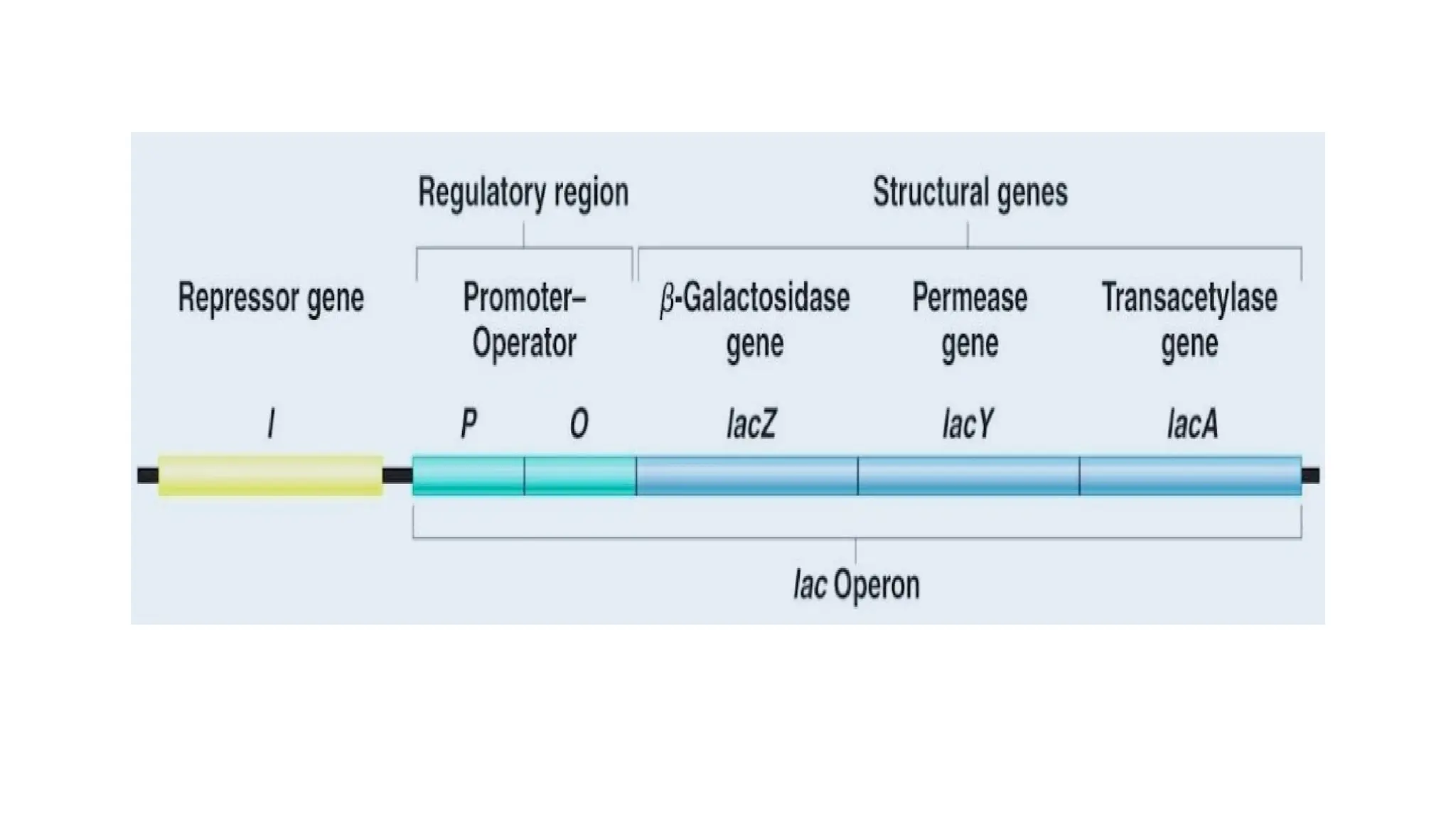
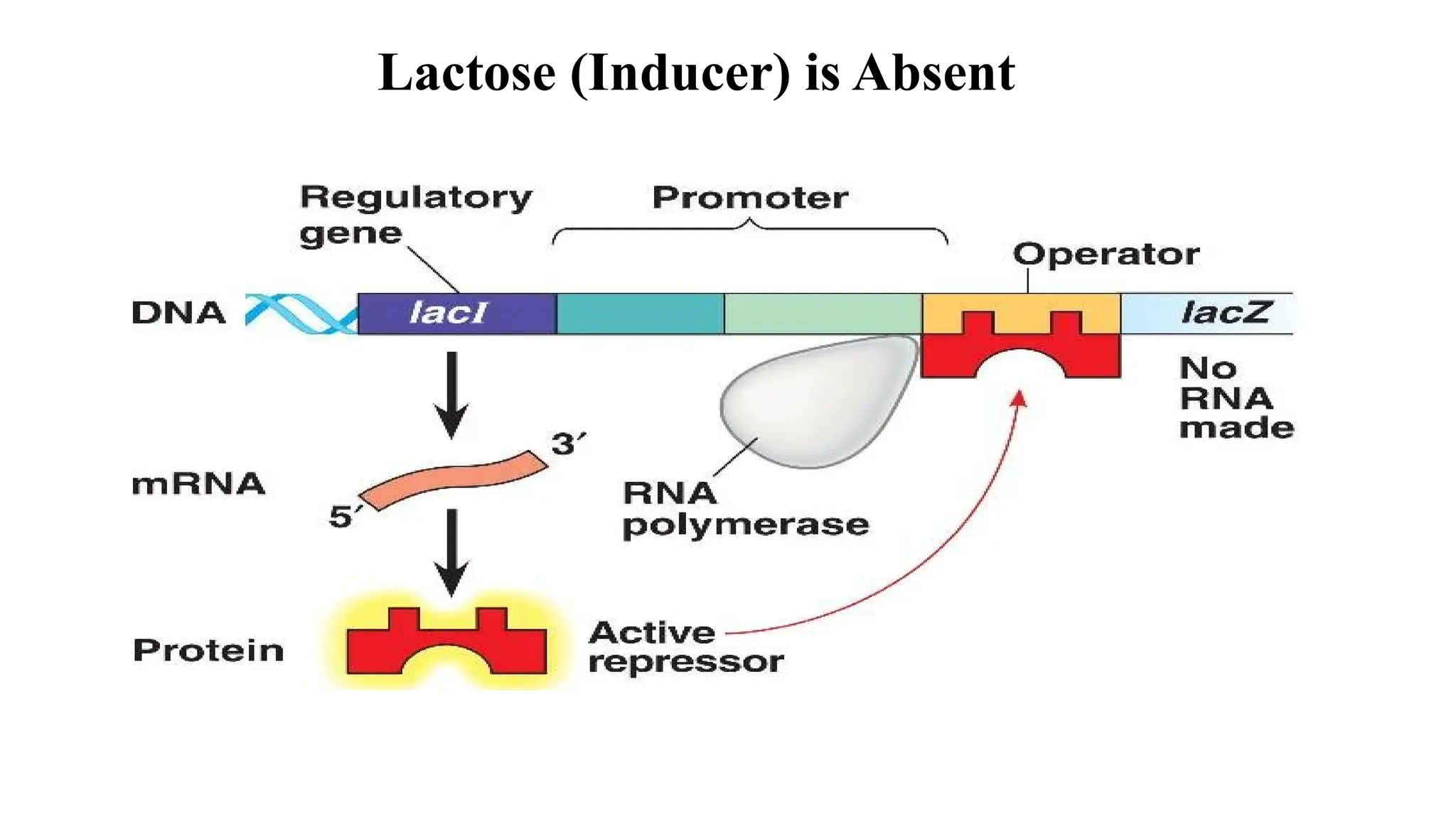
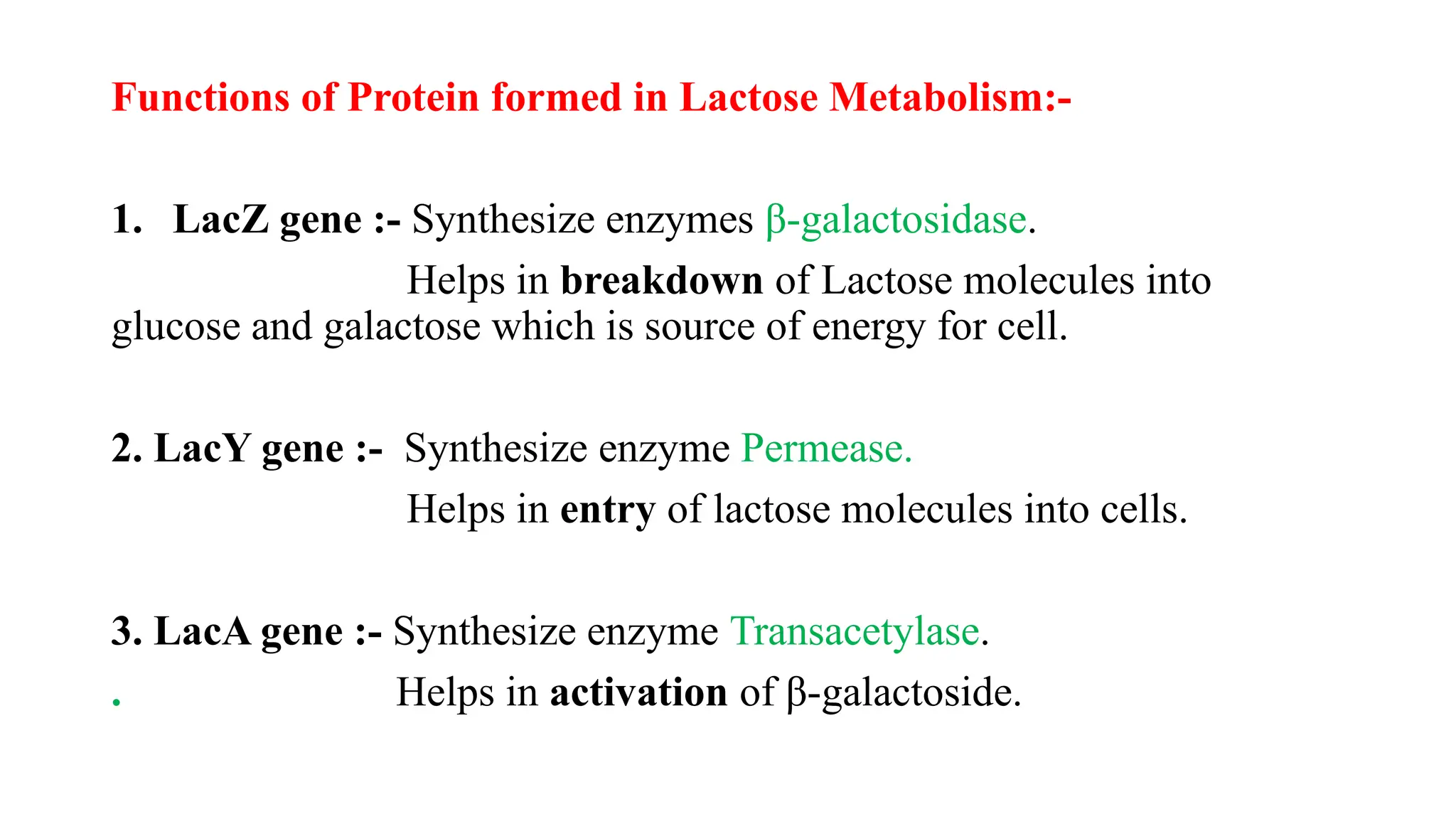
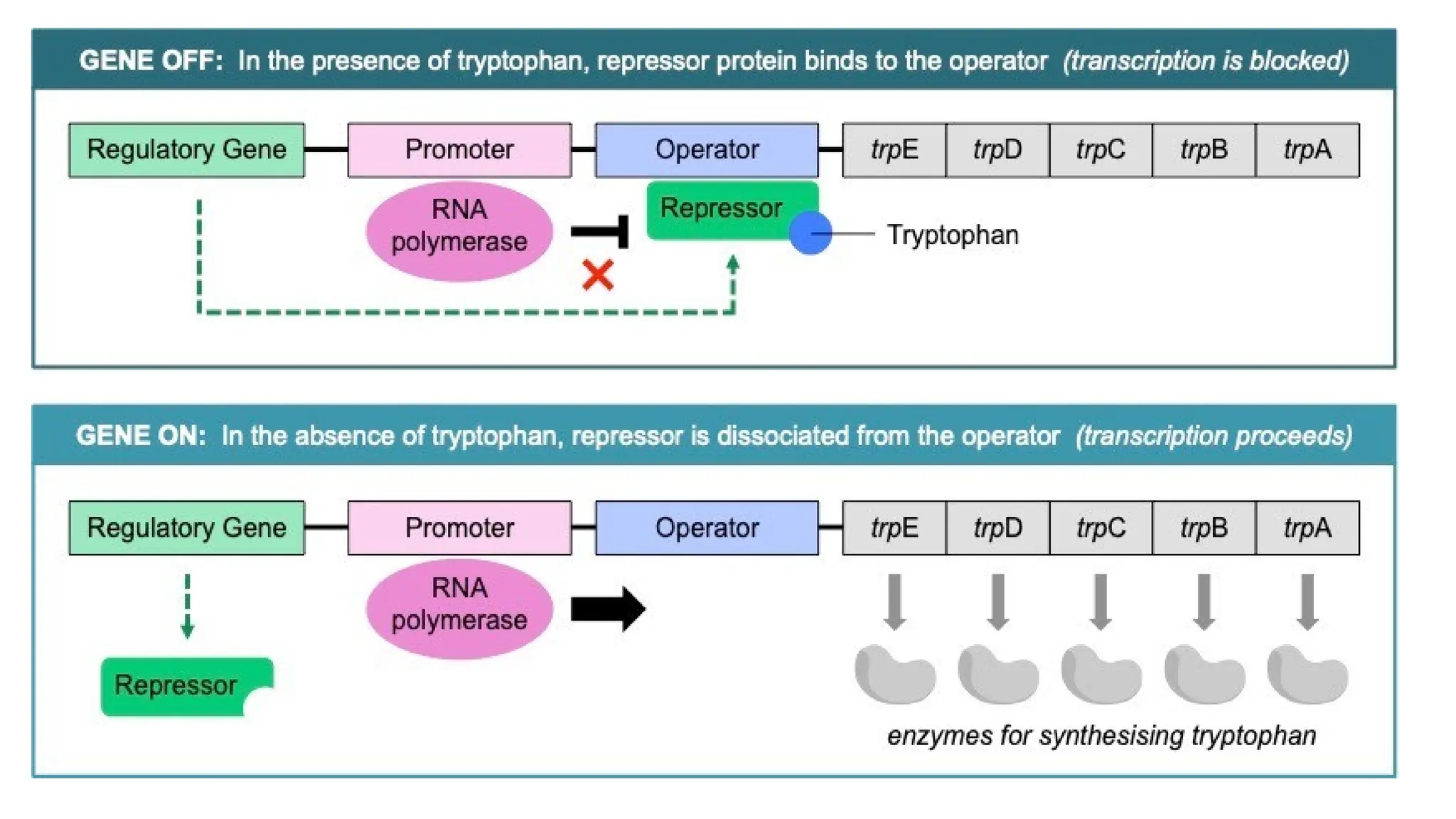
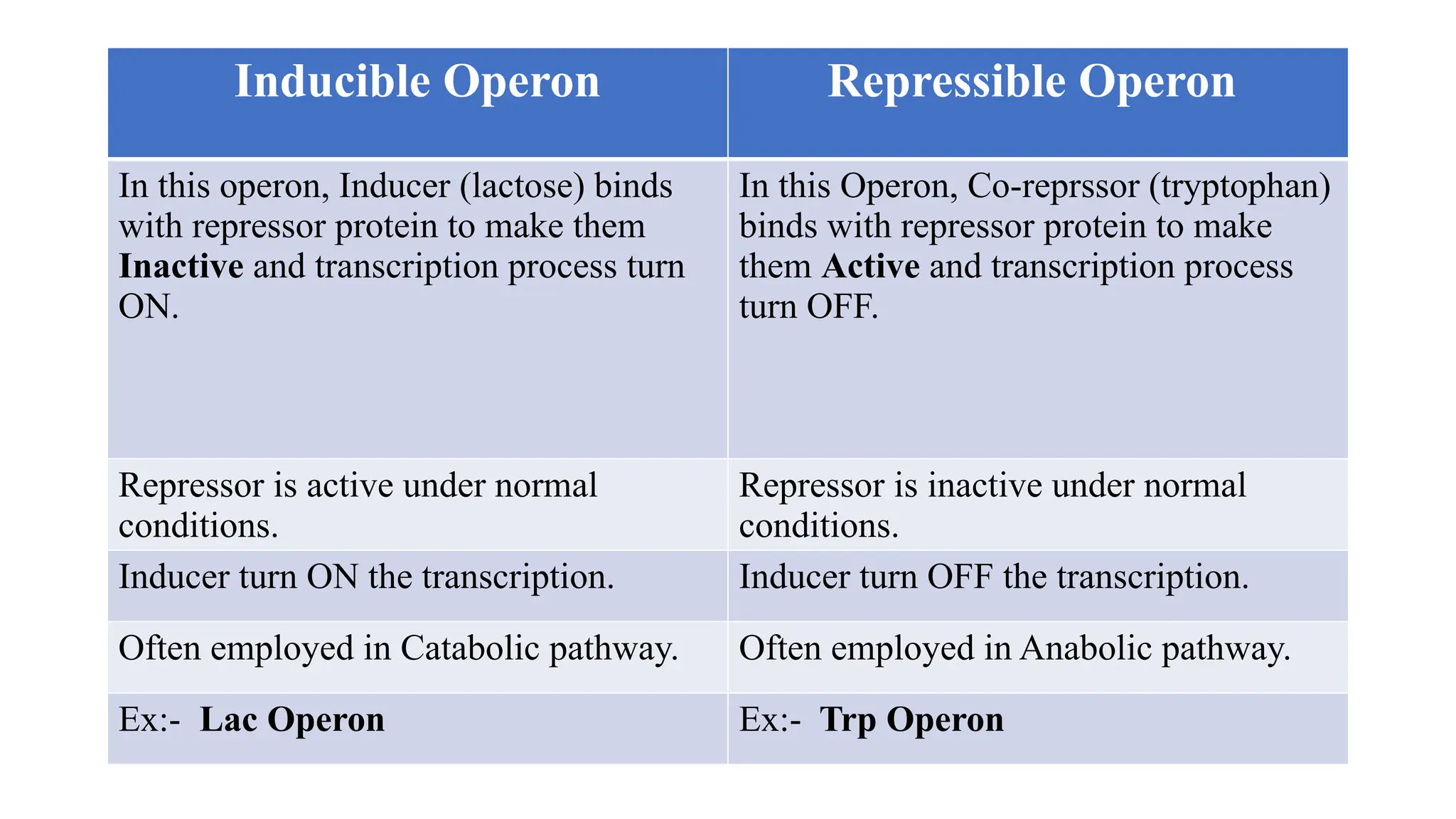
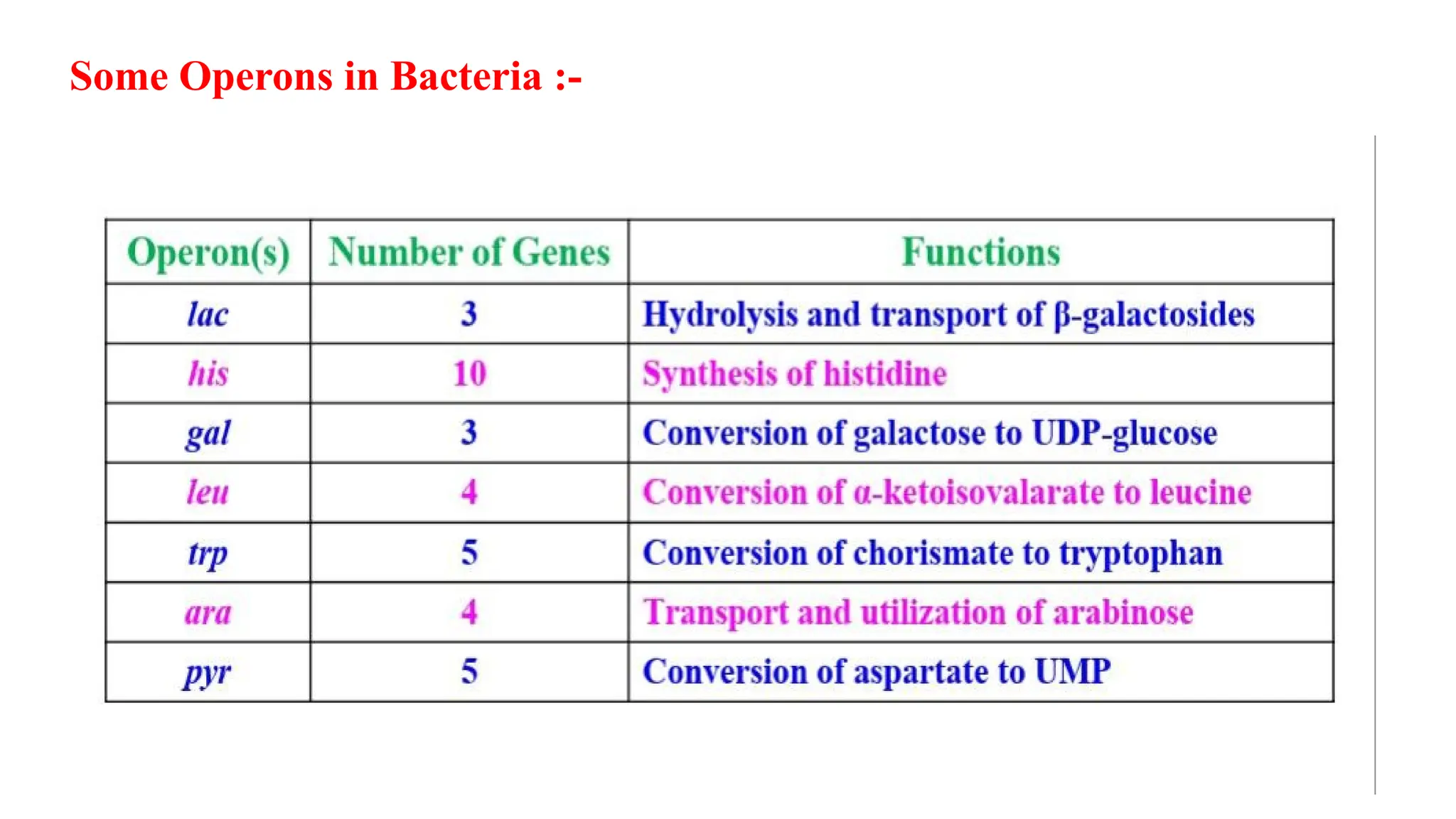
The presentation discusses gene regulation in prokaryotes, focusing on the transcriptional level and the lac operon model developed by Jacob and Monod. It explains the components of the lac operon including promoter, regulator gene, operator, structural genes, and inducer, alongside its role in lactose metabolism. Additionally, the document contrasts inducible and repressible operons, highlighting the function of the trp operon in tryptophan biosynthesis regulation.