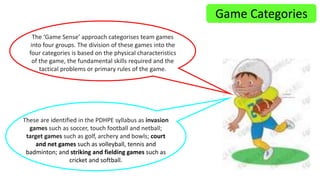
The document discusses the Game Sense approach to teaching physical education. Game Sense uses games as a learning tool to develop students' tactical and strategic thinking as well as skills. It is a student-centered approach that allows students to develop skills while actively participating in games. The document provides examples of how teachers can implement the Game Sense approach and the skills and outcomes students can gain from this style of learning.