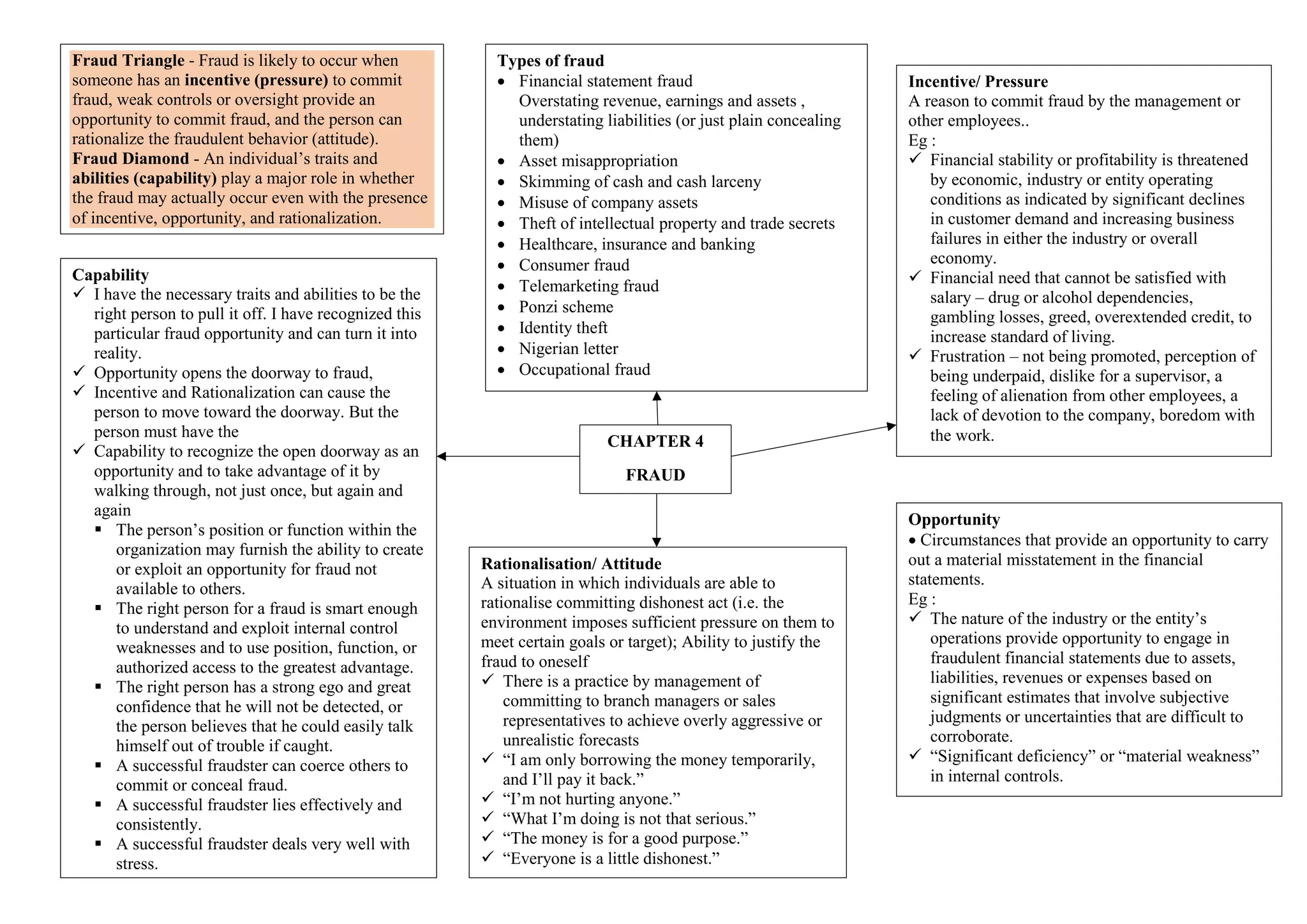
This document discusses fraud and the fraud triangle/diamond concepts. It explains that fraud is likely when there is incentive/pressure, opportunity, and rationalization/attitude (the fraud triangle). Additionally, an individual's capabilities play a role in whether fraud occurs (the fraud diamond). It provides examples of incentives, opportunities, and rationalizations that can contribute to fraud. Finally, it briefly outlines different types of fraud such as financial statement fraud, asset misappropriation, and occupational fraud.