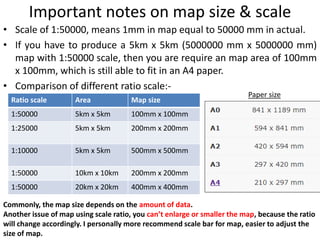
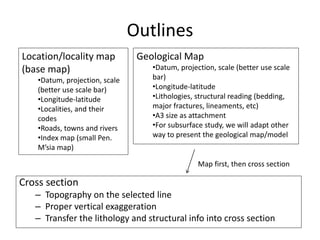
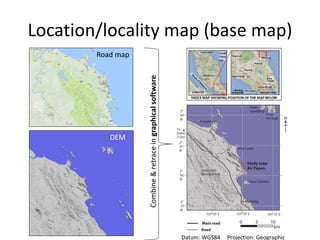
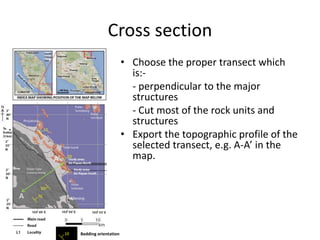
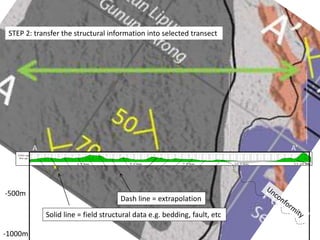
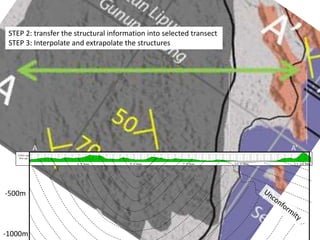
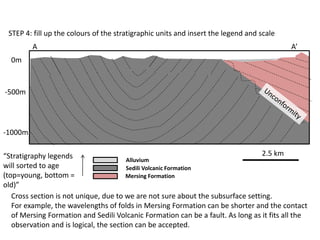
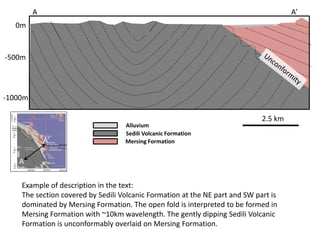
This document provides guidance on creating a geological map and cross section for a field project. It discusses scale and size for the map, with 1:50,000 scale fitting a 5x5 km area on an A4 page. The outlines section lists what to include on the map such as lithologies, structures, and location/locality maps. For the cross section, the document explains how to export topography, transfer structural data, interpolate structures, and add stratigraphic units with legends. An example cross section is provided with description.