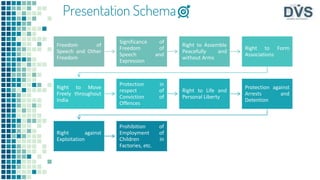
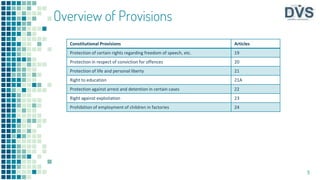
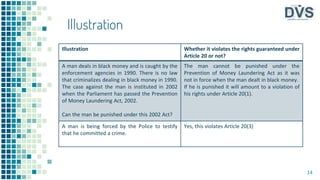
The document outlines fundamental rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution, specifically Articles 19 to 24, which include the right to freedom of speech, assembly, association, movement, education, and protection against exploitation and arbitrary arrest. It emphasizes that these rights are not absolute and can be subject to reasonable restrictions for public interest. Additionally, the document discusses the significance of these rights through various judicial precedents that have expanded their scope over time.