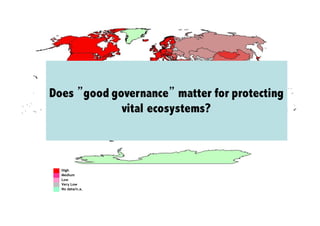
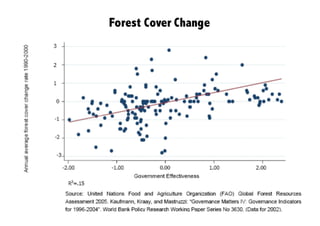
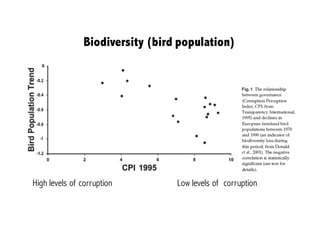
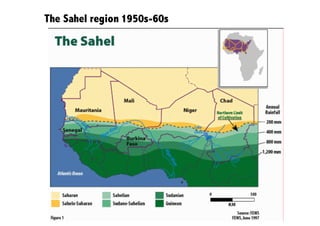
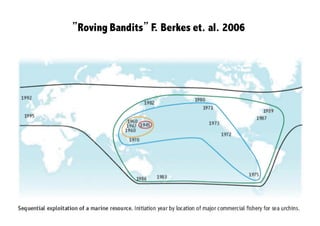
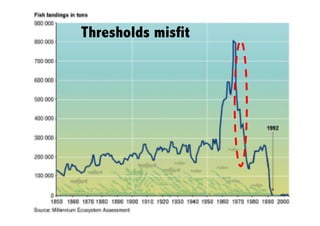
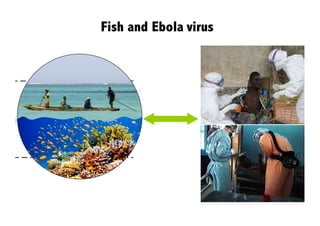
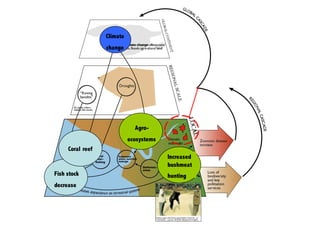
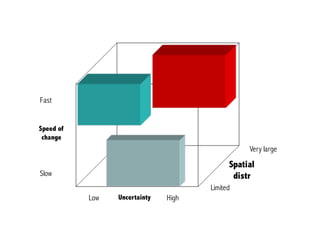
This document discusses the relationship between good governance and protecting vital ecosystems. It defines good governance according to the World Bank's indicators and examines how governance matters for outcomes like forest cover change and biodiversity. It then explores various "misfits" like temporal, spatial, thresholds, and cascading dynamics misfits that can occur between social and ecological systems. The document considers whether adaptive governance may help address these challenges and differences between governance, institutions, adaptive management, and adaptive co-management.