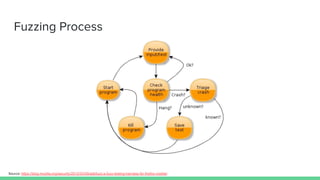
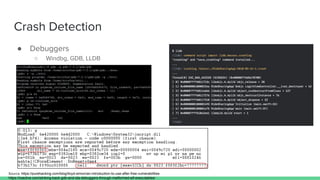
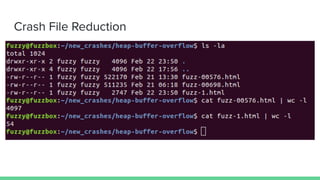
The document discusses different types of software fuzzing techniques. It provides an overview of the fuzzing process, which involves generating test cases, feeding them to the target program, monitoring for crashes, saving any crash cases, and repeating. It then describes two main types of fuzzing: mutation-based using tools like AFL, and generation-based using techniques like Domato. The document demonstrates mutation-based fuzzing on tcpdump using AFL. It provides steps to set up AFL and tcpdump, generate test cases, run AFL in parallel, and analyze any crashes found.