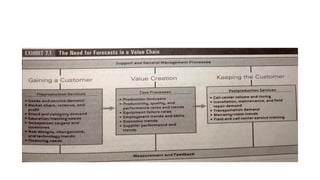
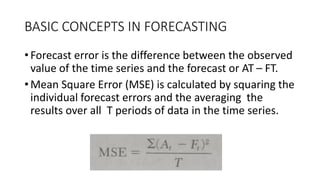
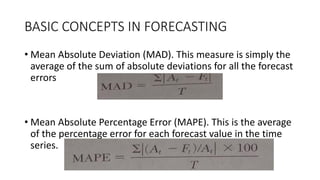
The document outlines the significance of forecasting in operations and its role in various integrated operating systems. It covers basic forecasting concepts including different forecasting time horizons, data patterns in time series, and statistical forecasting techniques. Additionally, it discusses the importance of understanding forecast errors and accuracy through various measures such as mean square error and mean absolute deviation.