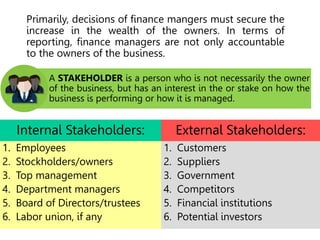
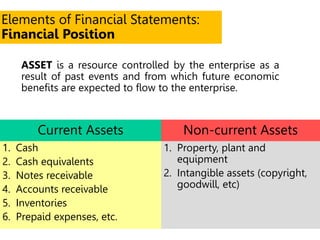
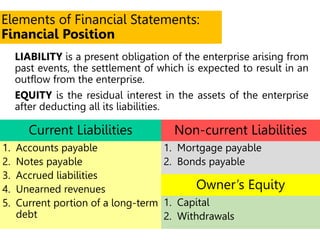
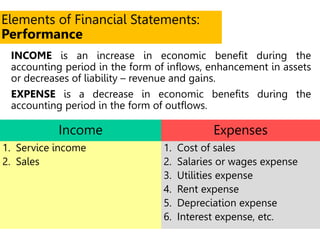
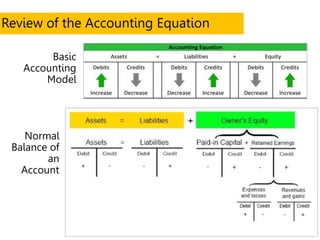
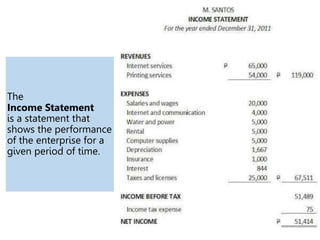
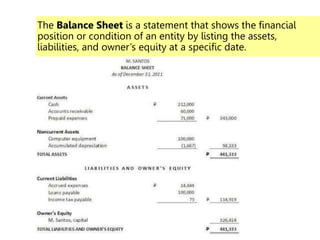
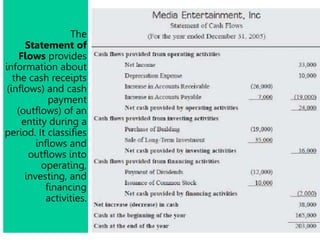
This document defines key terms and concepts related to financial reporting standards. It discusses internal and external stakeholders that financial statements are reported to. The document outlines Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and International Financial Reporting Standards that provide uniformity in financial reporting. It also defines the key components of financial statements, including the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of changes in equity. Elements such as assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses are also defined.