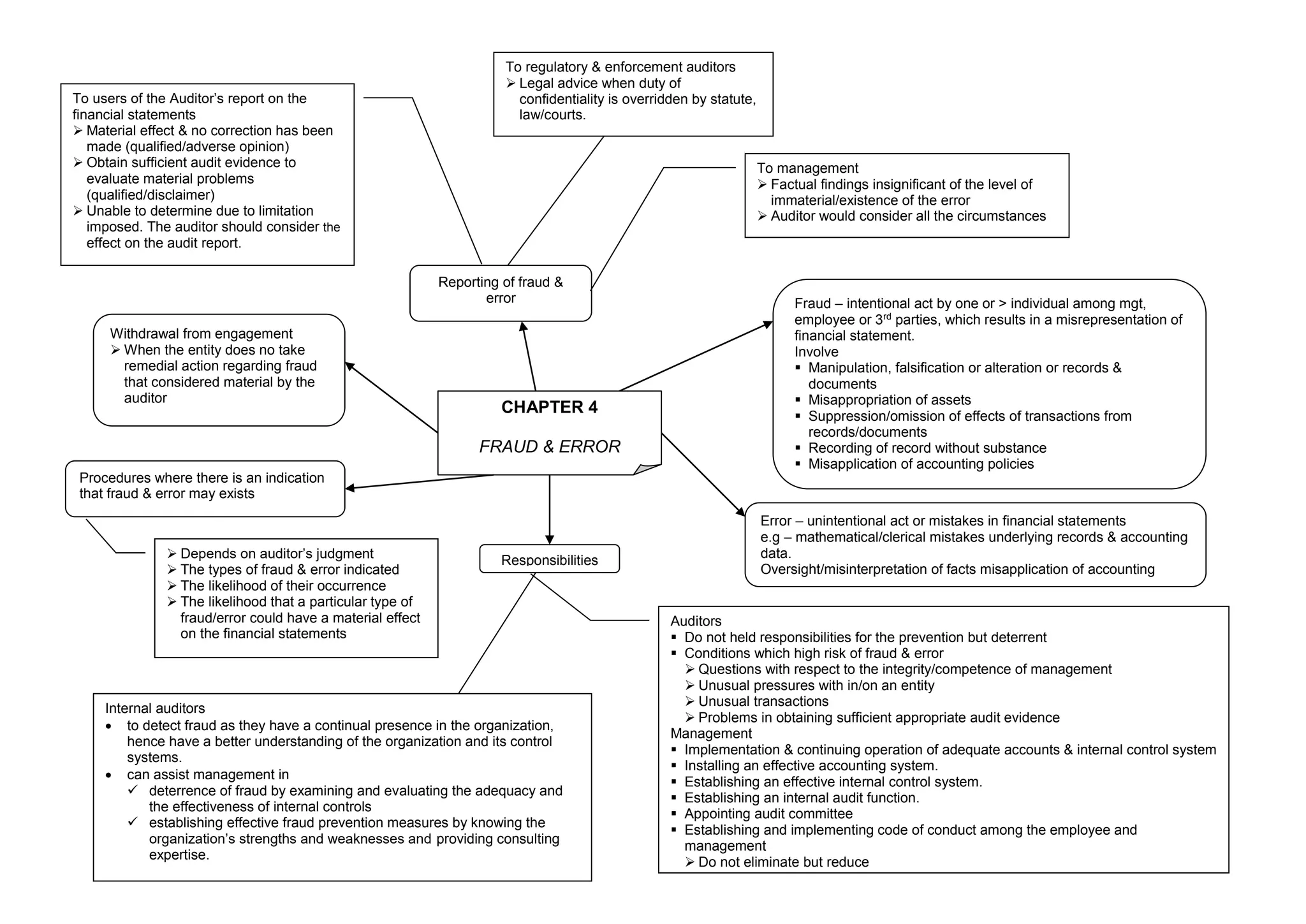
This document discusses fraud, error, and the responsibilities of auditors, management, and internal auditors related to detecting and reporting on financial statement misrepresentations. It defines fraud as intentional acts that misrepresent financial statements, while error refers to unintentional mistakes. Auditors are responsible for deterring, but not preventing, fraud and error. They must evaluate risks and obtain sufficient evidence. Management must implement adequate internal controls and accounting systems to reduce fraud and error risks. Internal auditors can help detect fraud by continually evaluating controls and advising on prevention measures using their deep organization knowledge.