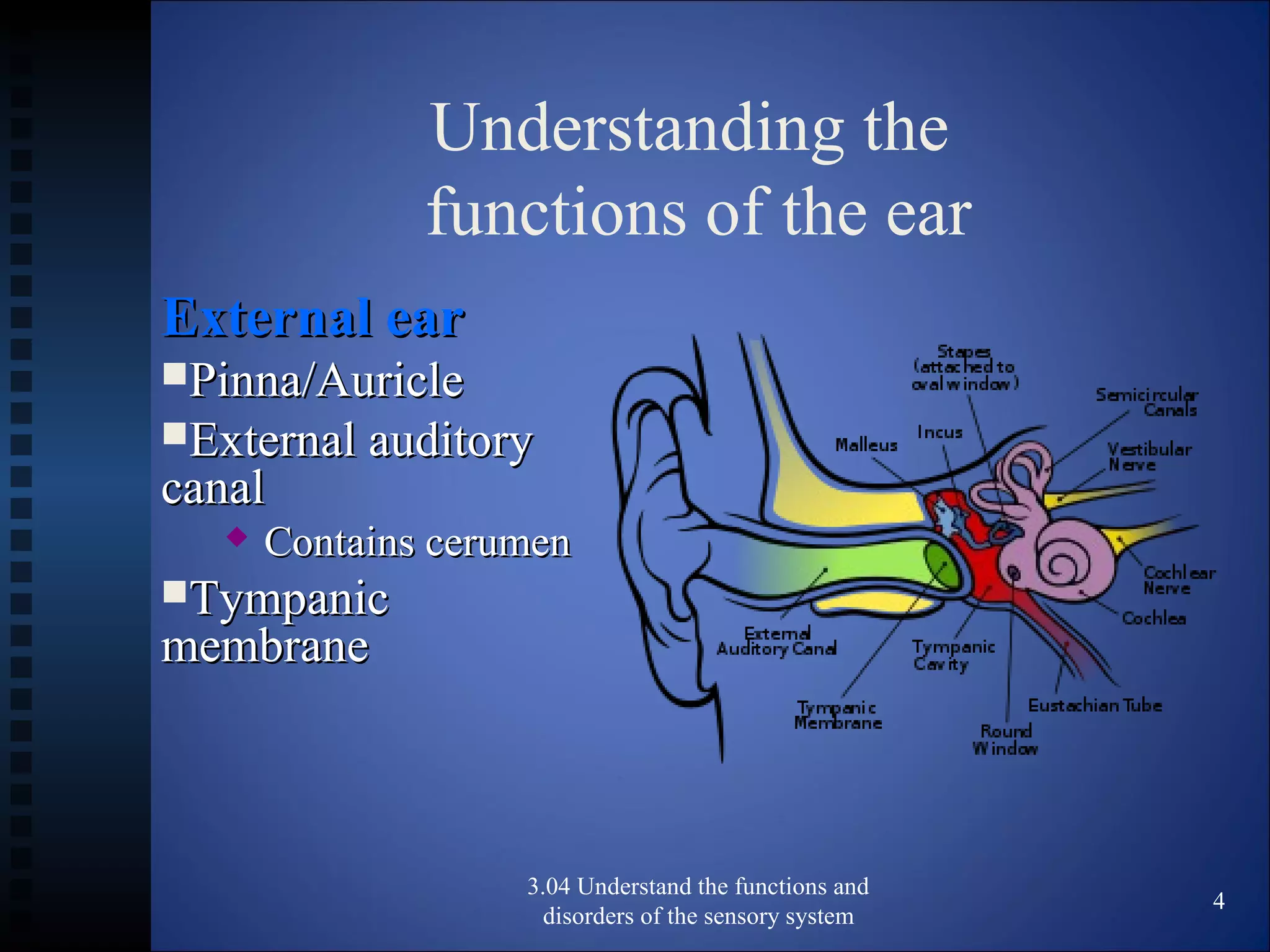
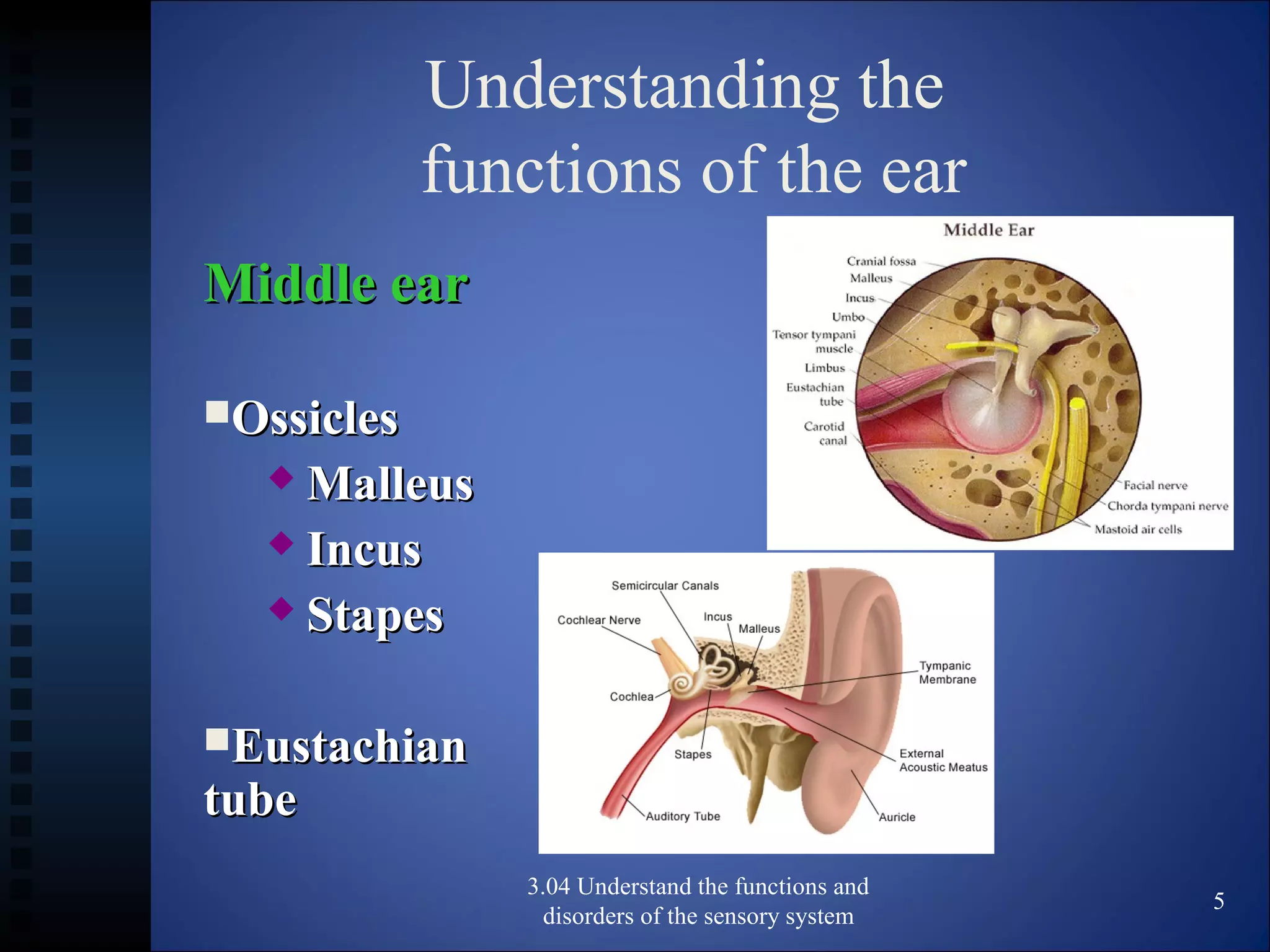
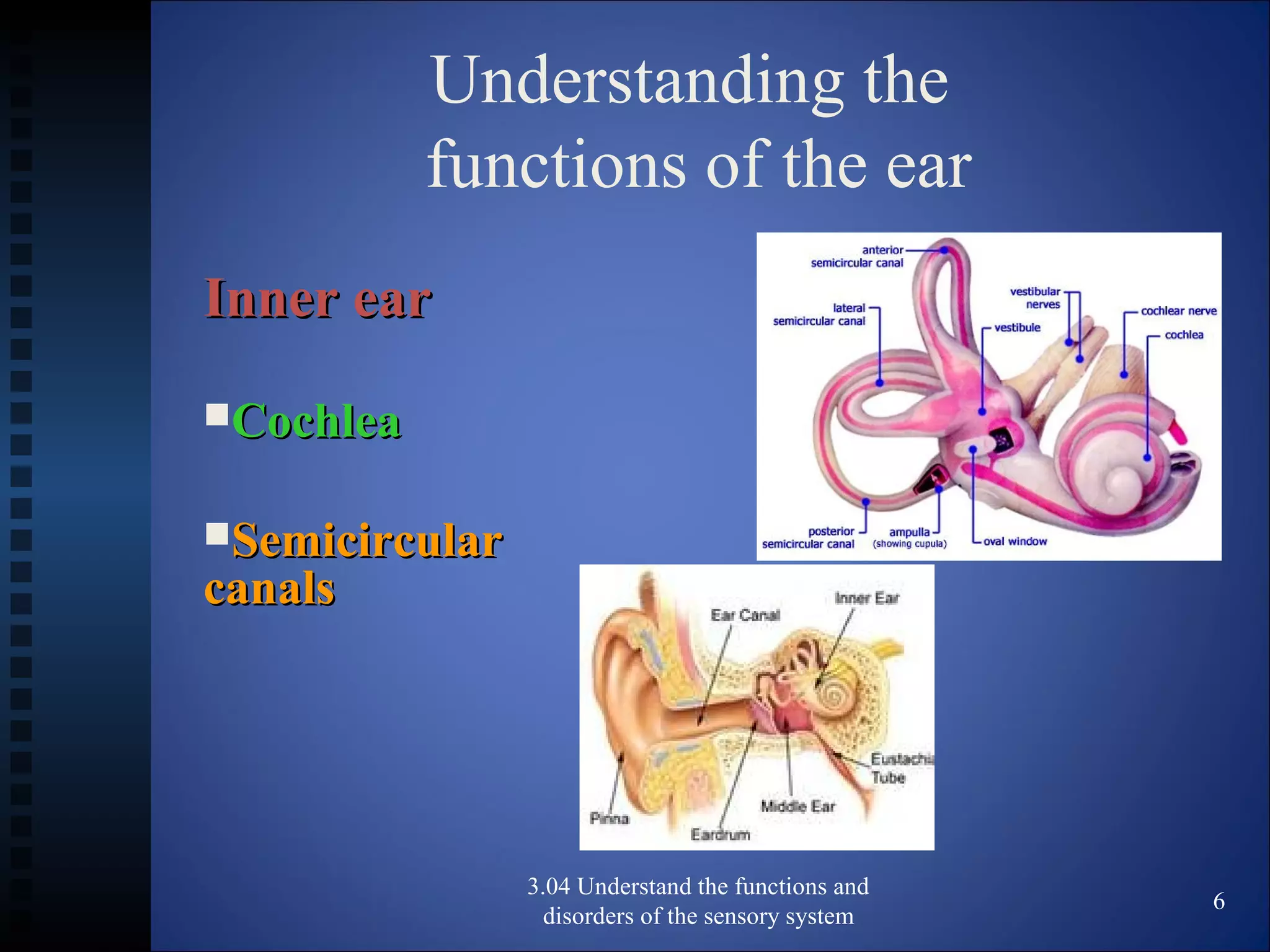
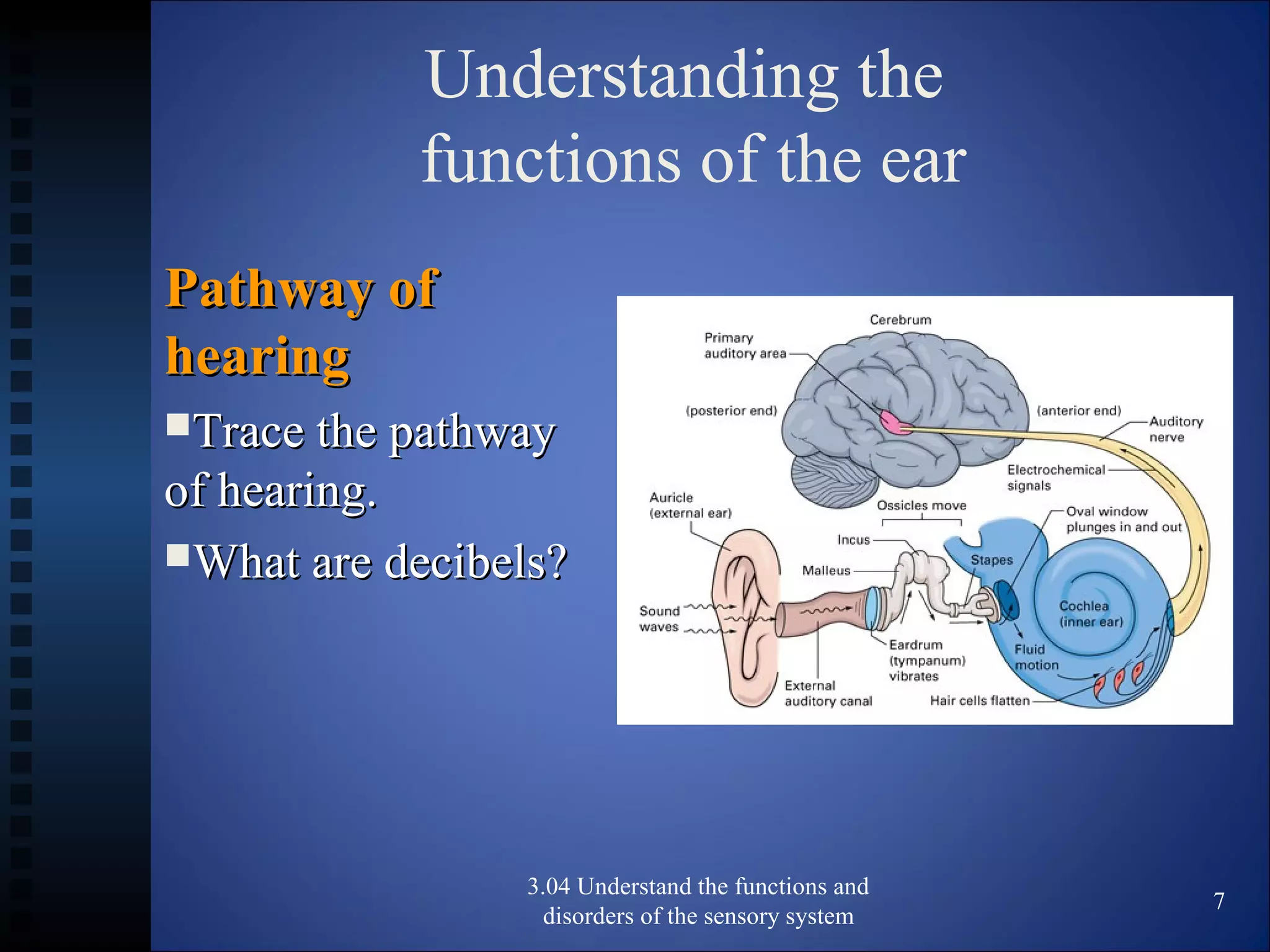
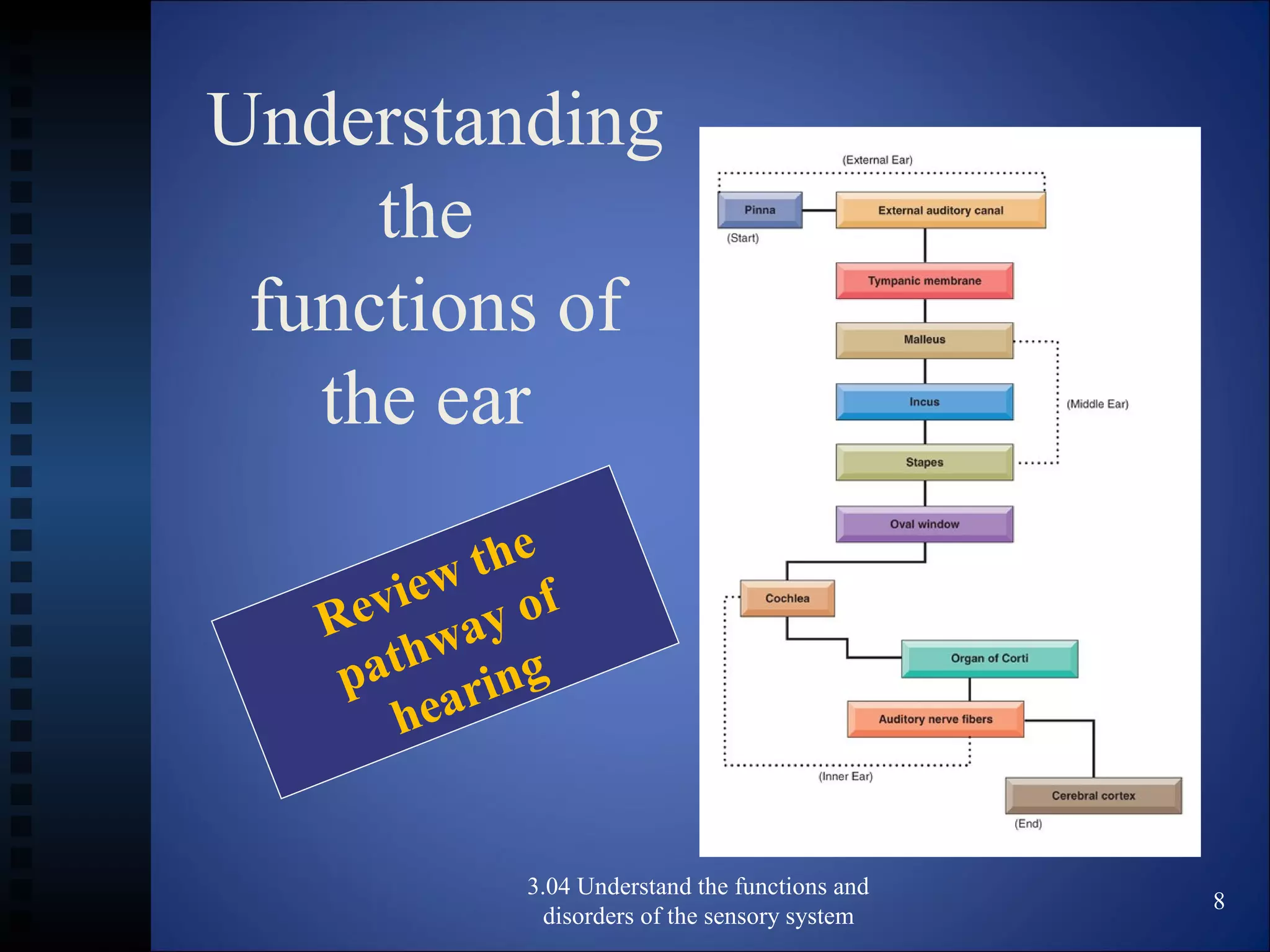
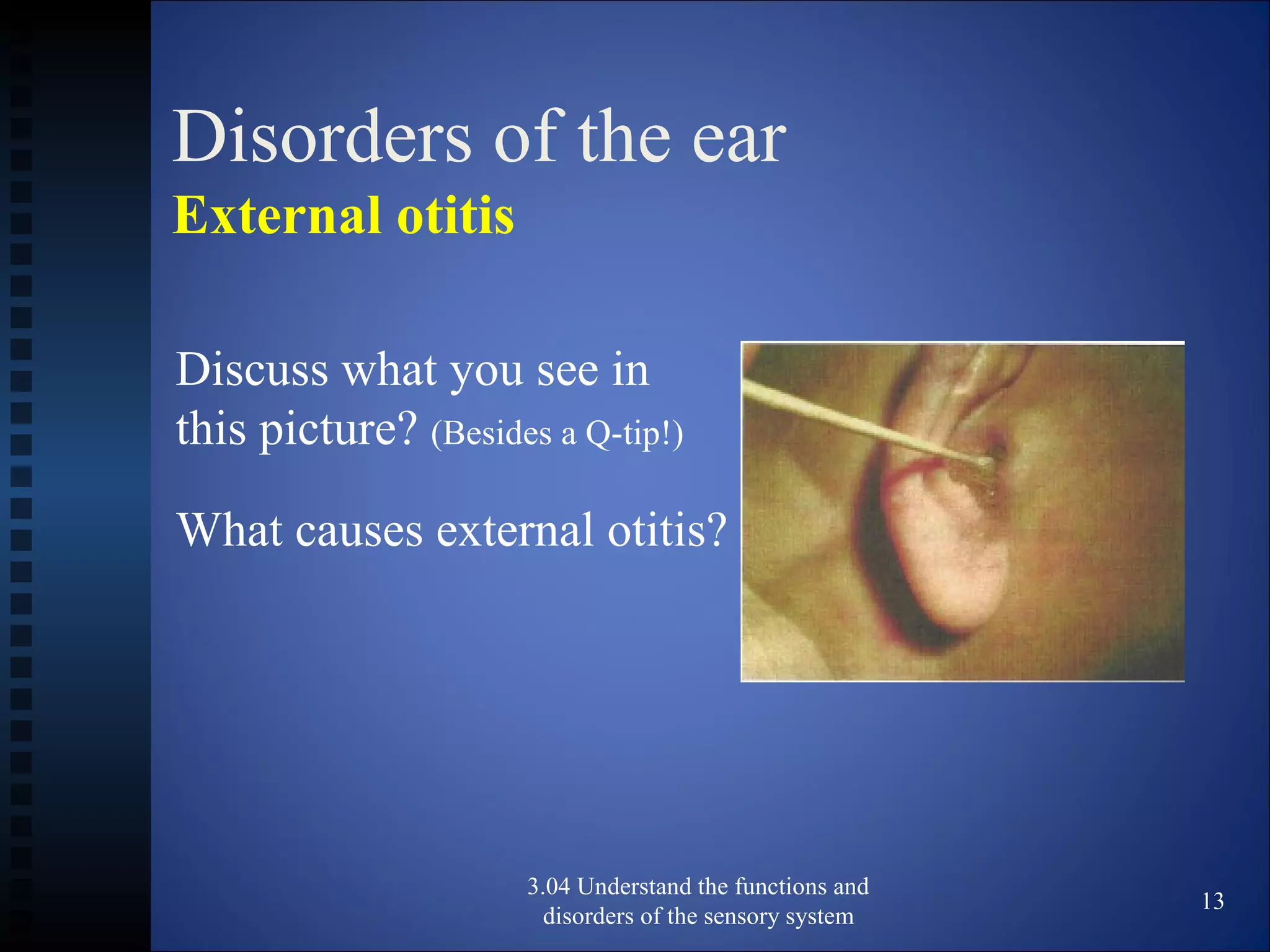
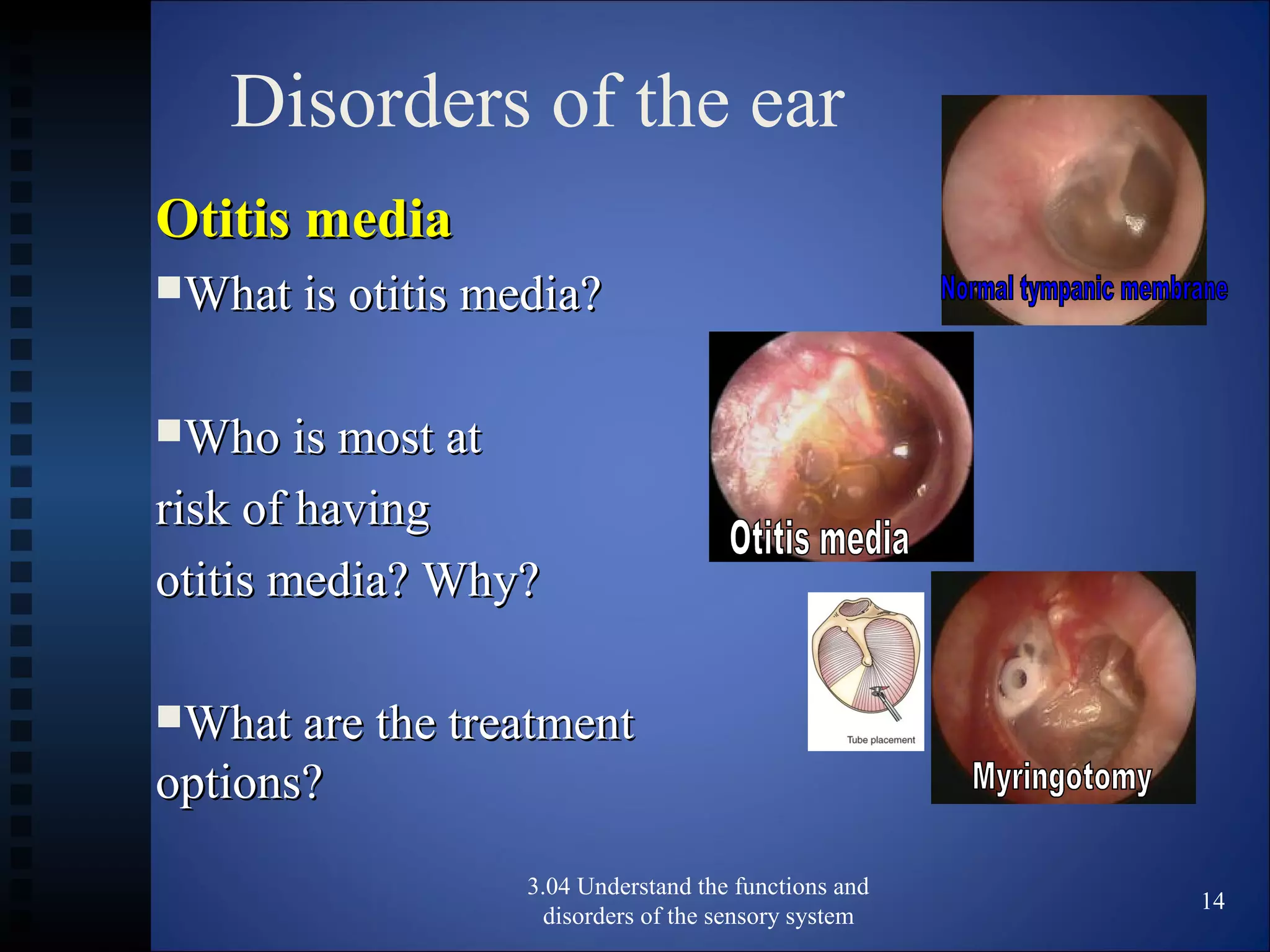
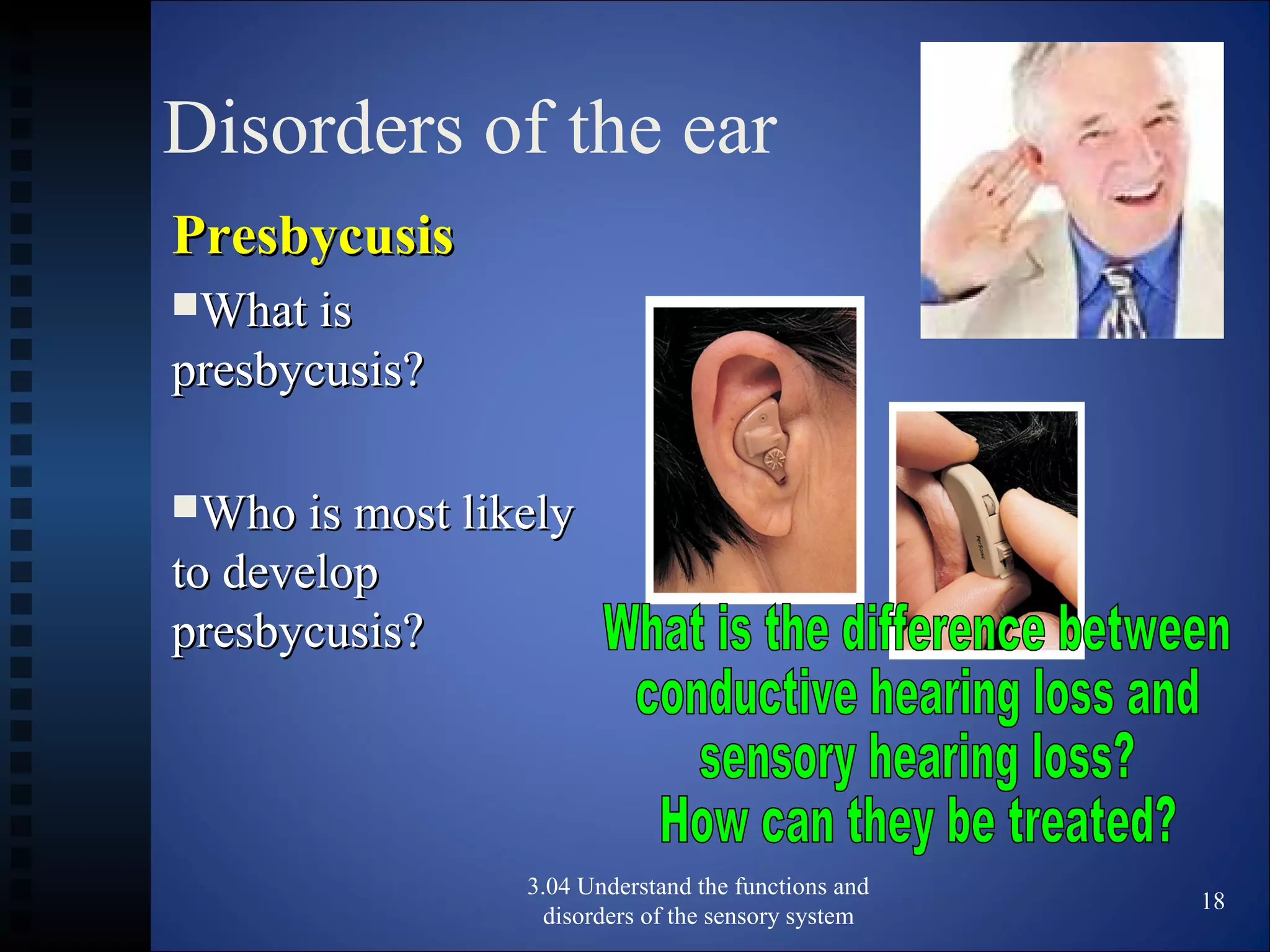
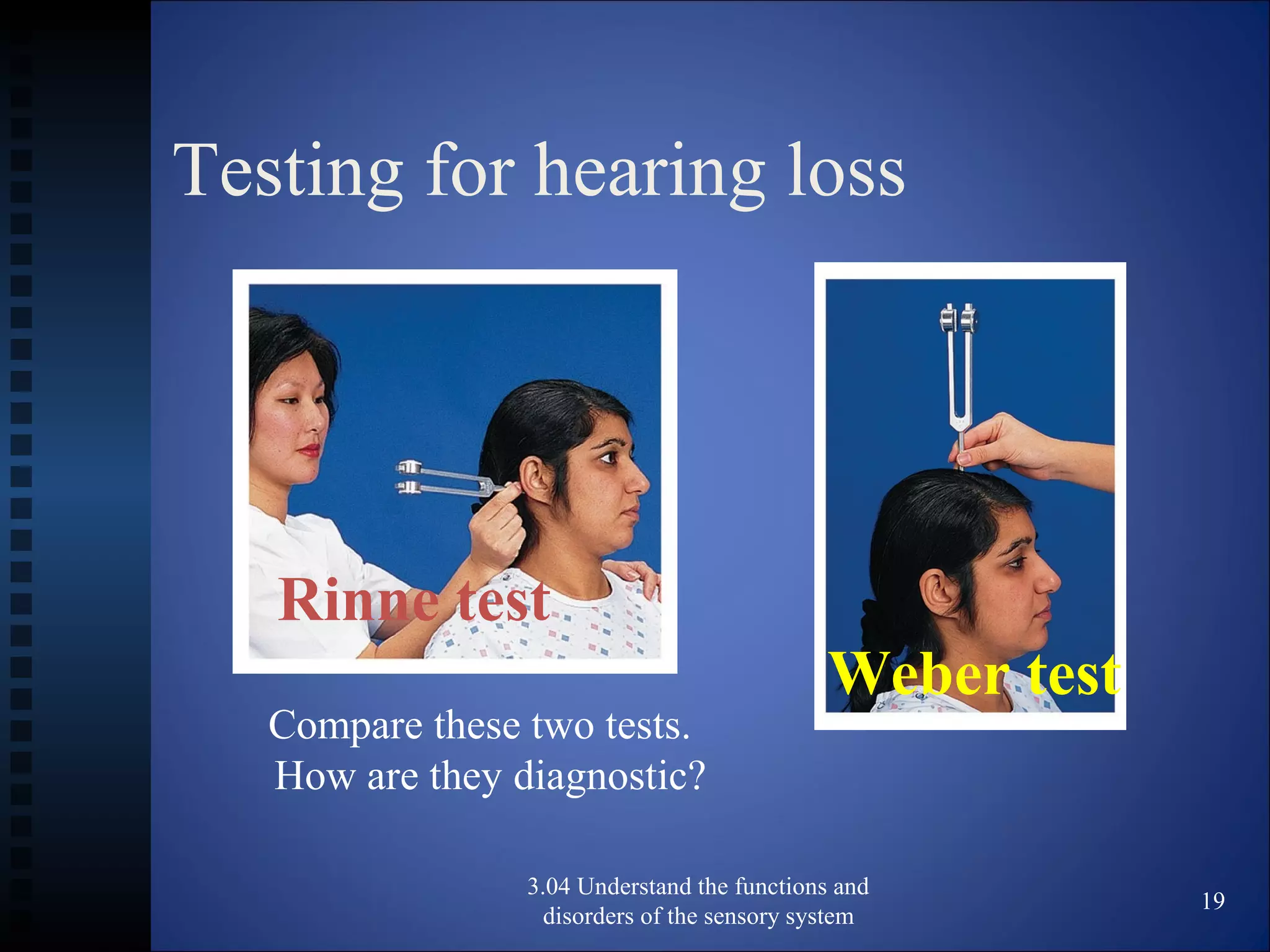
The document discusses the functions and disorders of the ear and sensory system. It begins by reviewing the anatomy and functions of the external, middle, and inner ear. It then discusses common ear disorders like otitis media, otosclerosis, Meniere's disease, tinnitus, and presbycusis. The document concludes by reviewing tests for hearing loss like the Weber test and Rinne test.