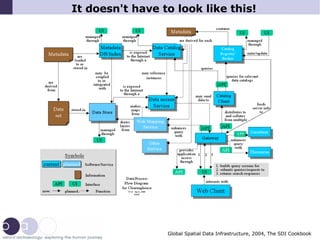
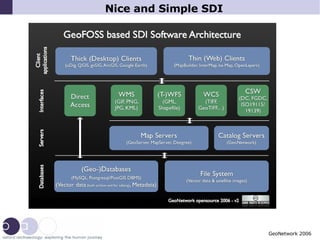
1) The document discusses how INSPIRE aims to increase sharing and reuse of spatial data by reducing data gaps and barriers between incompatible datasets.
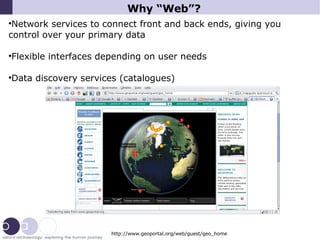
2) It argues that open source software and putting data on the web using modular, interoperable tools can help meet INSPIRE goals and make spatial data infrastructure accessible to all organizations at local levels.
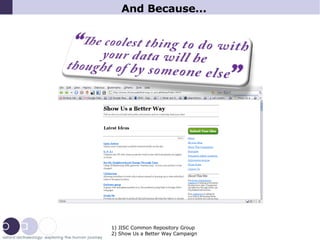
3) Choosing open source and web-based approaches provides benefits like flexibility, sustainability, and independence from any single supplier.
![Getting Your Maps on the Web A Philosophical Approach Gateway Group Seminar- INSPIRE and Web Mapping Sandford on Thames, July 2008 Jo Cook Senior Applications Support and Development Officer Oxford Archaeological Unit Ltd [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gateway-seminar-090514100127-phpapp02/85/Gateway-Seminar-1-320.jpg)