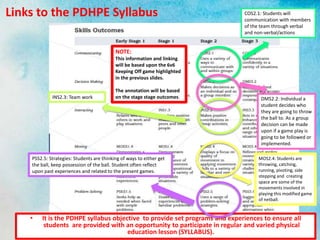
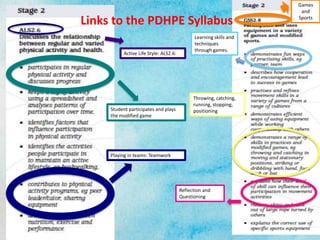
Game Sense is an alternative approach to coaching and teaching physical education and sports. It focuses on tactical understanding and decision making rather than just physical skills. Students learn through modified games and questioning from the teacher. This helps students learn what to do rather than just how to do physical skills. Two common ways to implement Game Sense are through small sided games that gradually increase players, and mid-sized games where complexity is added over time. Game Sense aims to increase participation and provide positive learning experiences for students.