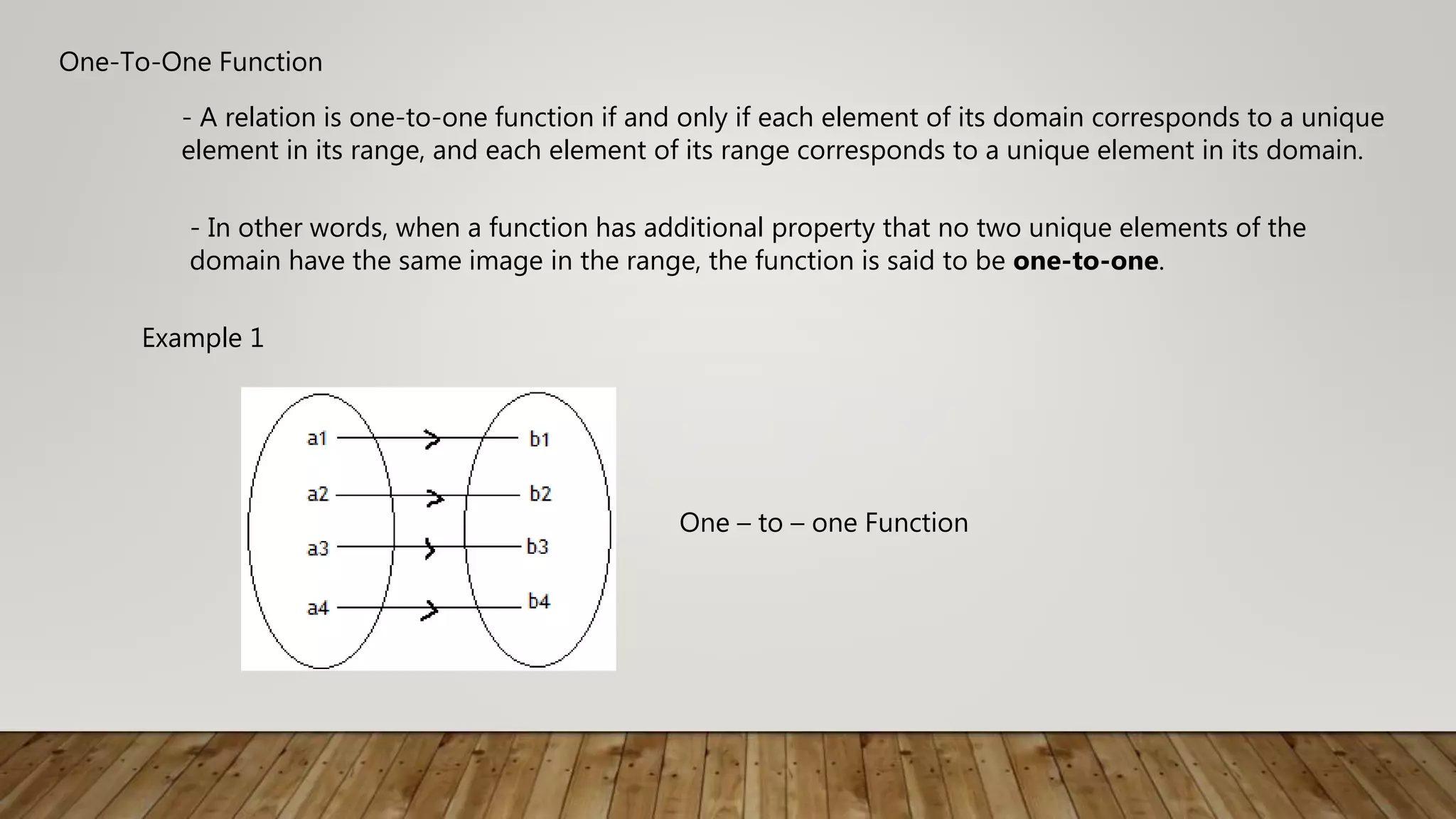
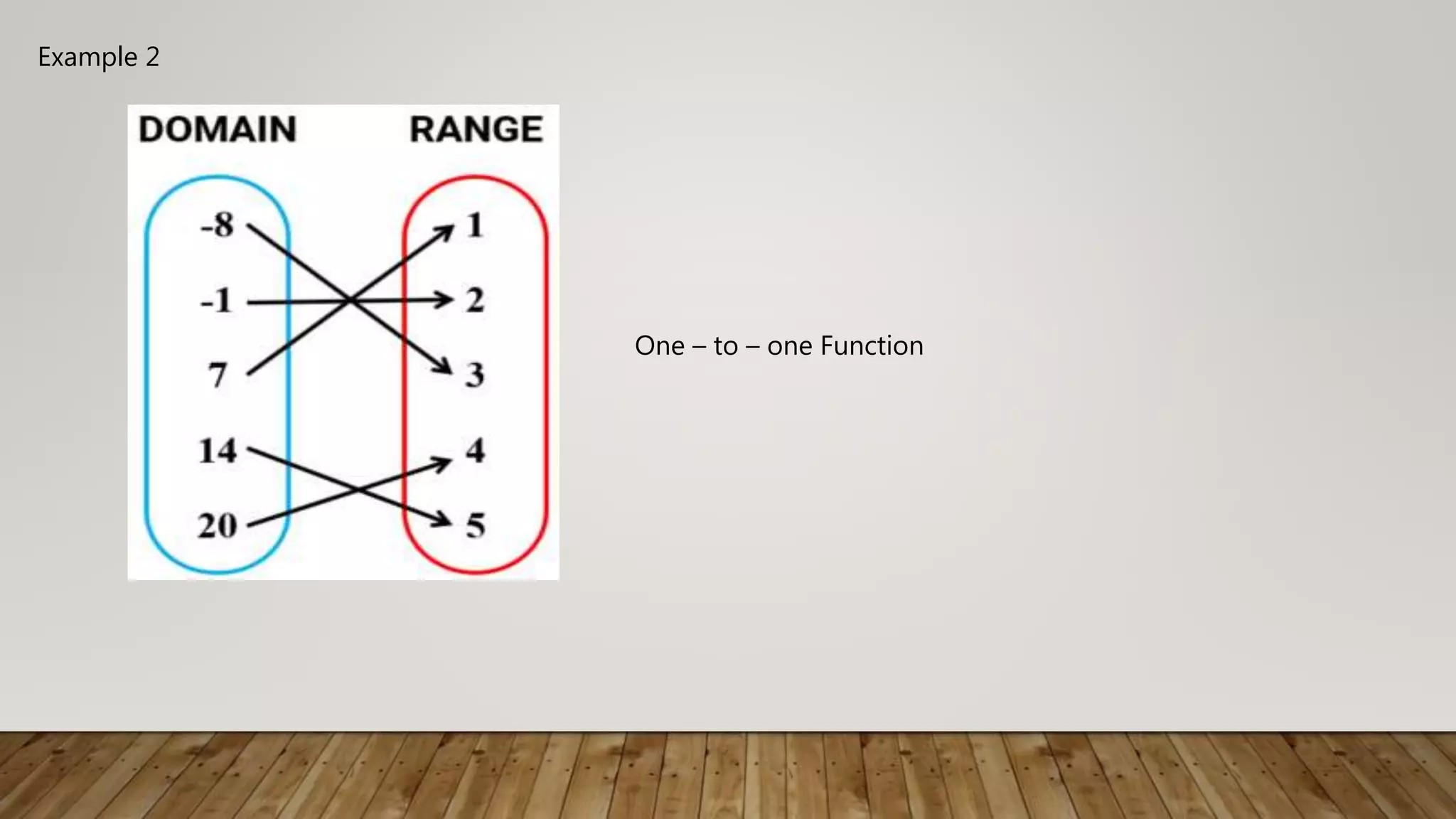
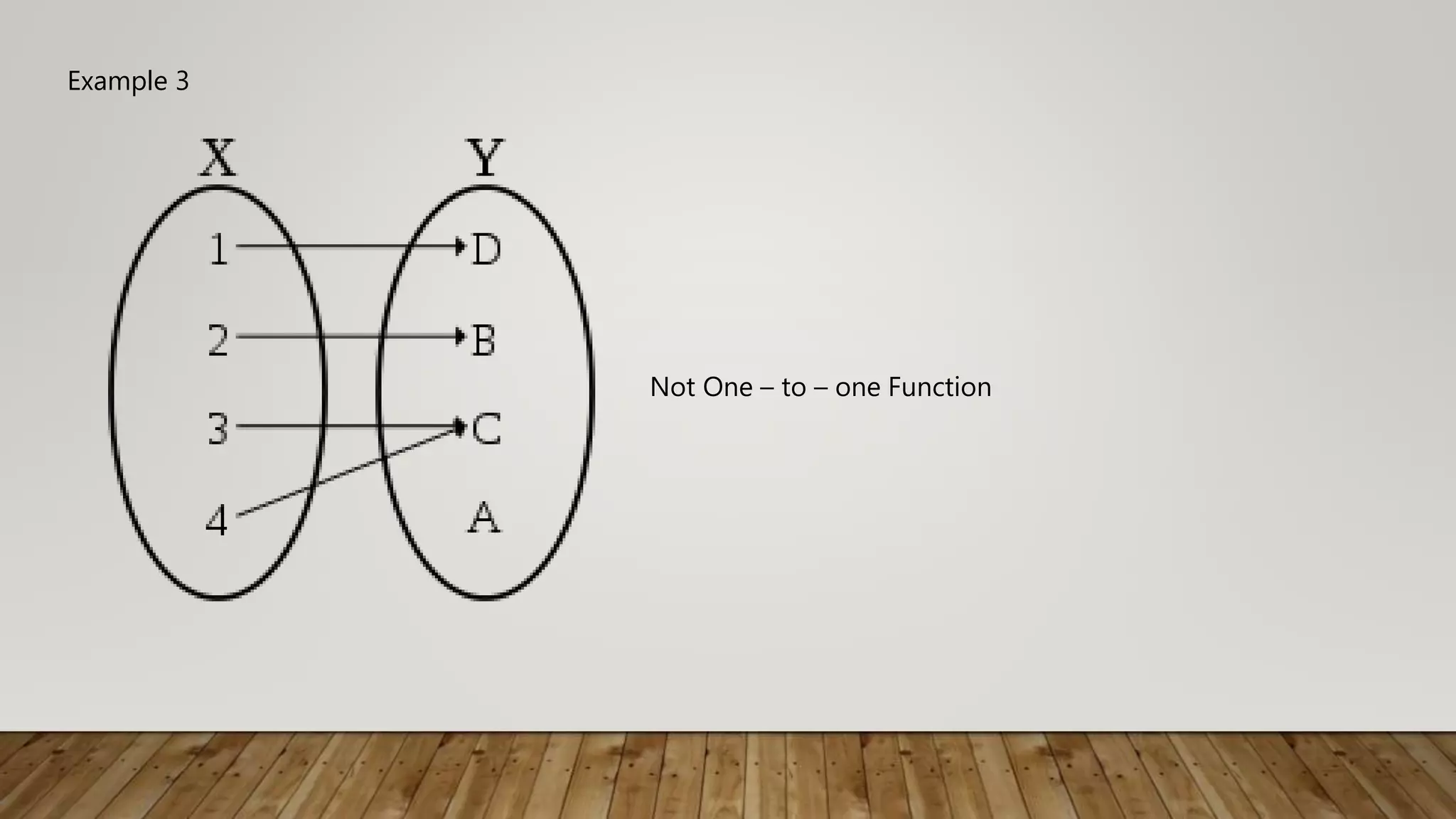
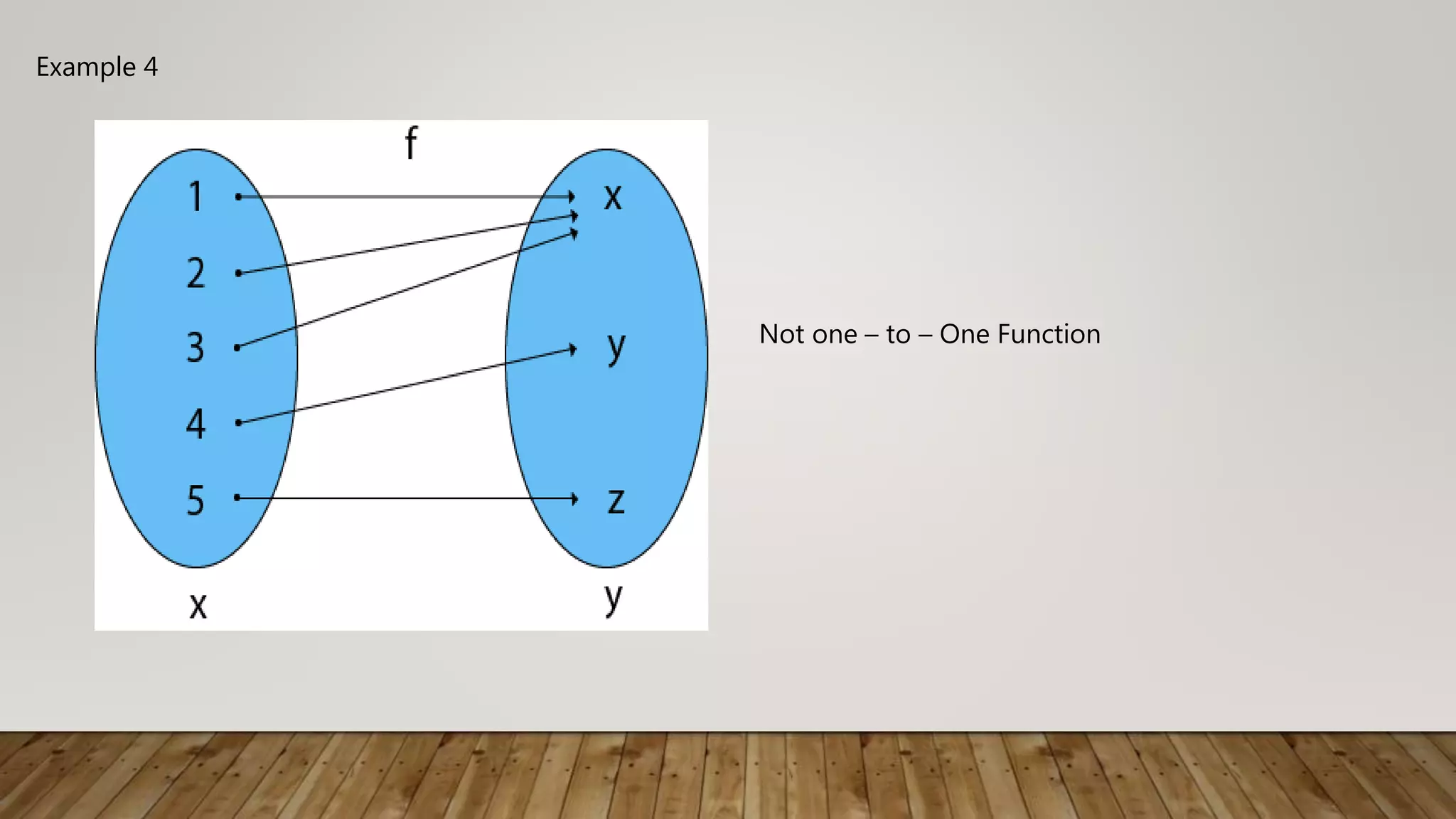
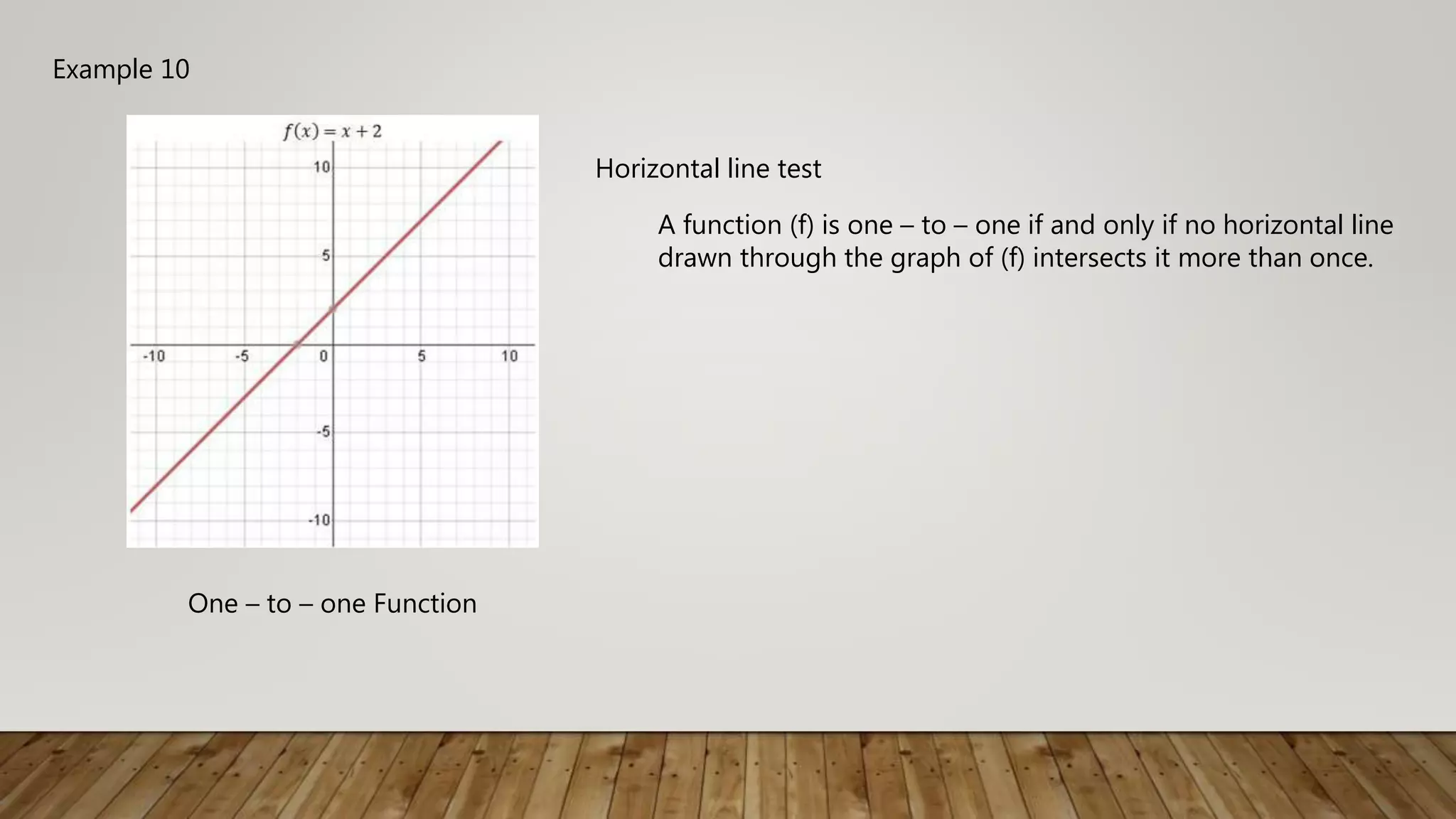
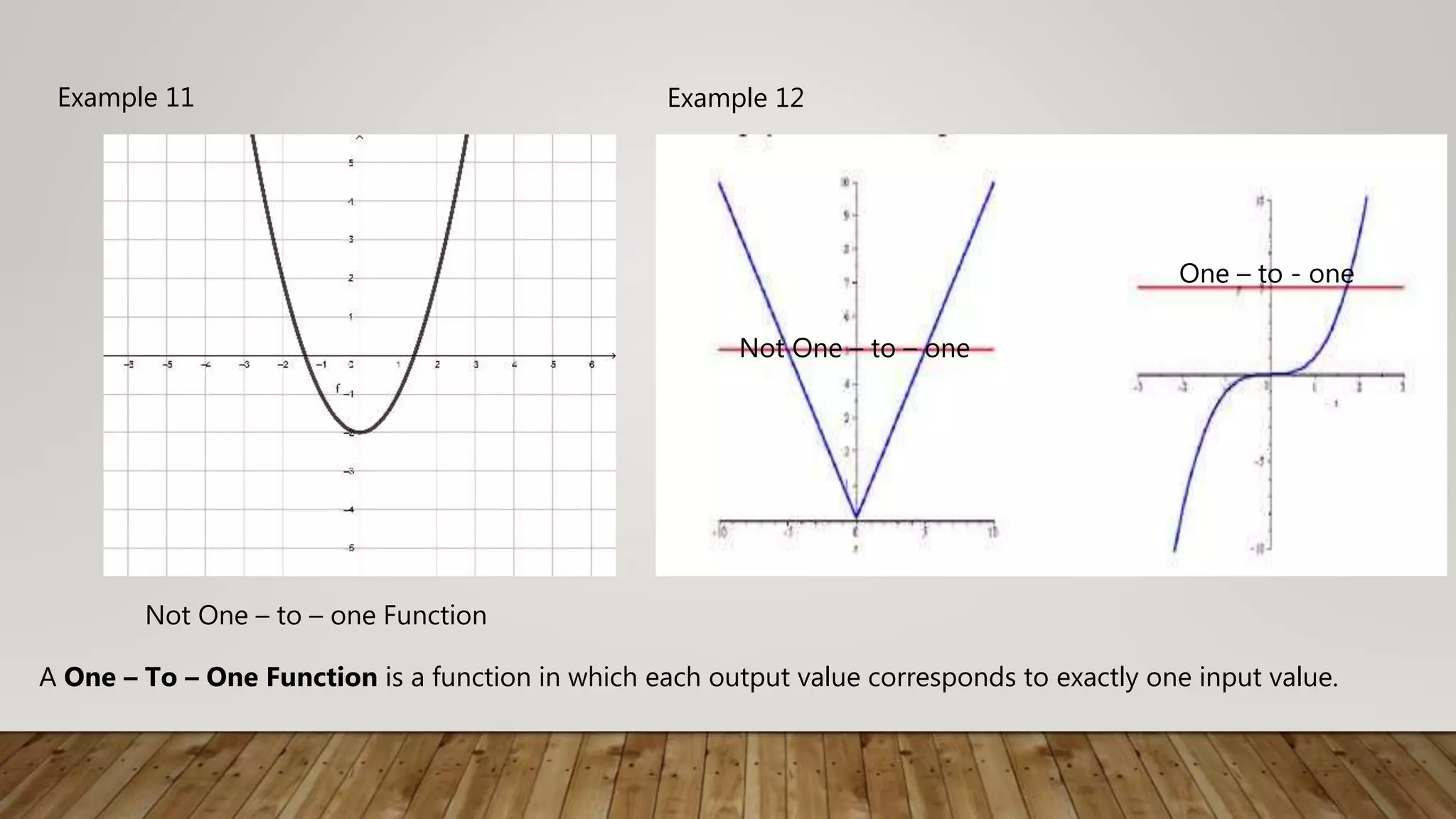
The document defines and provides examples of one-to-one functions. A function is one-to-one if each element of the domain maps to a unique element in the range, and vice versa. This can be tested graphically using the horizontal line test, where no horizontal line intersects the graph in more than one point. Examples demonstrate one-to-one functions, including linear functions like f(x)=2x-5, and non one-to-one functions where the highest degree of an even polynomial allows multiple inputs to map to the same output.