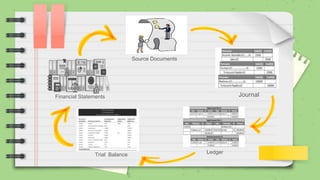
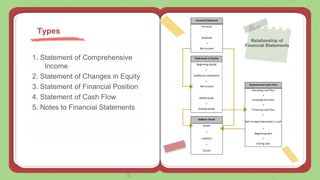
The document provides an overview of financial statements, their purposes, components, and the characteristics that make them useful for various stakeholders. It discusses key types of financial statements, such as the statement of comprehensive income, changes in equity, financial position, and cash flow, while explaining their roles in reflecting an entity's financial performance and position. Additionally, the document outlines the fundamental and enhancing qualitative characteristics of financial information that aid in decision-making.

































![Statement of Comprehensive Income
[Company Name]
Income Statement
For the Year Ended
Revenue
Less: Operating Expenses
Earnings before interest and tax
Less: Interest expense
Less: Tax Expense
Net income after tax
[Company Name]
Income Statement
For the Year Ended
Sales
Less: Cost of goods sold
Gross profit
Less: Operating expenses
Earnings before interest and tax
Less: Interest expense
Less: Tax Expense
Net income after tax
Service Business
Merchandising and
Manufacturing
Business](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ducojhoanamarielledemoteaching-220105170759/85/General-Purpose-Financial-Statements-36-320.jpg)

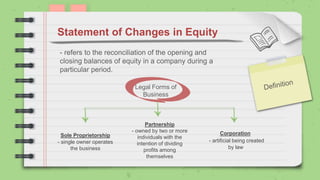

![Statement of Changes in Equity
[Company Name]
Statement of Changes in
Owner's Equity
For the Year Ended
[Name], Capital, beginning
Net income
Less: Withdawals
[Name], Capital, ending
[Company Name]
Statement of Changes in Partners' Equity
For the Year Ended
[Name],
Capital
[Name],
Capital
Capital balances, beginning
Additional investments
Net income
Less: Withdrawals
Capital balances, ending
Sole proprietorship
Partnership](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ducojhoanamarielledemoteaching-220105170759/85/General-Purpose-Financial-Statements-40-320.jpg)
![Statement of Changes in Equity
[Company Name]
Statement of Changes in Shareholders' Equity
For the Year Ended
Common
stock
Paid-in
capital
Retained
earnings
Treasury
Stock
Total
Beginning balance
Issued shares
Net income
Less: Dividends
Ending balance
Corporation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ducojhoanamarielledemoteaching-220105170759/85/General-Purpose-Financial-Statements-41-320.jpg)



![Statement of Financial Position
Sole Proprietorship
[Name], Capital Partnership
[Name], Capital
[Name], Capital Corporation
Share Capital
Reserves/ Additional Paid-in
Capital
Accumulated profit/ loss
Less: Treasury shares](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ducojhoanamarielledemoteaching-220105170759/85/General-Purpose-Financial-Statements-45-320.jpg)
![Statement of Financial Position
[Company Name]
Statement of Financial Position
As of the period
Assets
=
Liabilities
+
Equity
[Company Name]
Statement of Financial Position
As of the period
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Report Form Account Form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ducojhoanamarielledemoteaching-220105170759/85/General-Purpose-Financial-Statements-46-320.jpg)

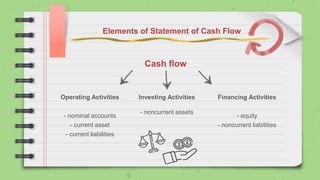
![Statement of Cash Flow
[Company name]
Statement of Casf Flow
Year Ended
Cash flow for operating activties
Cash from customers
Cash from suppliers
Cash for opeerating expenses
Cash for interest
Cash for taxes
Net cash provided for operating activities
Cash flow for investing activties
Cash flow for financing activties
Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning
Cash and cash equivalents, ending
[Company name]
Statement of Casf Flow
Year Ended
Cash flow for operating activties
Net income
Amortization expense
(Increase) decrease adjustments in net income
Increase (decrease) in current asset and liability
Net cash provided for operating activities
Cash flow for investing activties
Cash flow for financing activties
Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning
Cash and cash equivalents, ending](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ducojhoanamarielledemoteaching-220105170759/85/General-Purpose-Financial-Statements-49-320.jpg)







