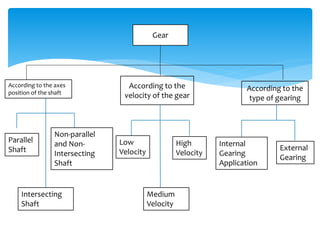
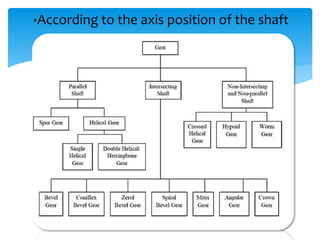
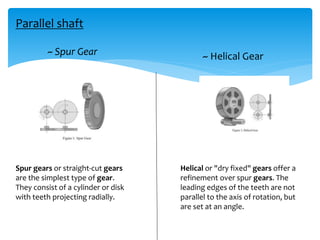
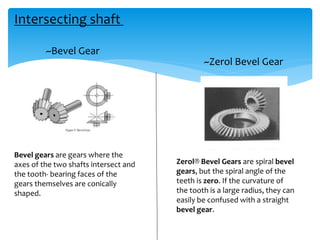
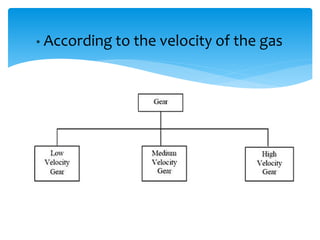
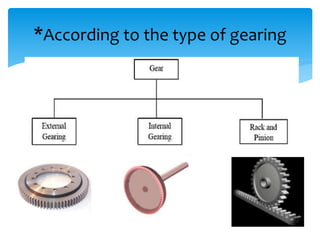
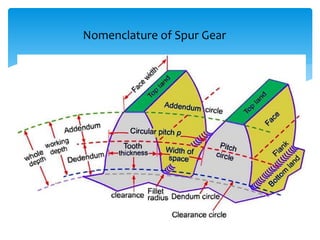
Gears can be classified in three ways: by shaft position (parallel, intersecting, non-parallel/non-intersecting), velocity (low, medium, high), and type (external, internal, rack and pinion). Common gears include spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, worm gears, and crown gears. Gears are also classified by materials like aluminum, brass, magnesium, and steel. Aluminum gears are lightweight while brass gears are low-cost. Steel gears are used for medium power applications and cast iron for large, moderate power gears.