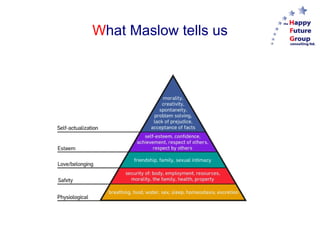
Food security has been a priority since the beginning of agriculture to control resources and reduce vulnerability. However, feeding the projected 9 billion people by 2050 poses major challenges. Food security requires a globalized, knowledge-based approach rather than isolation. Strategies depend on local situations but may include self-sufficiency, imports, trade agreements, outsourcing, or subsidies. Proper analysis of needs, resources, infrastructure, and leadership are needed to develop sustainable food security plans.