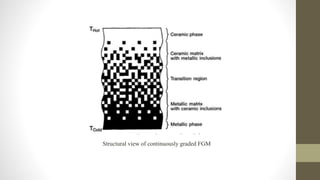
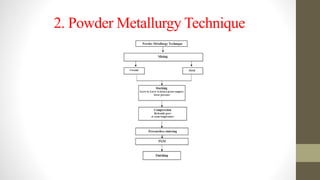
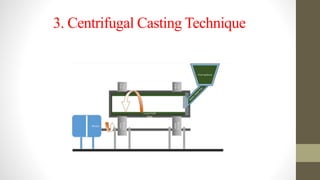
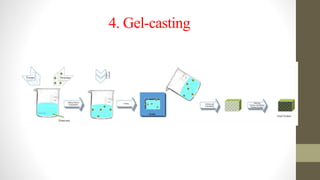
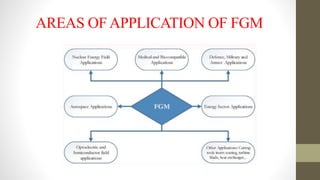
Functionally graded materials (FGMs) are characterized by a gradual variation in composition and structure, enhancing their properties for specific applications across various fields such as aerospace and engineering. They can be categorized by structure (continuous and discontinuous) and manufacturing processes (thin and bulk), with several processing techniques available for producing FGMs. Although FGMs offer significant advantages, including improved bond strength and stress reduction, challenges such as high costs and the need for further research persist.