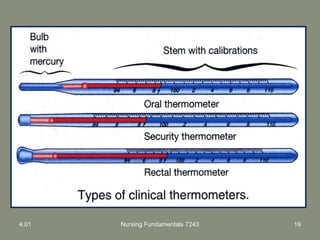
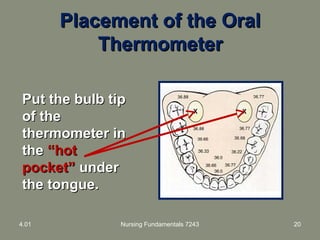
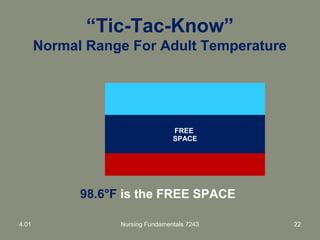
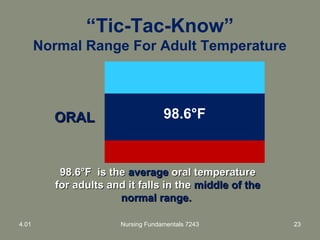
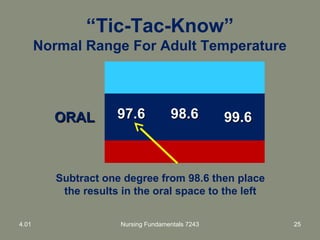
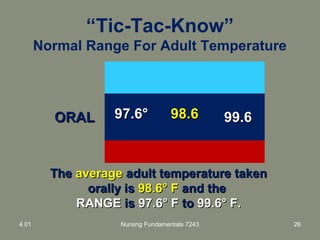
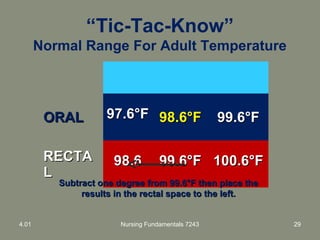
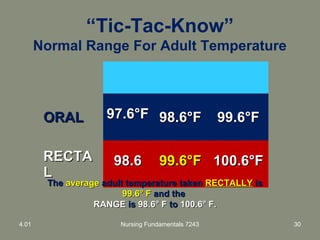
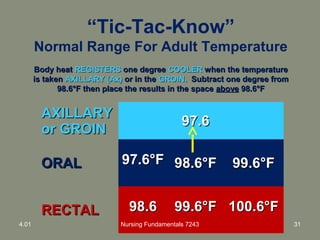
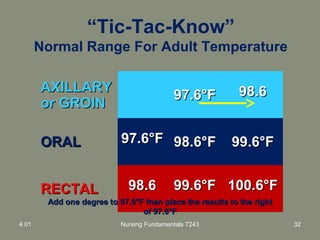
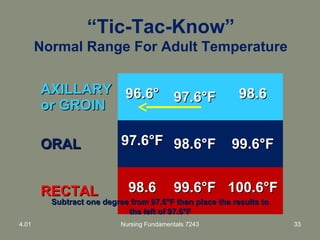
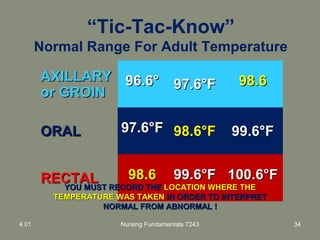
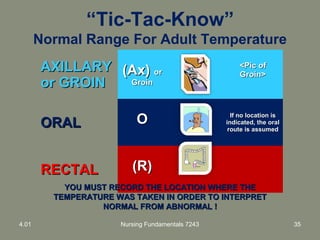
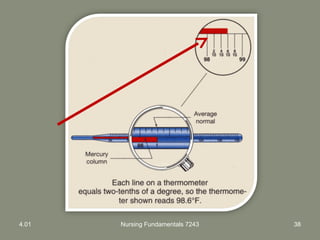
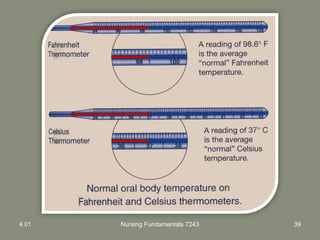
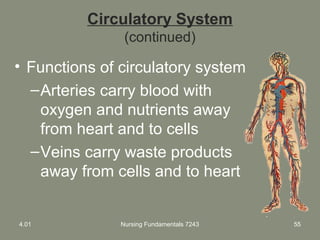
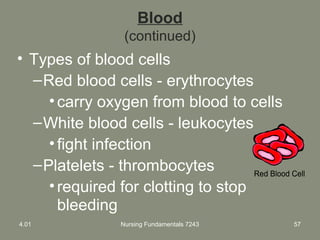
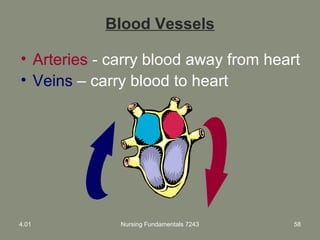
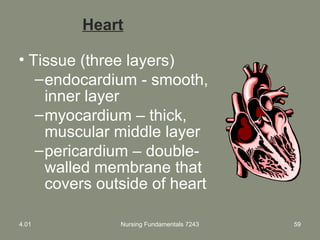
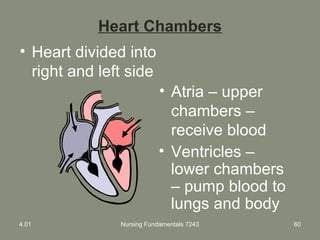
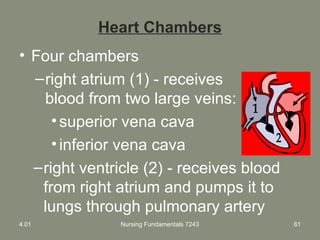
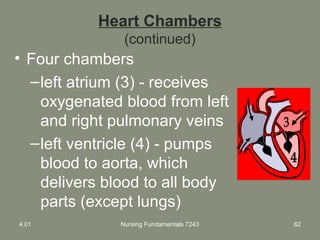
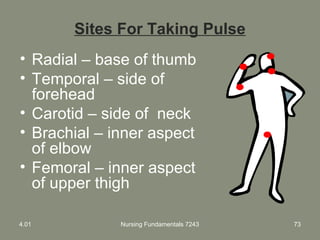
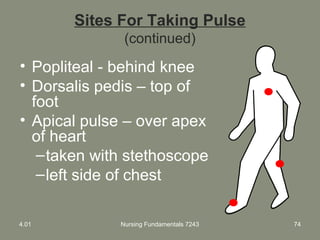
This document provides information about measuring and understanding vital signs including temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure. It focuses on temperature measurement, describing the normal temperature ranges for adults, different methods and sites for taking a temperature, and safety considerations. Temperature is an important vital sign that can provide information about a resident's health status and response to treatment.