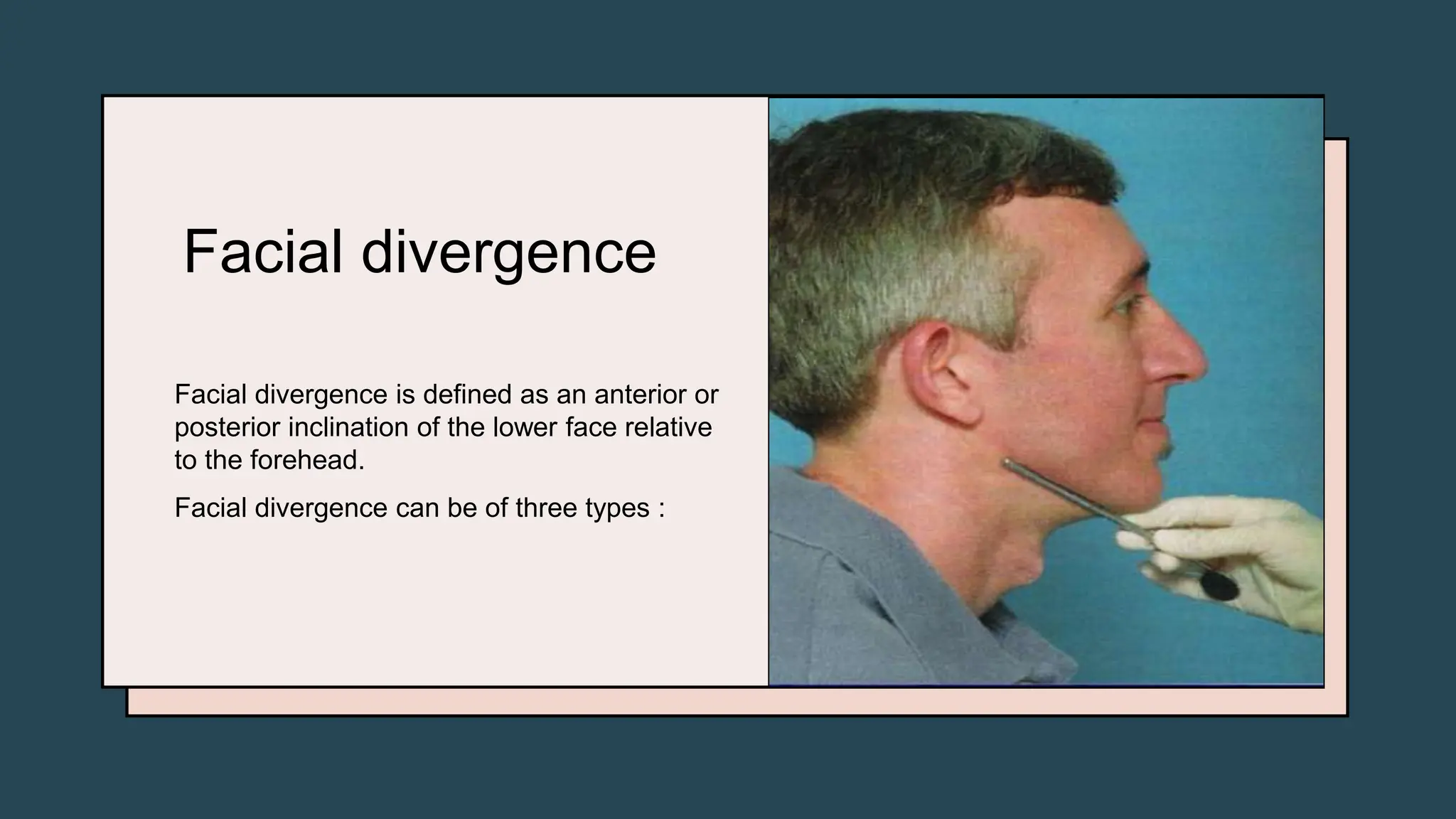
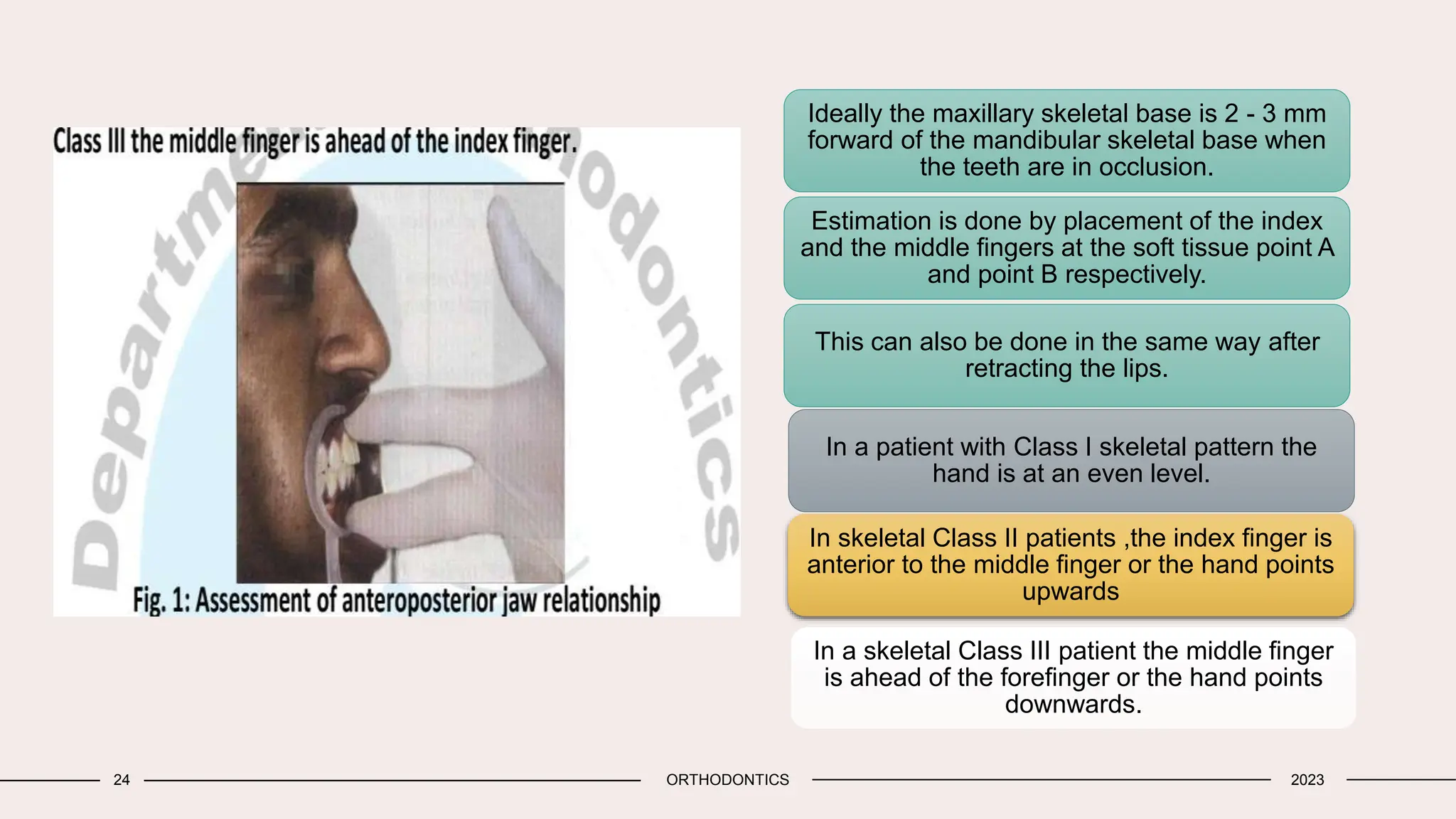
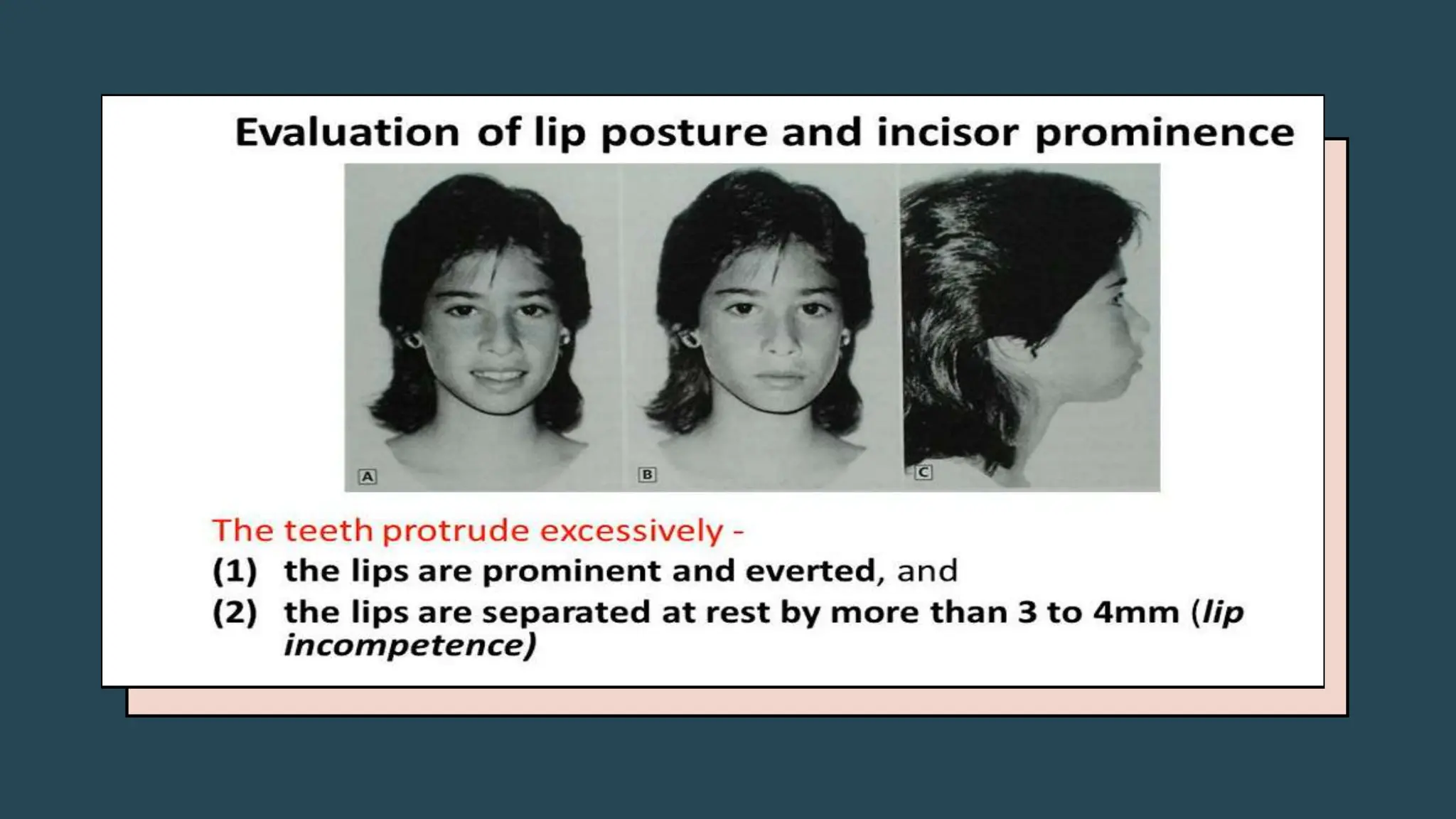
The document outlines the general examination procedures in orthodontics, including assessments of patient height, weight, gait, posture, body build, and facial symmetry. It categorizes various physical forms and abnormalities that may have dental correlations, along with methods for evaluating jaw relationships and facial proportions. Additionally, it describes specific features such as lip competence and nose symmetry that can affect overall facial aesthetics.