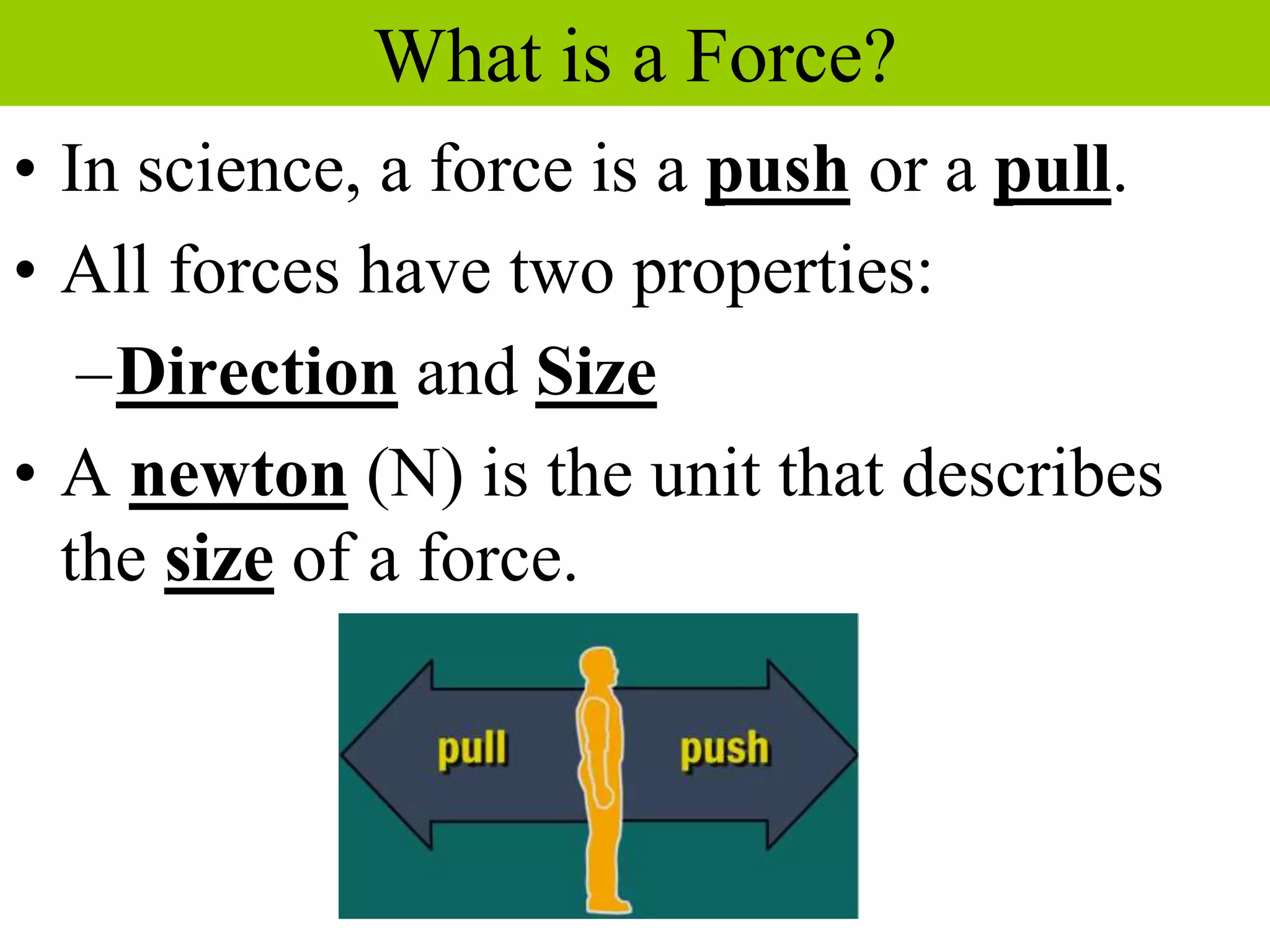
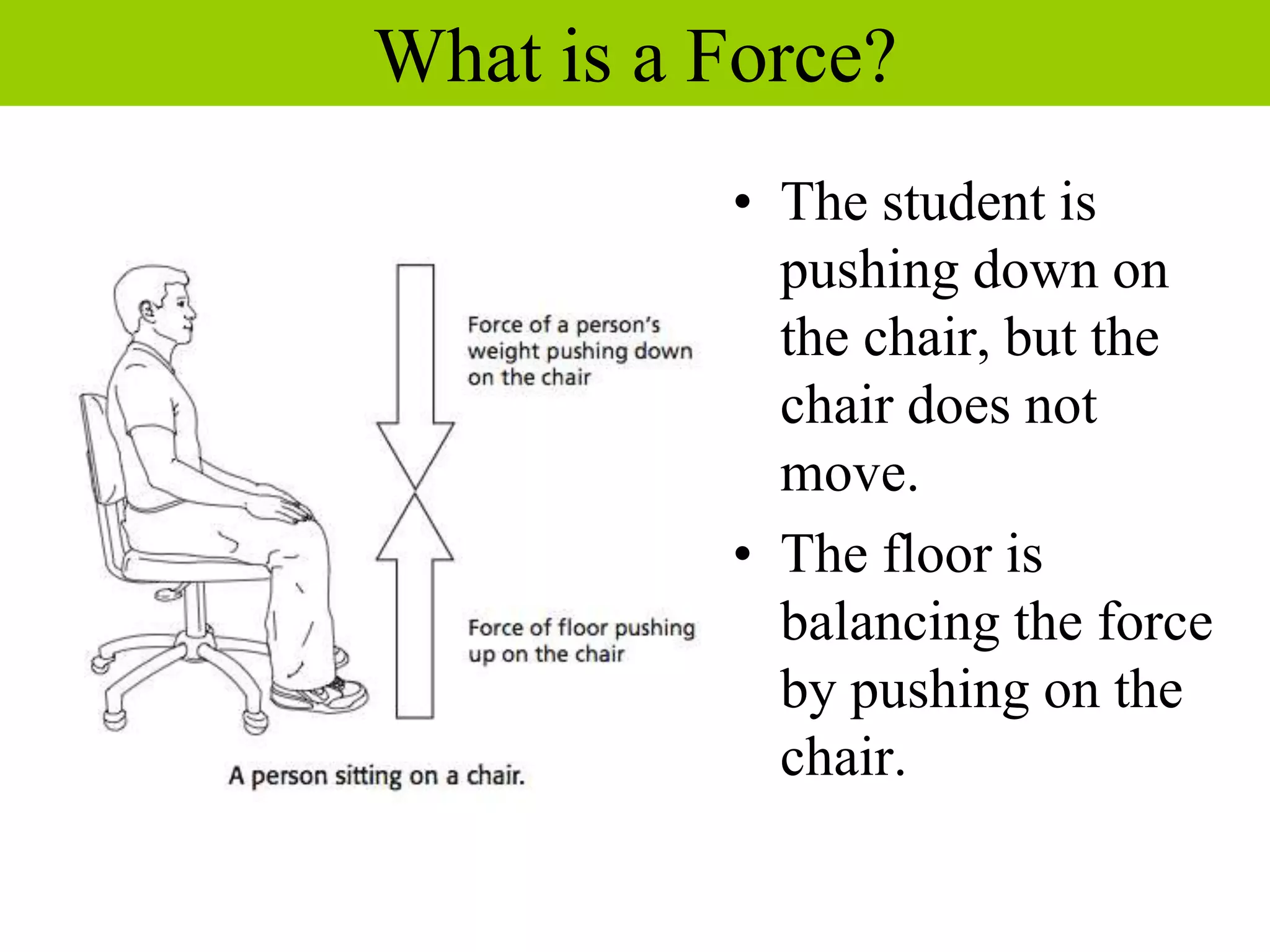
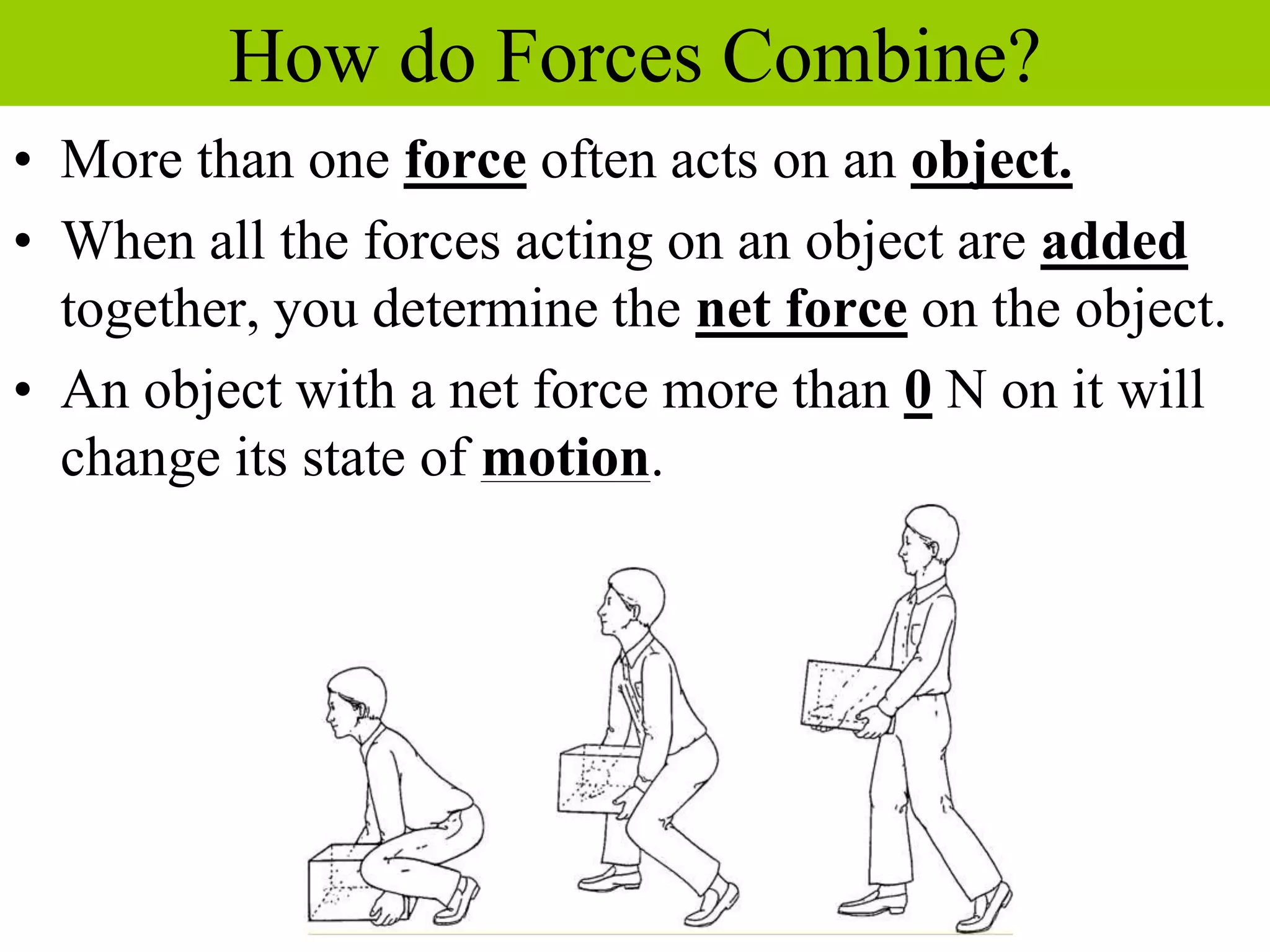
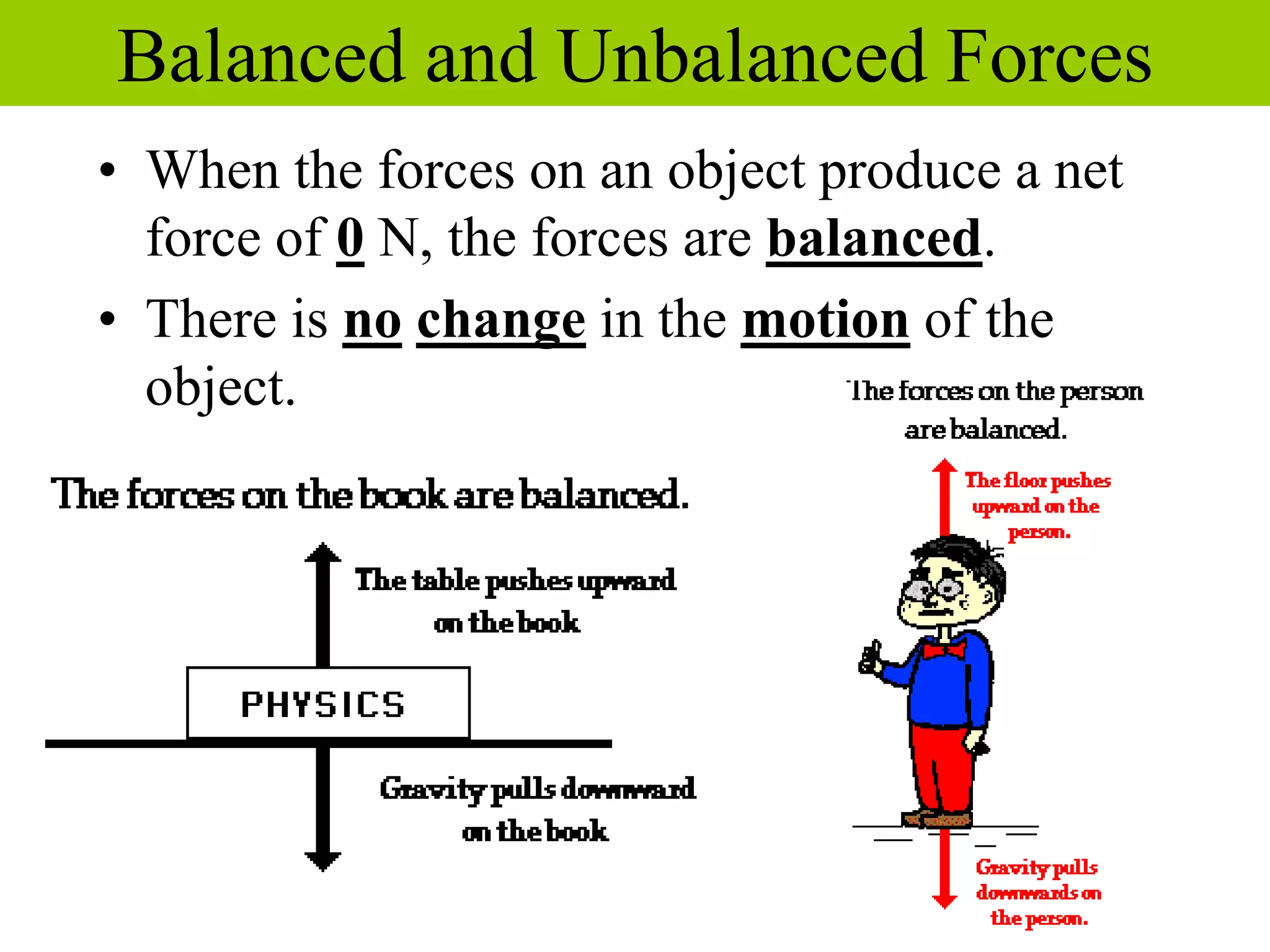
This document discusses forces, how forces combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes how the direction and size of forces are measured. It explains that the net force on an object is determined by adding all individual forces together, and that a net force is needed to change an object's motion. The document also defines friction as the force that opposes the motion of two touching surfaces, and describes the different types of friction and how friction can be both helpful and harmful.