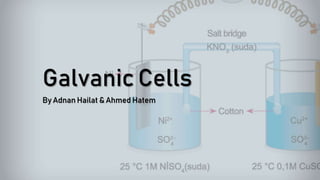
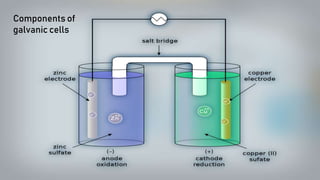
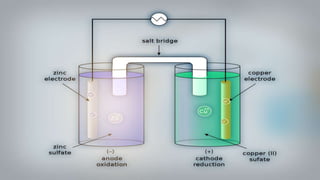
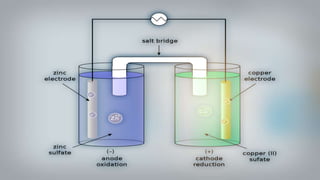
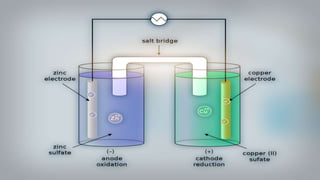
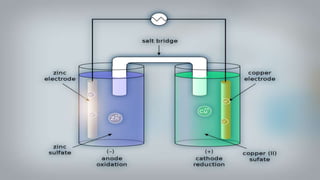
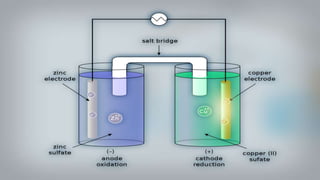
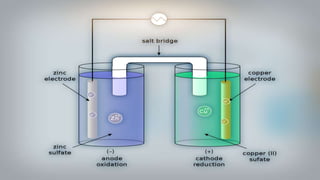
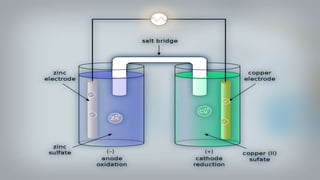
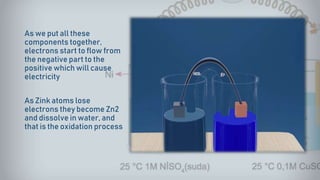
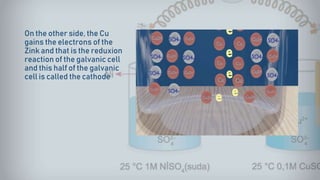
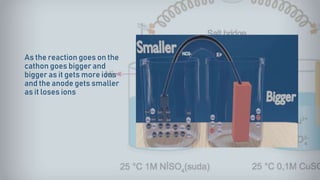
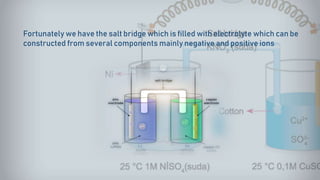
Galvanic cells are electrochemical cells that convert the chemical energy of spontaneous redox reactions into electrical energy. They contain an oxidation half-cell and a reduction half-cell separated by a salt bridge or porous membrane. In a galvanic cell, zinc metal oxidizes and loses electrons which flow through an external circuit to the copper ion reduction half-cell. The spontaneous electron flow produces an electric current useful for powering devices. Galvanic cells provide the foundation for generating spontaneous electric current from chemical reactions and are an important component of batteries used widely in modern technology.