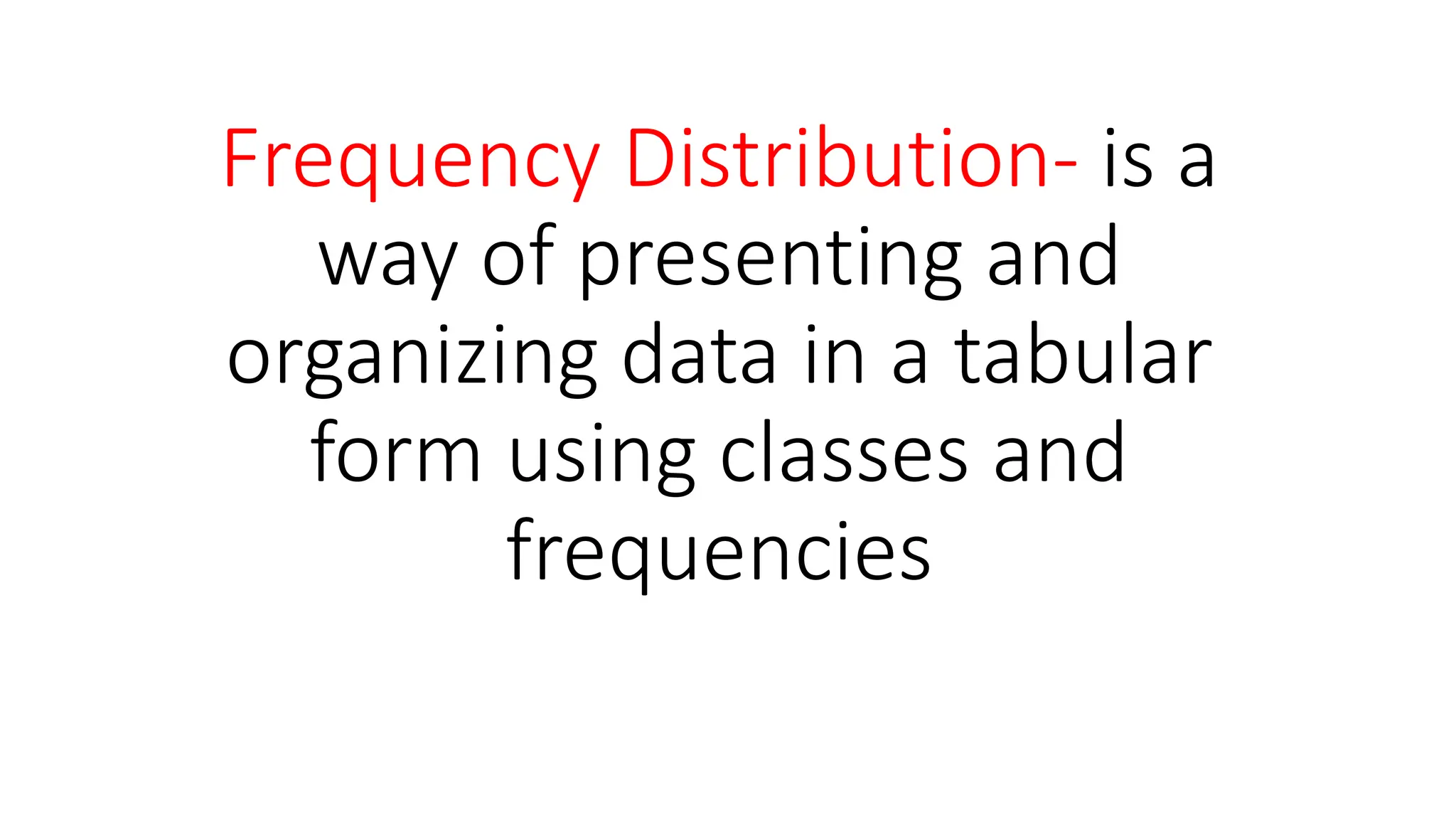
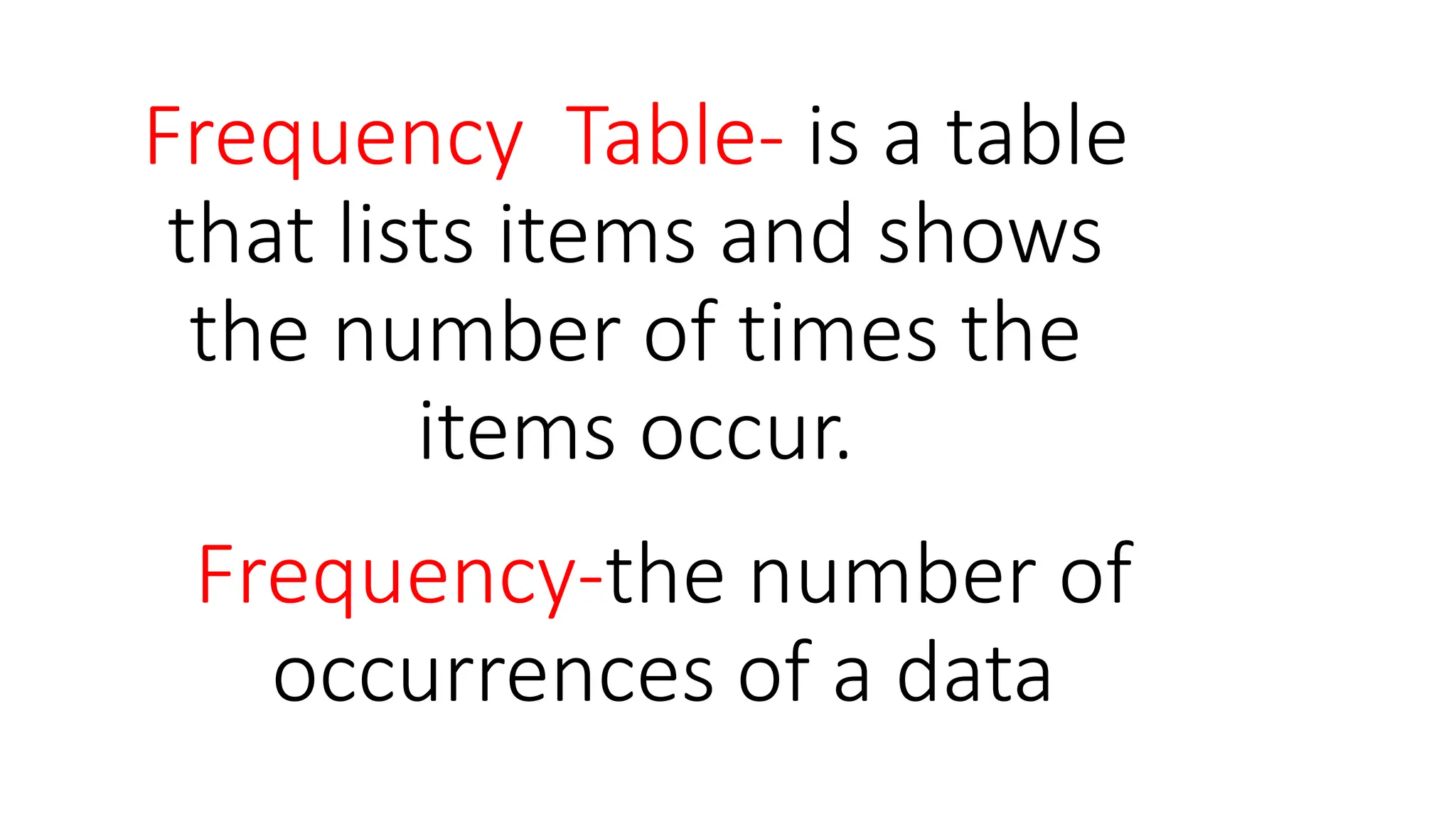
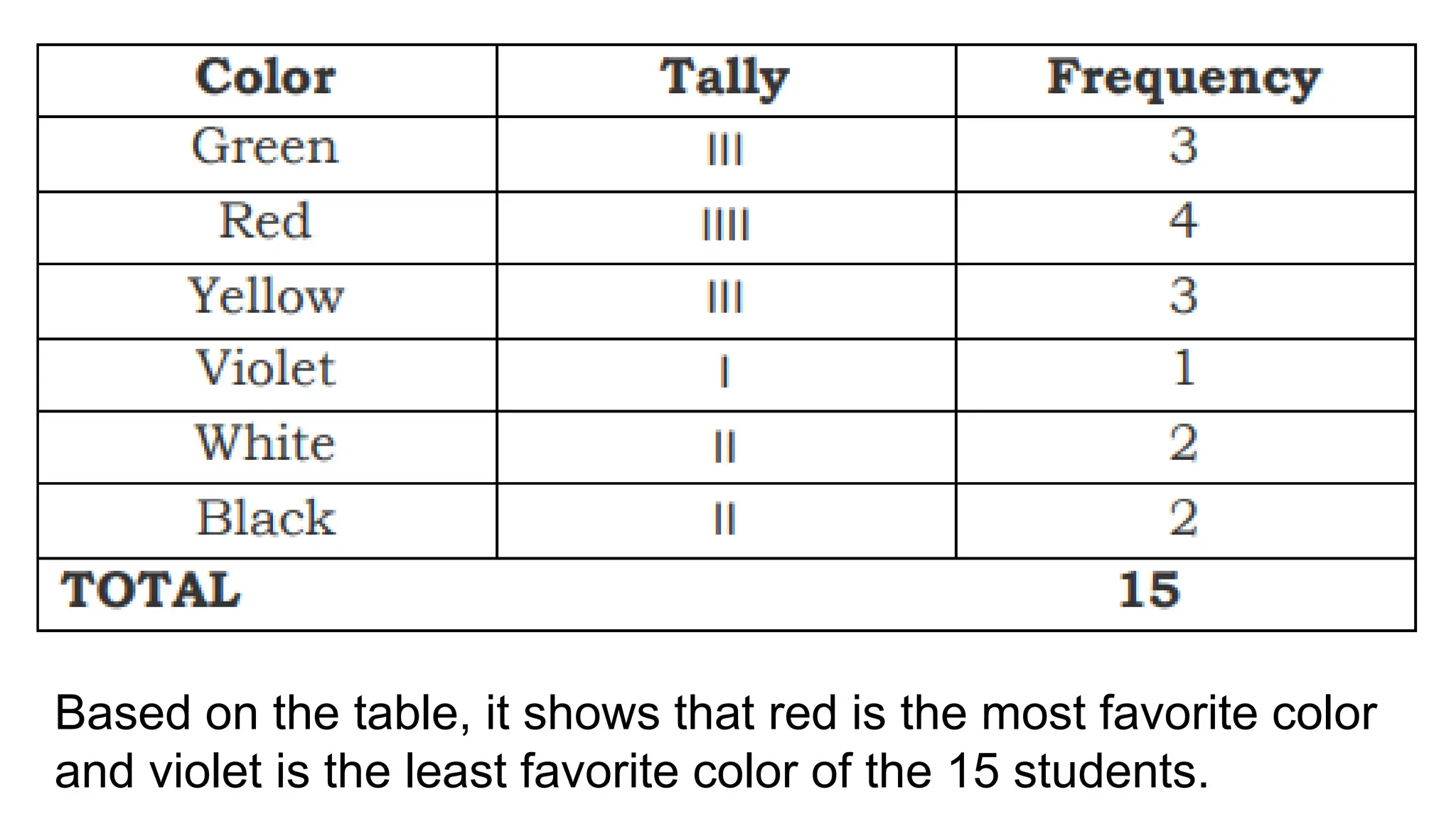
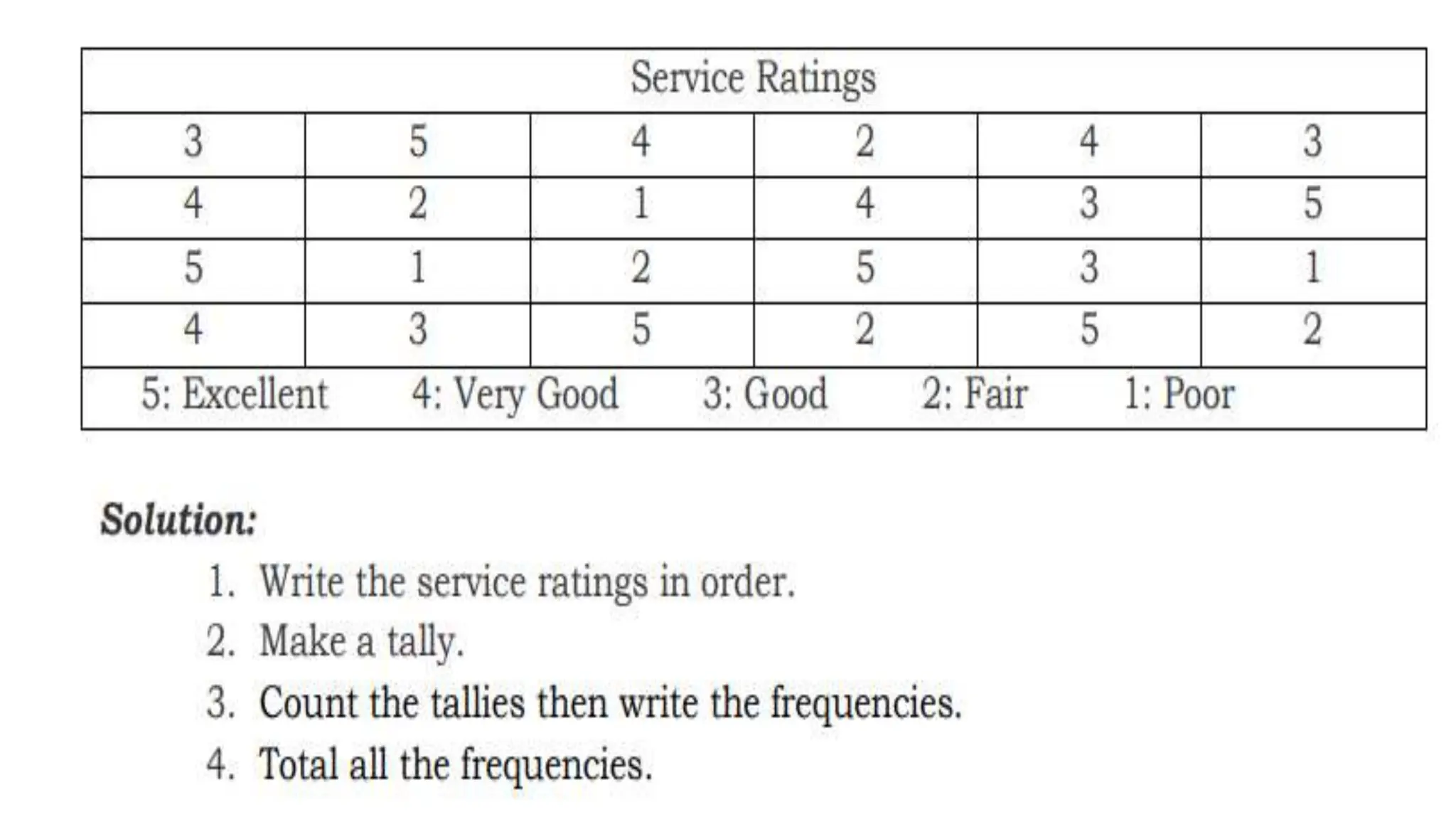
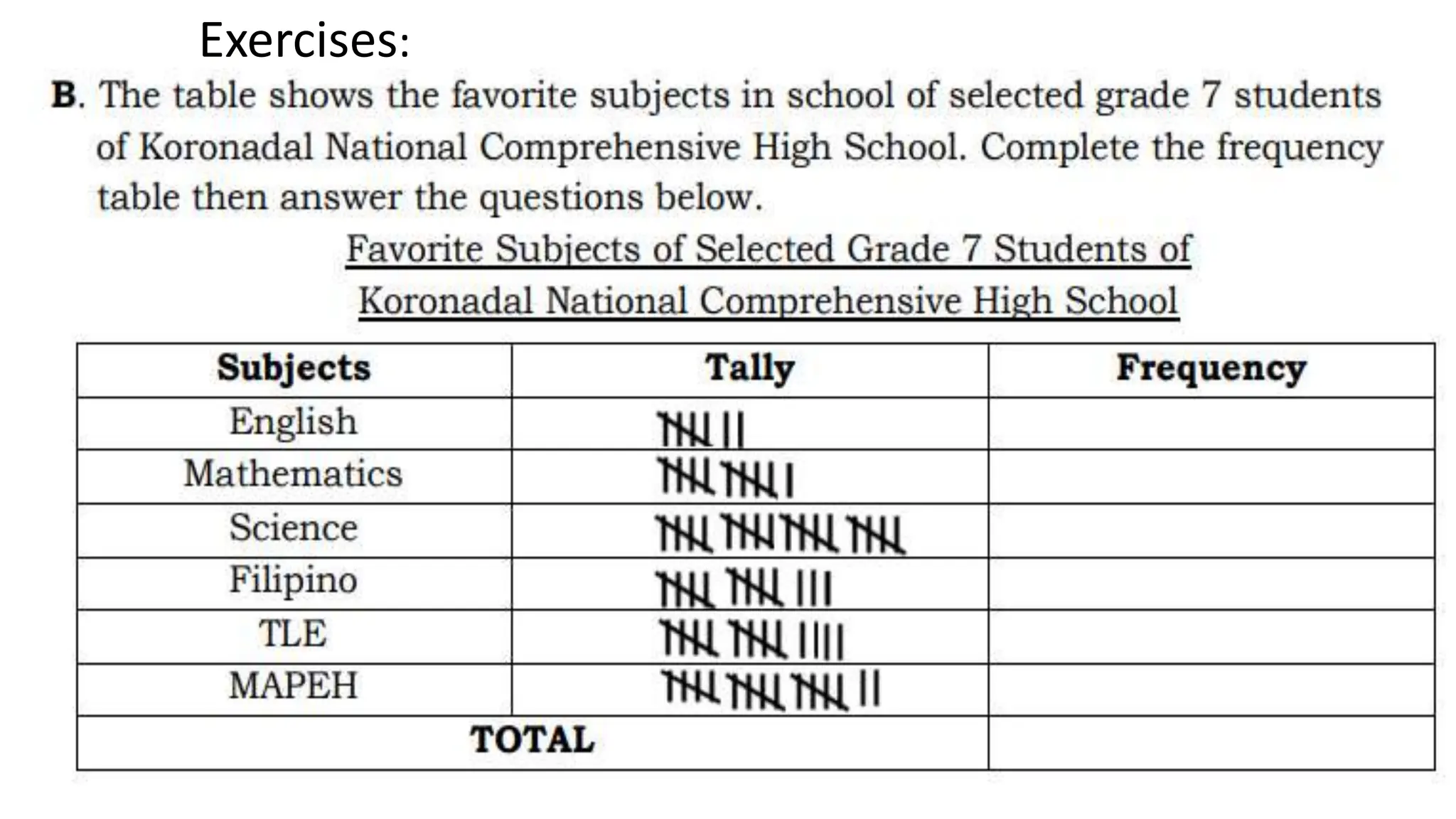
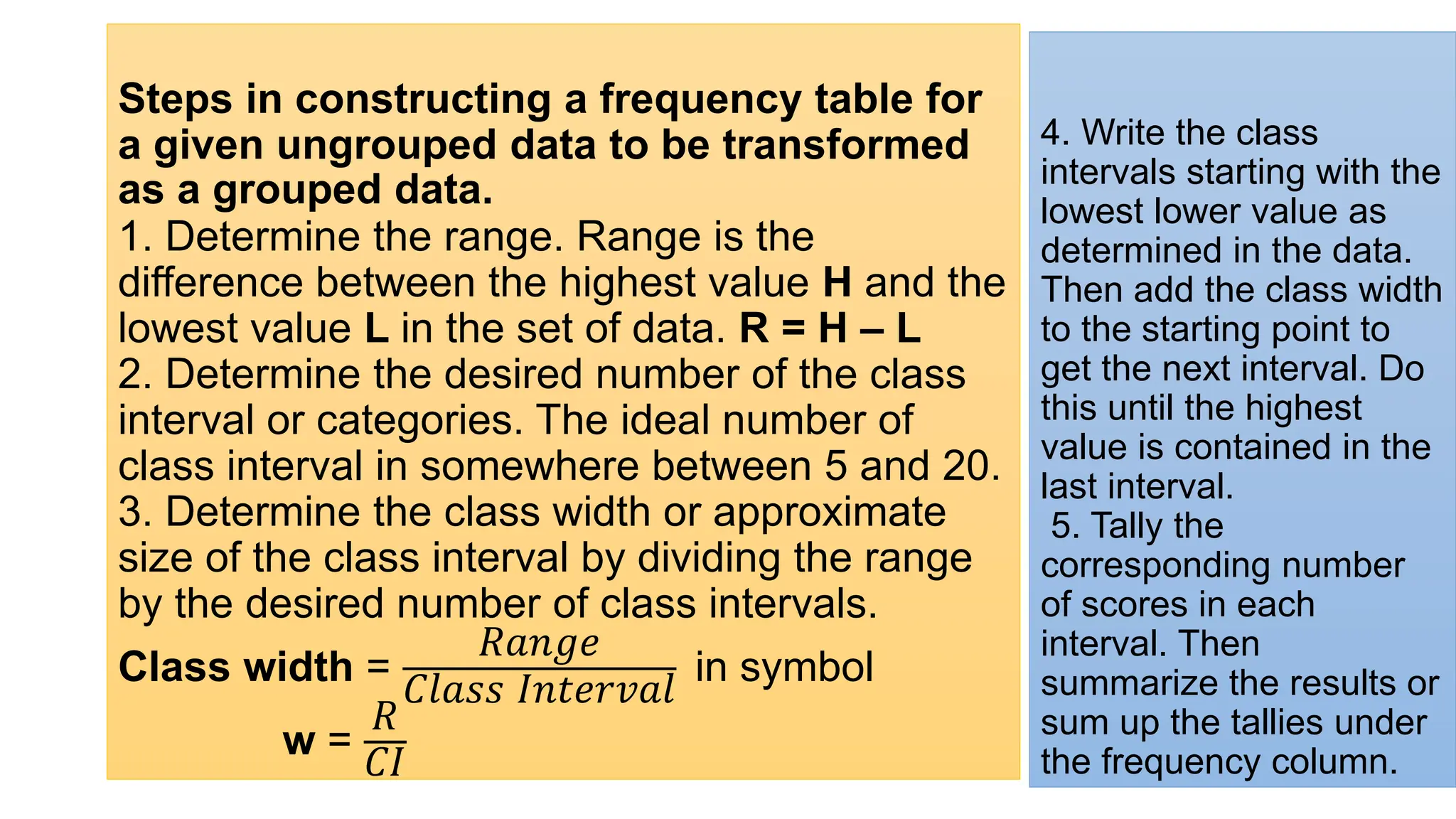
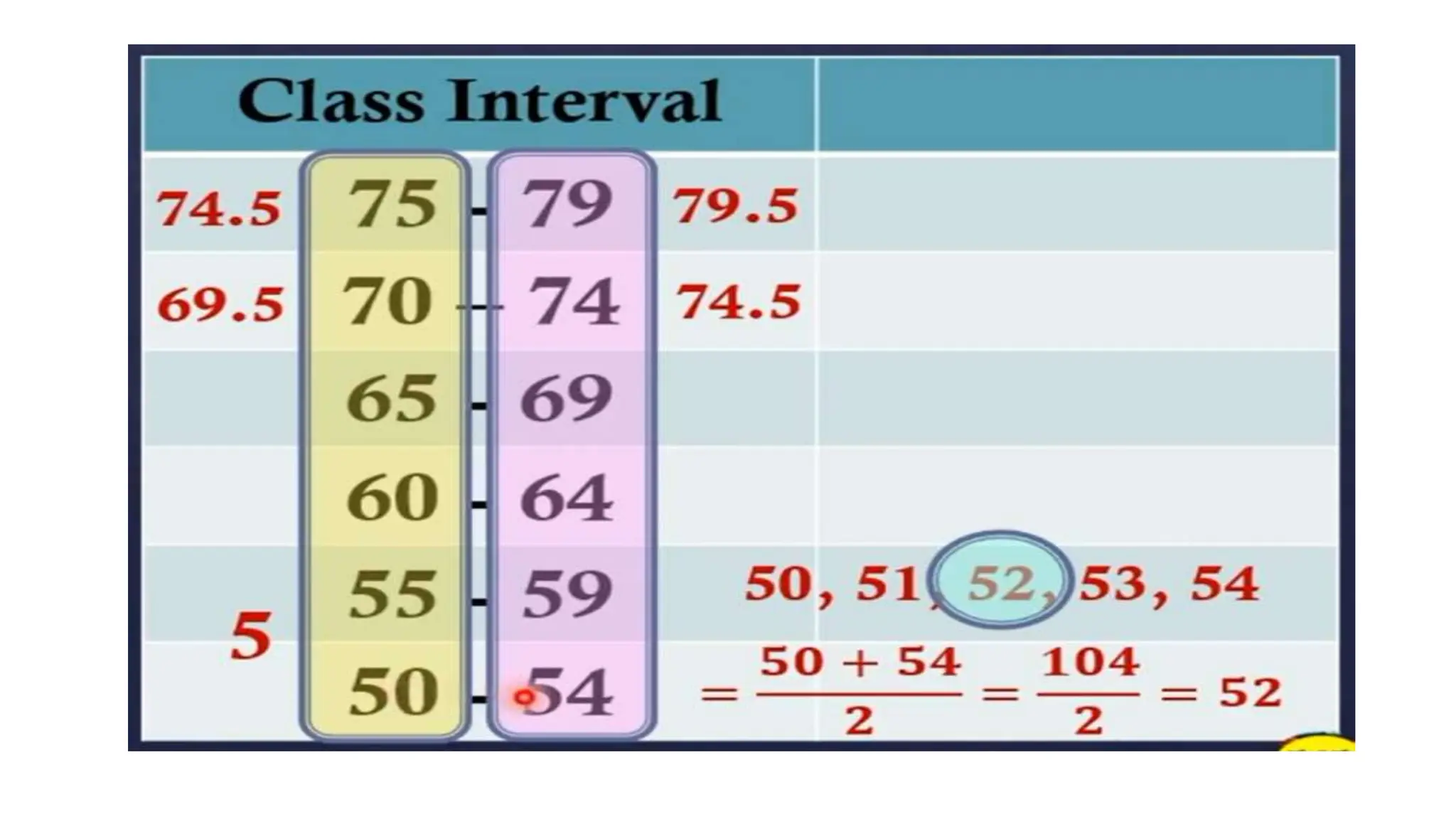
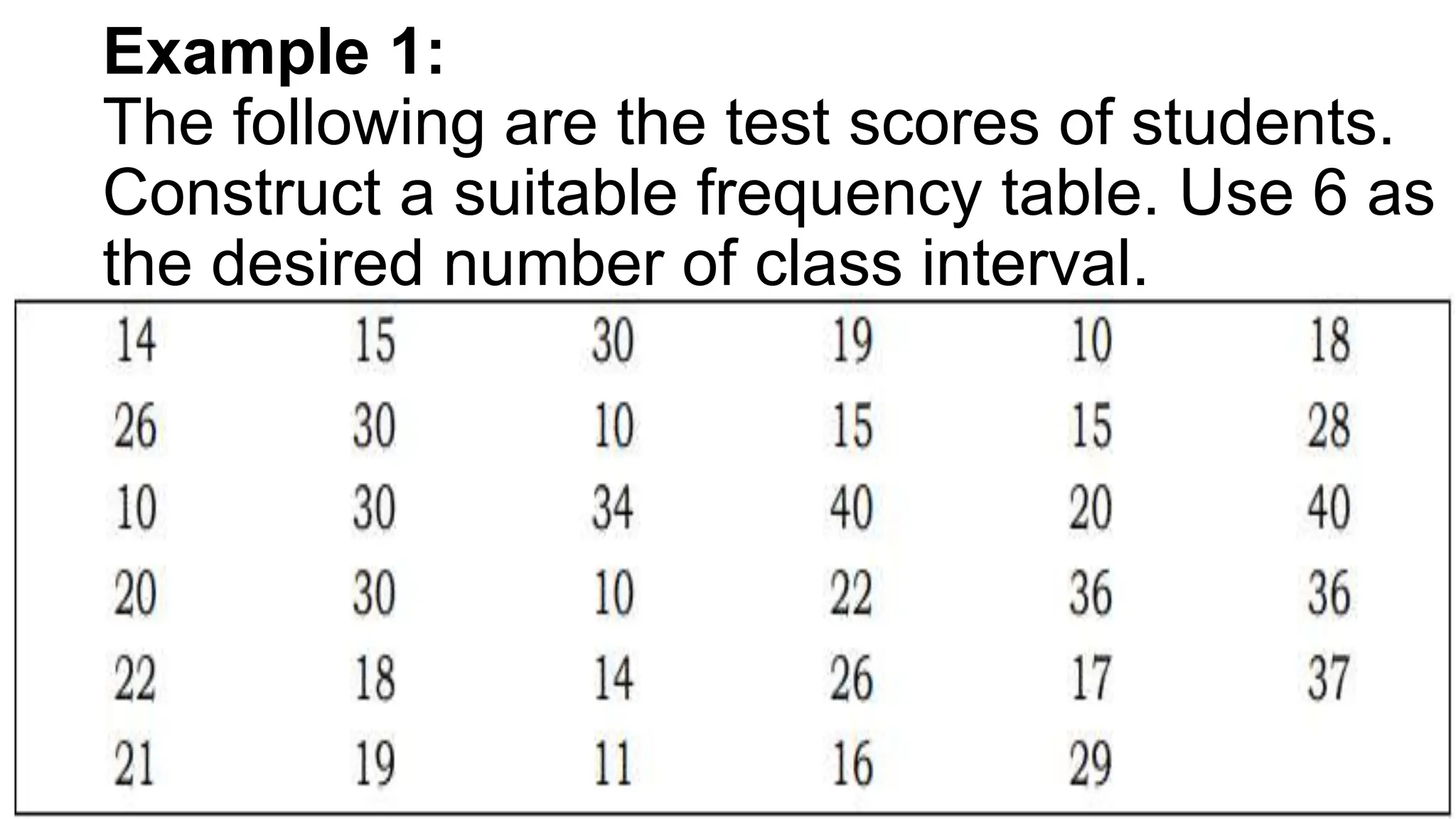
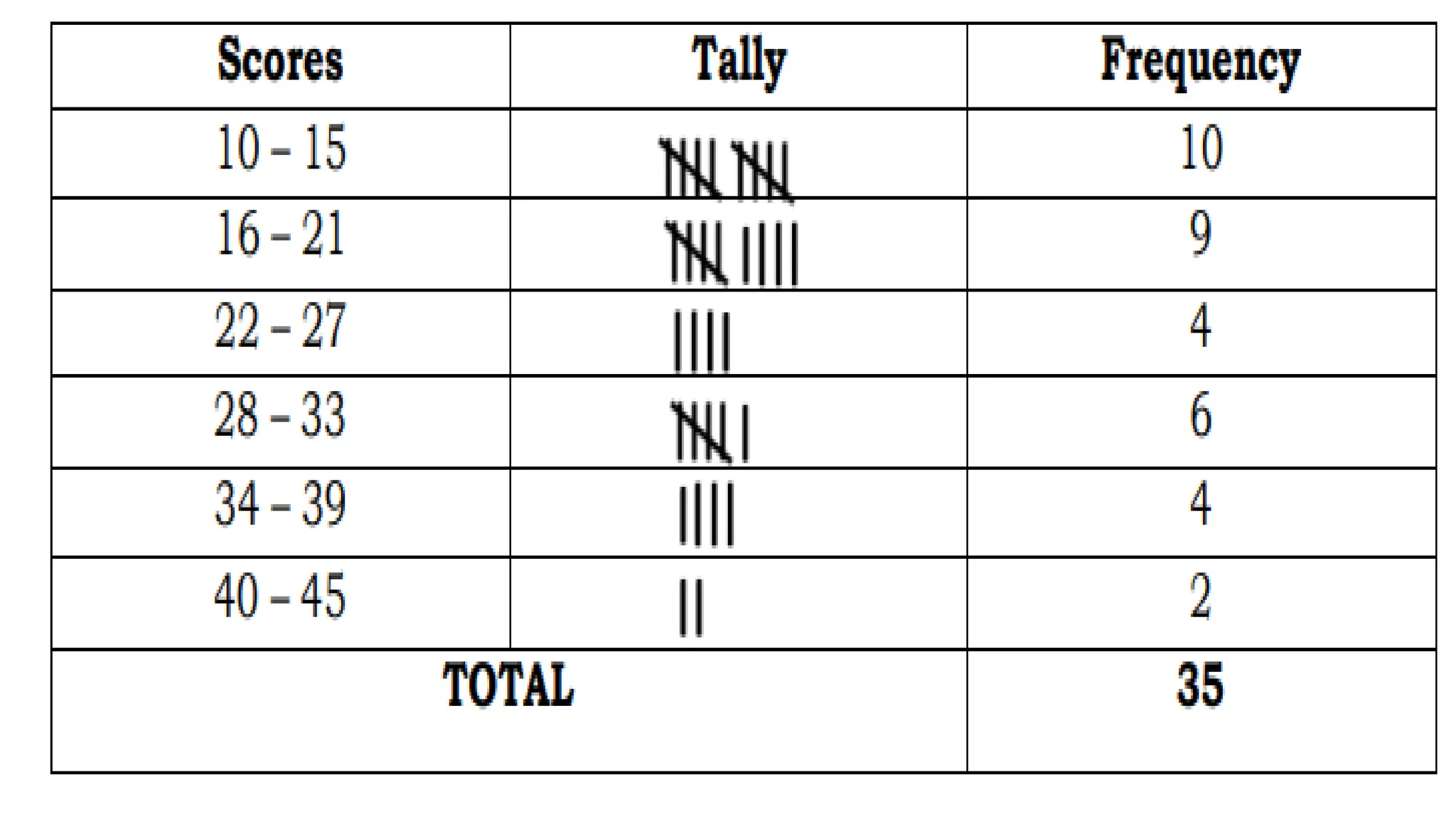
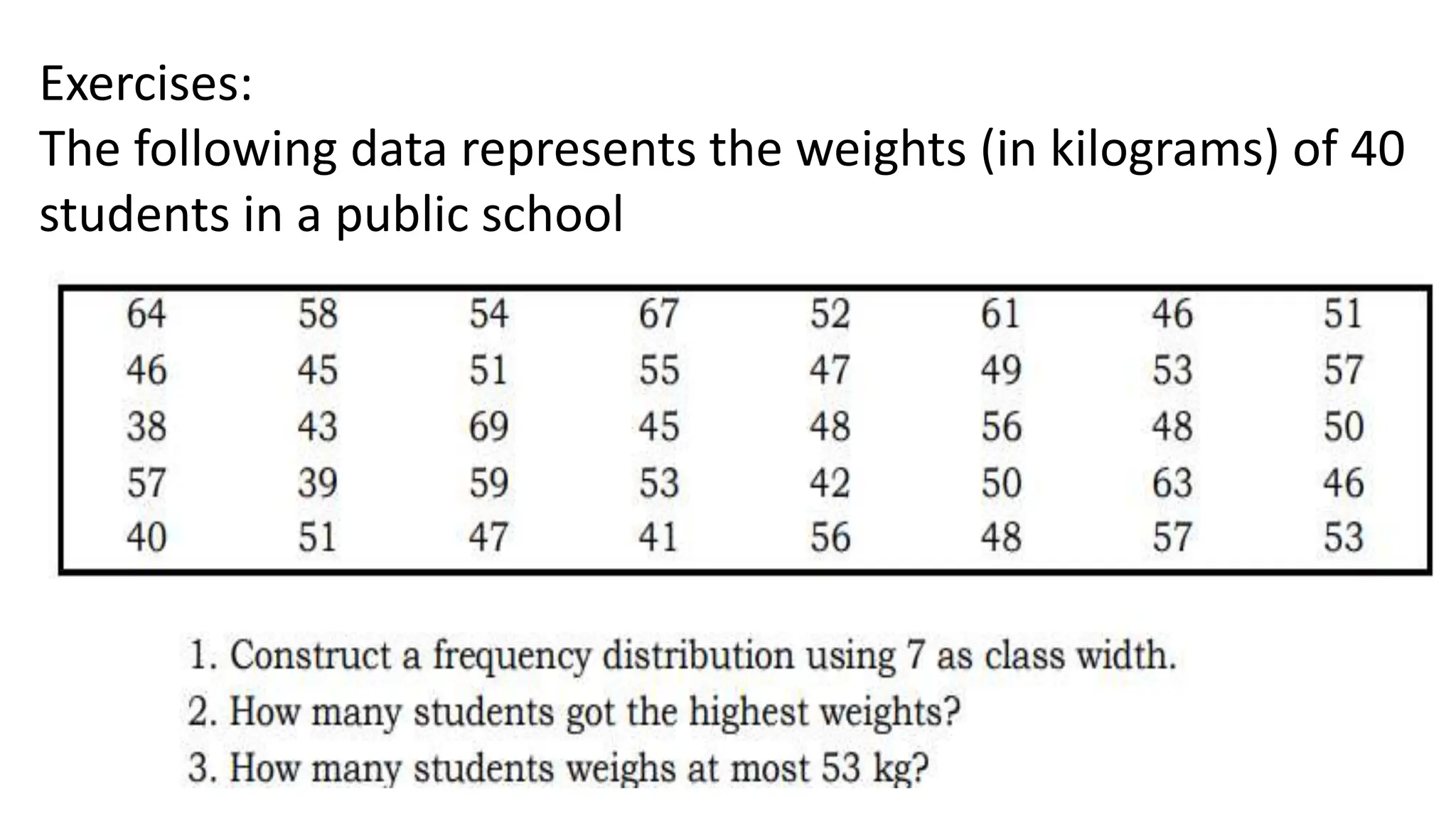
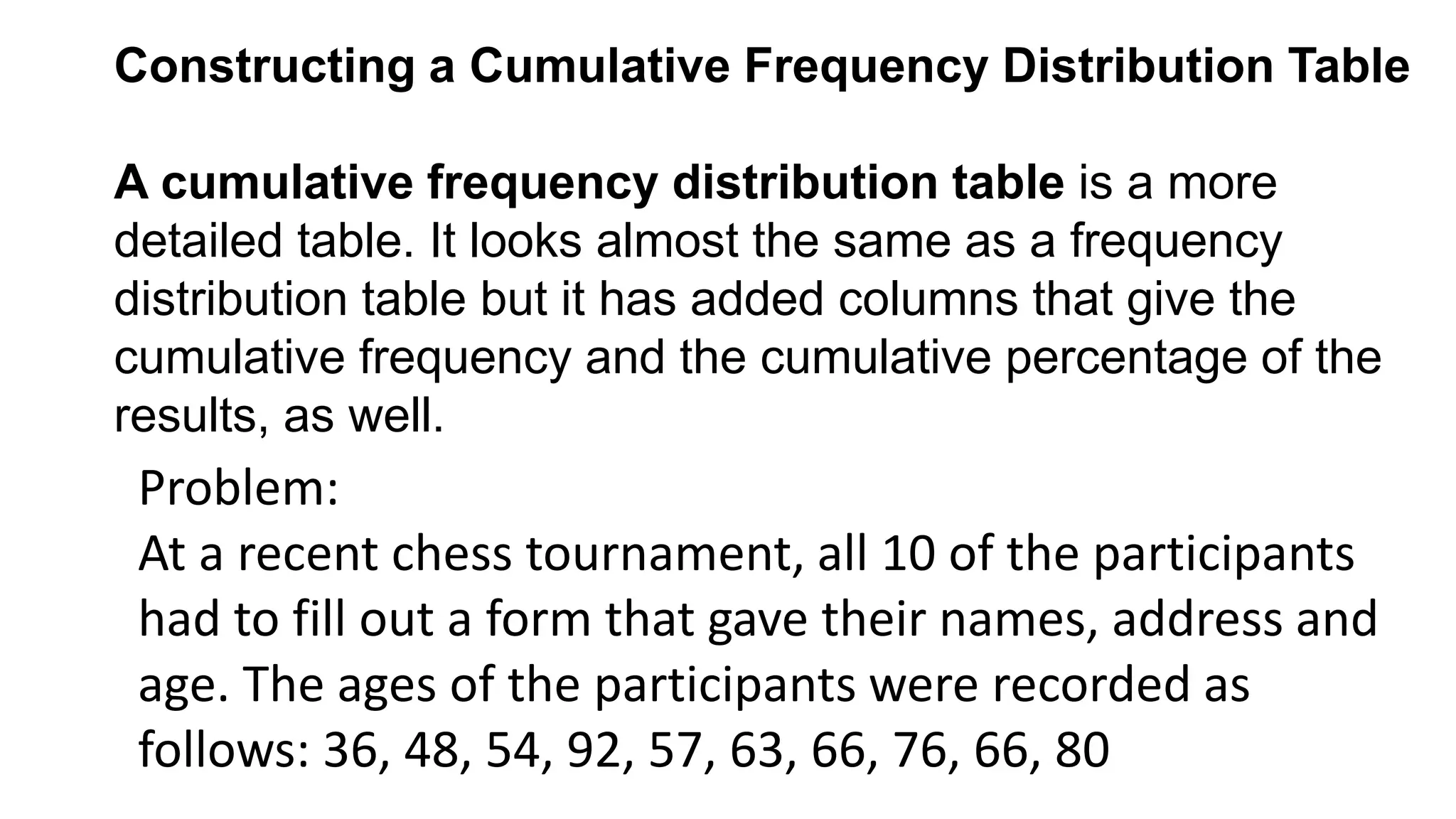
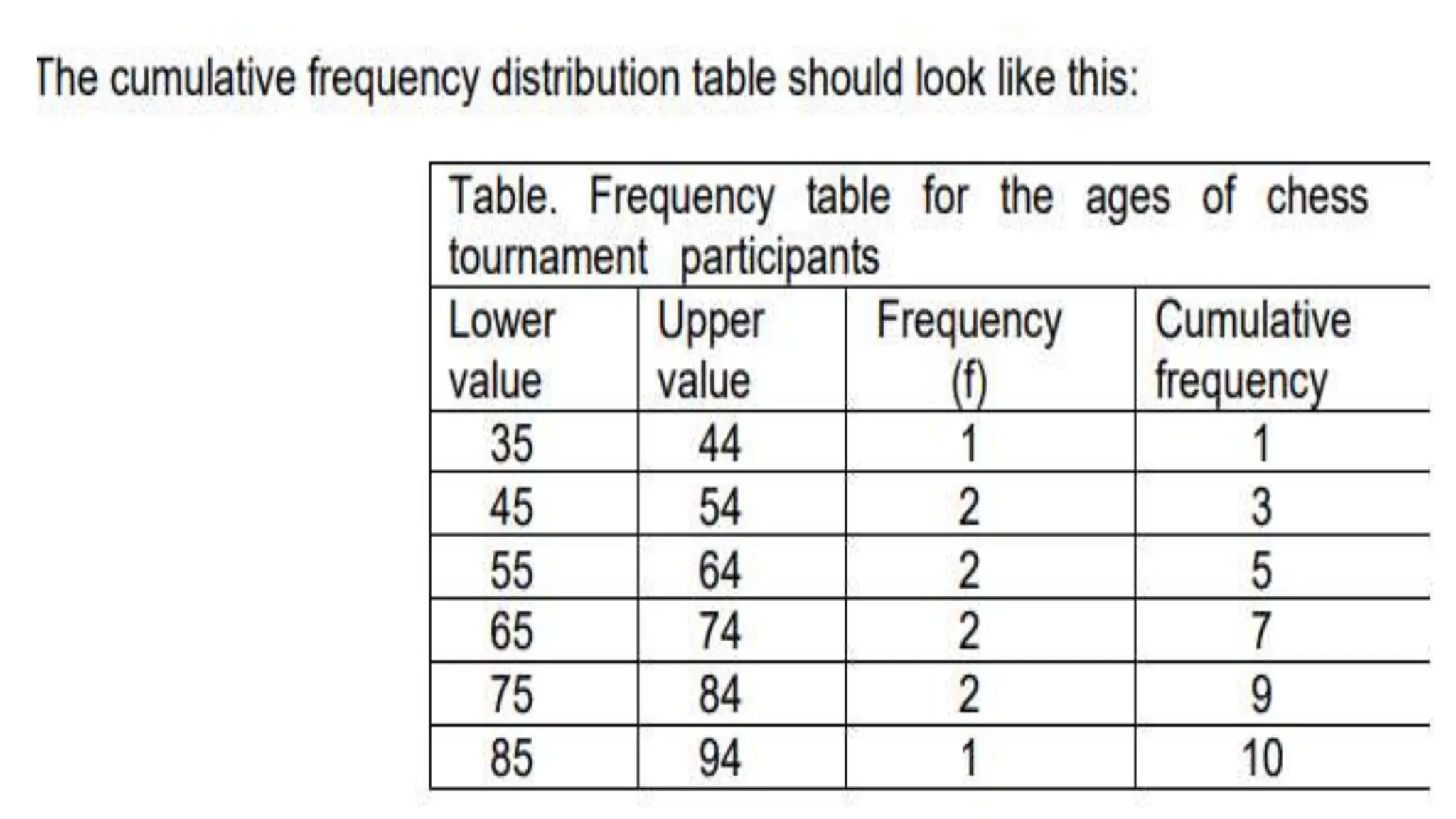
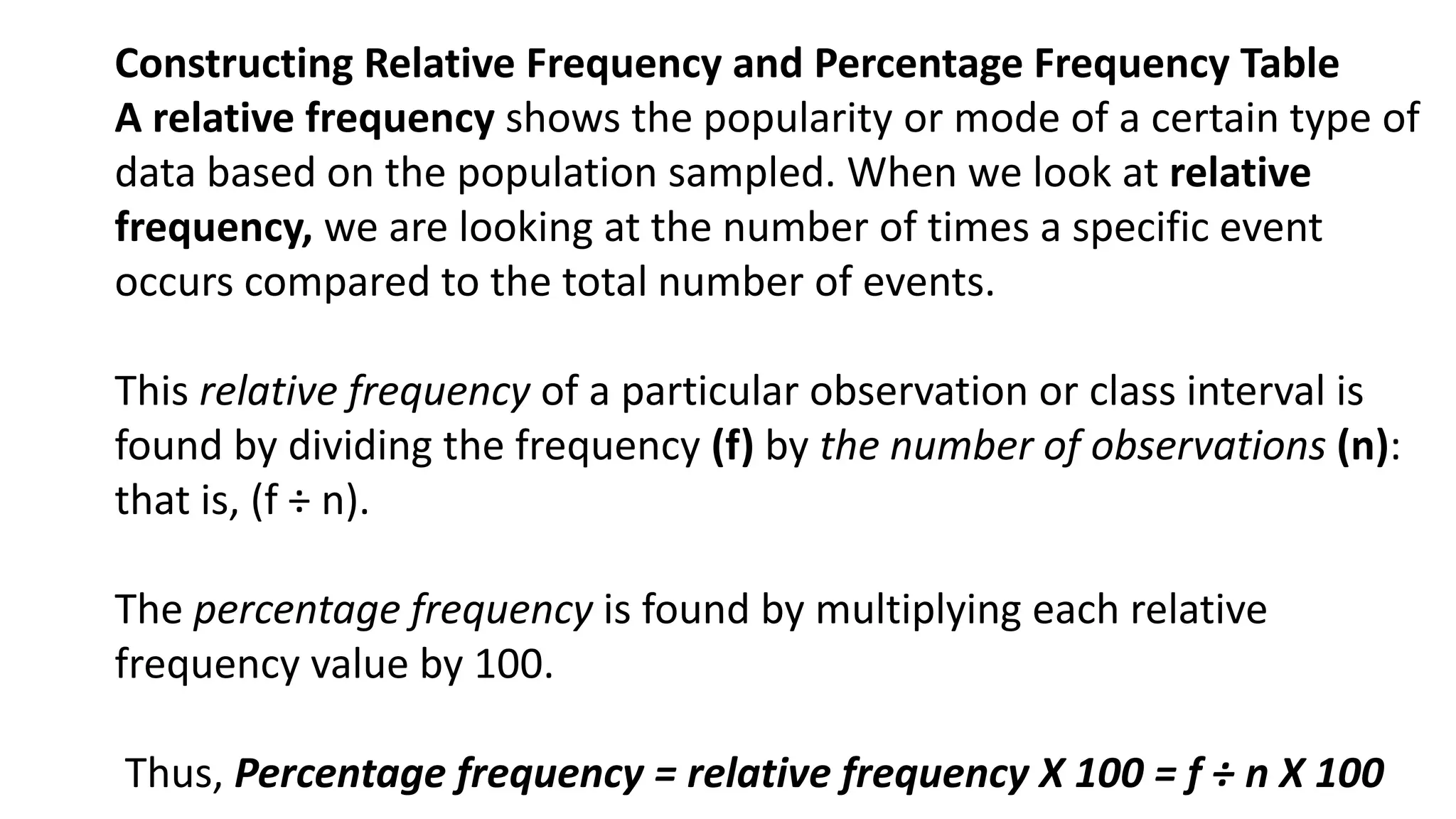
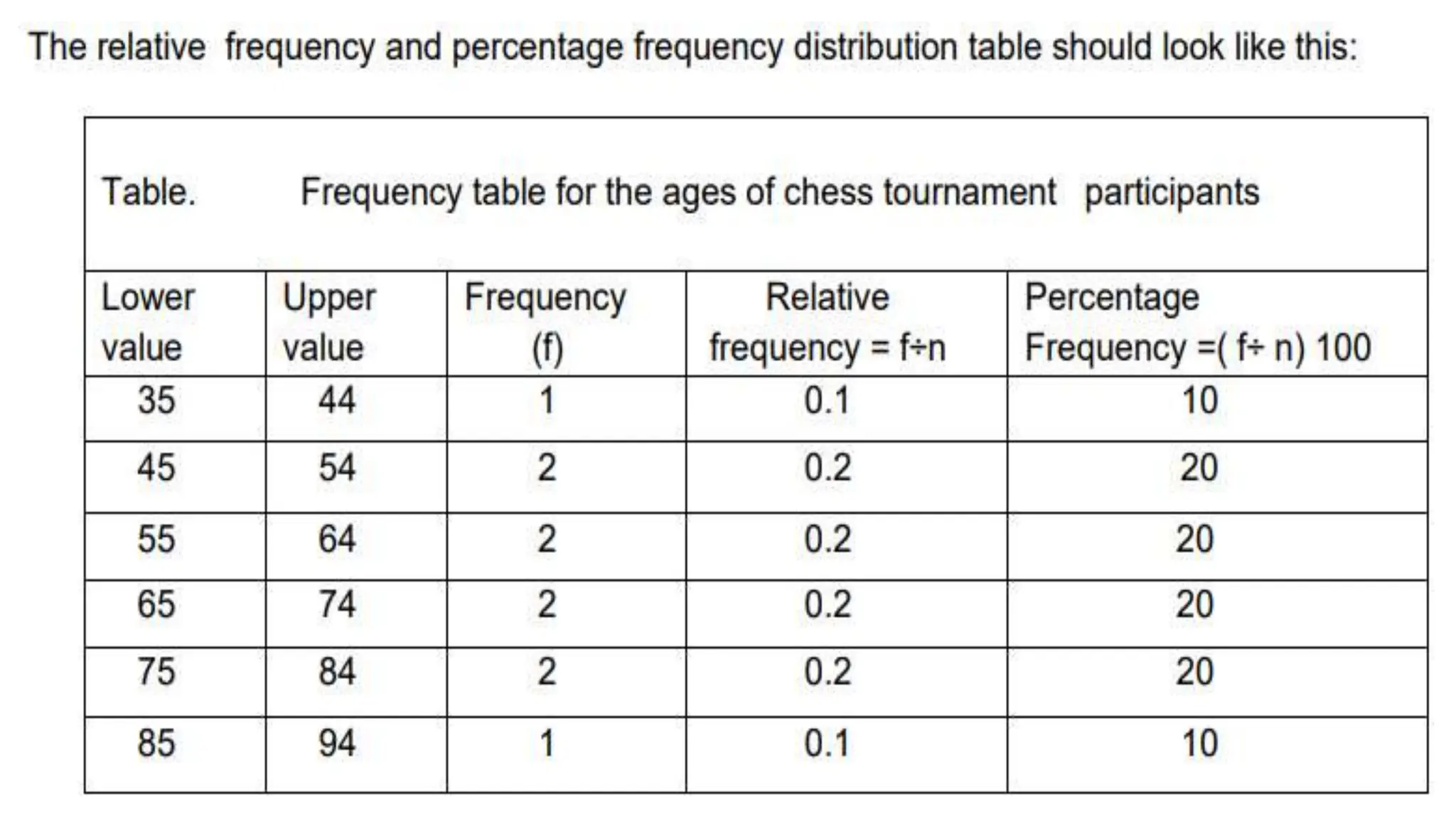
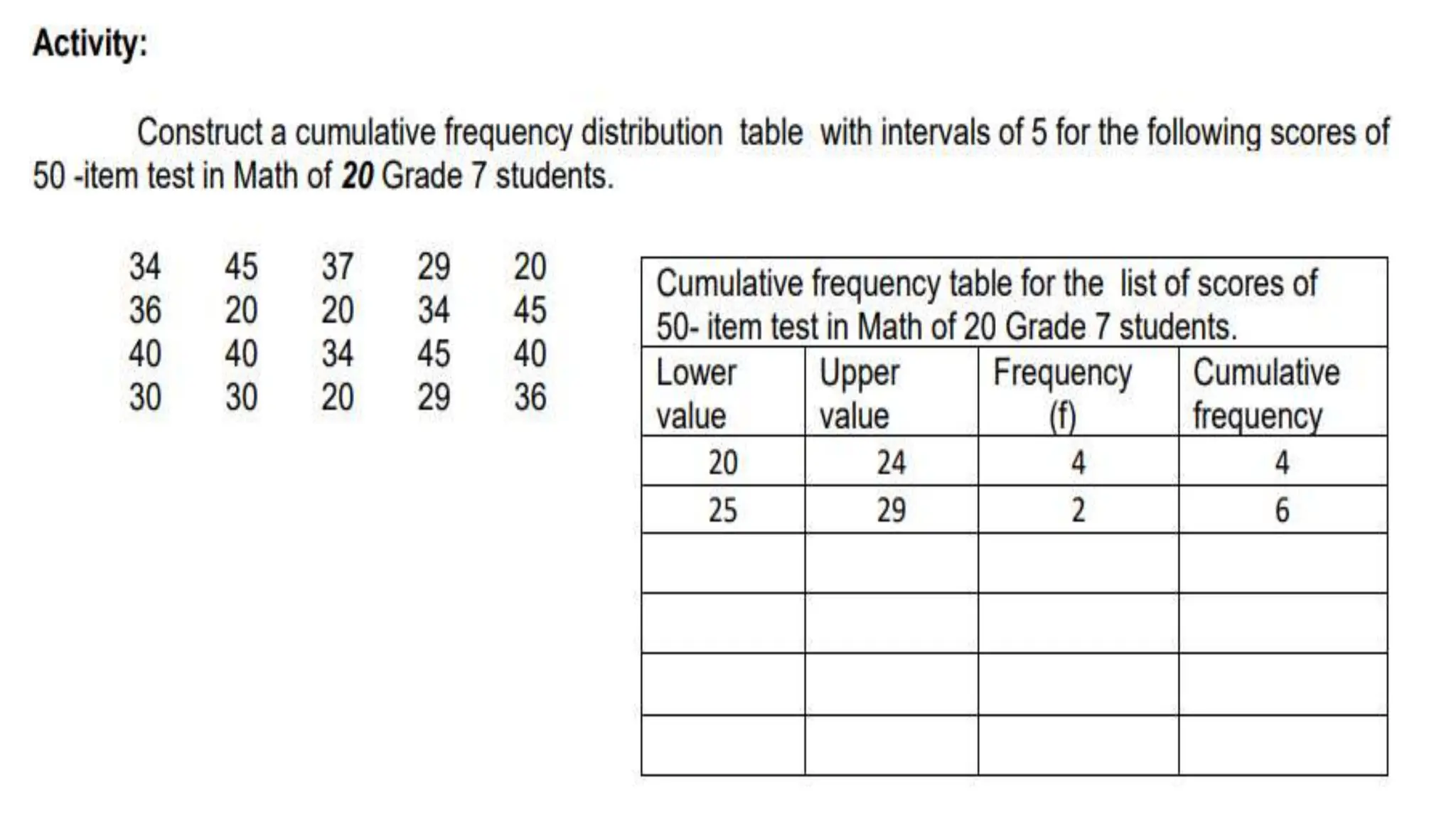
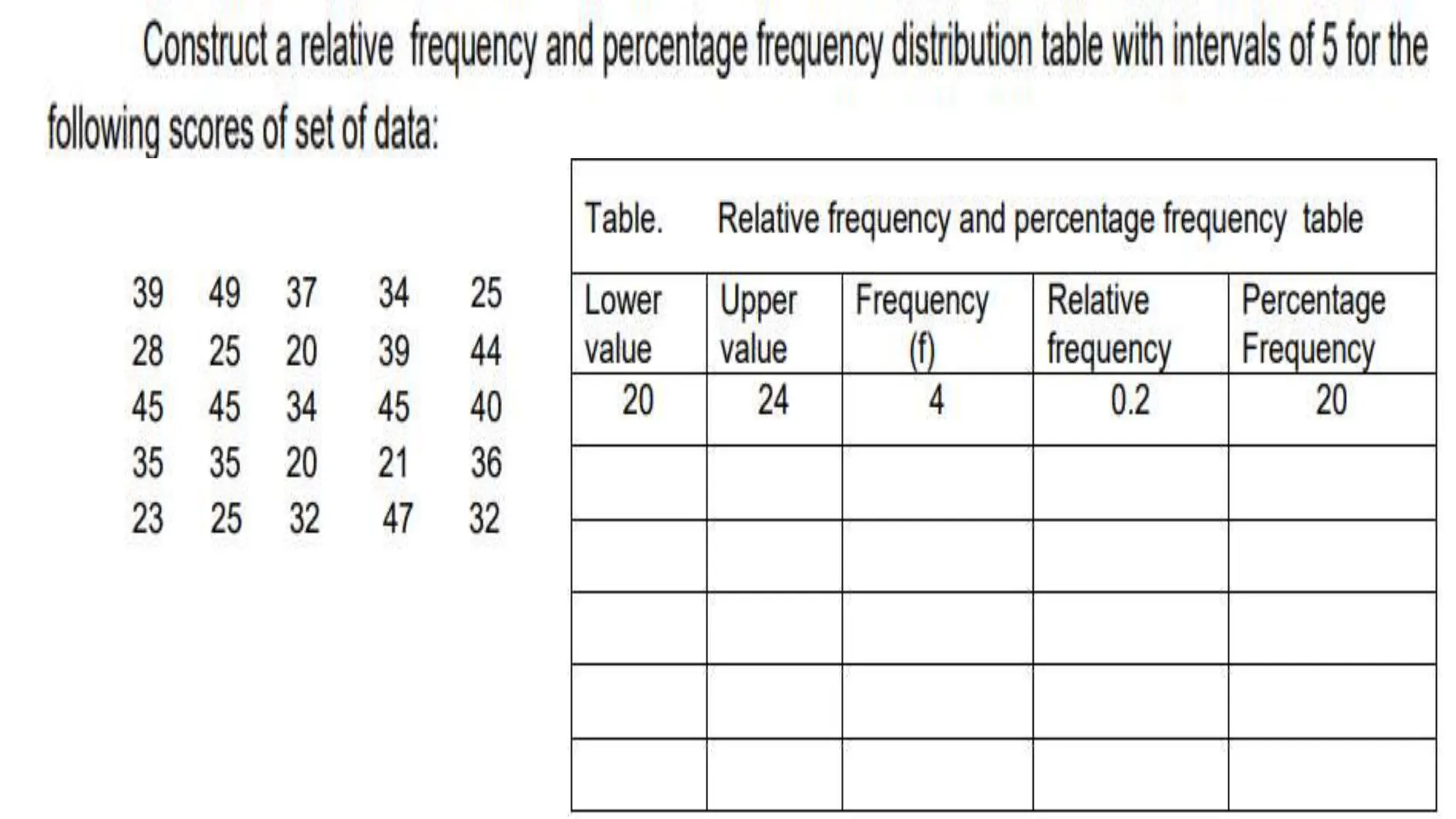
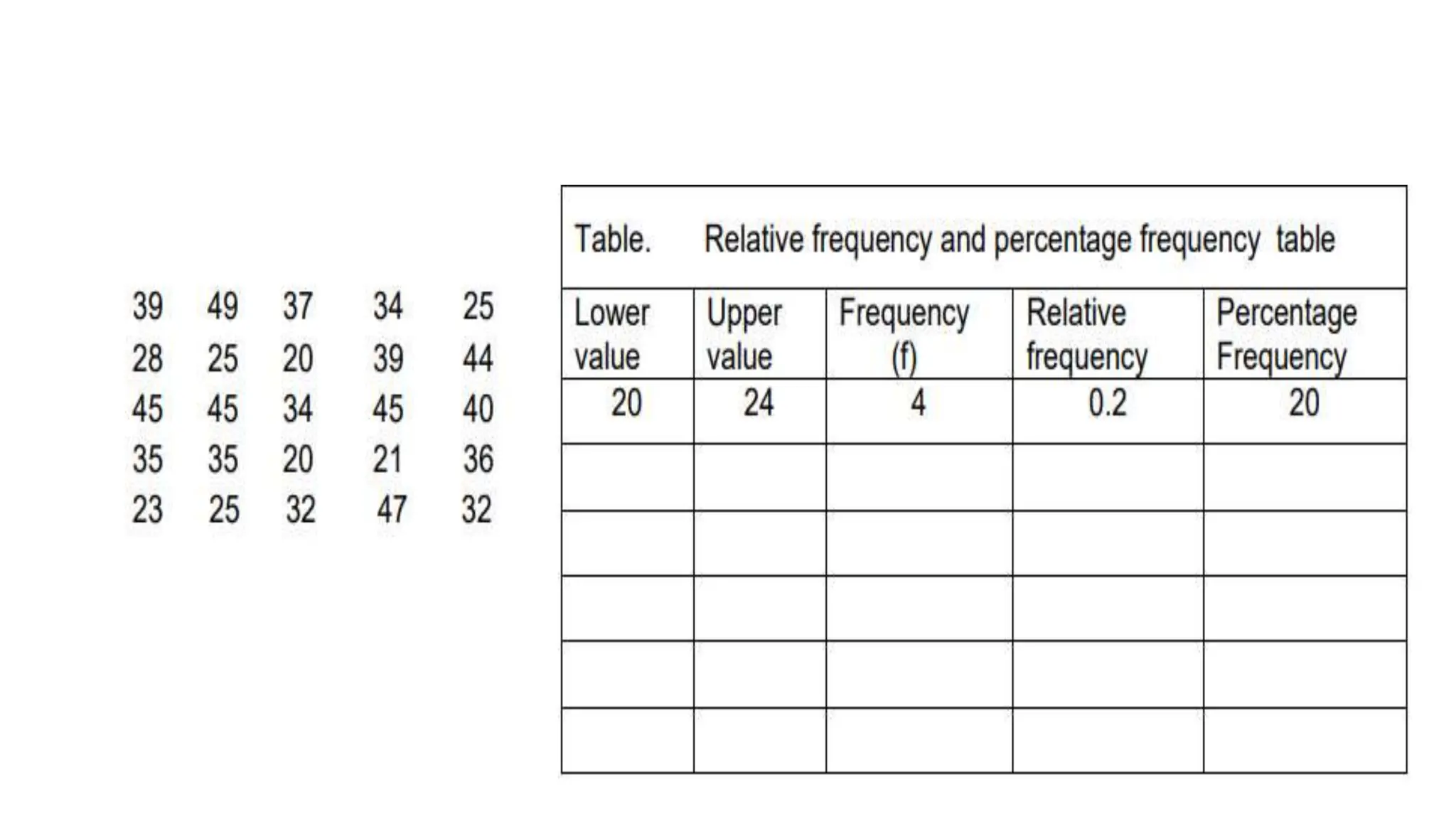
The document explains how to construct frequency distribution tables to organize data through various examples, including surveys on vehicle registration, favorite colors, and service ratings. It outlines the steps for making a frequency table for both ungrouped and grouped data, including determining ranges and class intervals. Additionally, it covers relative and cumulative frequency tables, illustrating their applications with sample data from various scenarios.