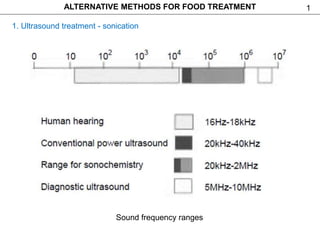
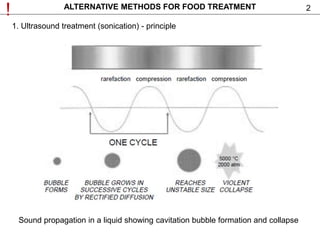
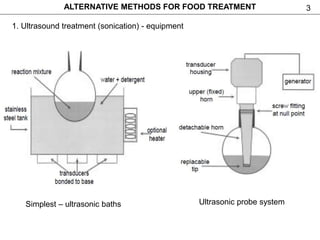
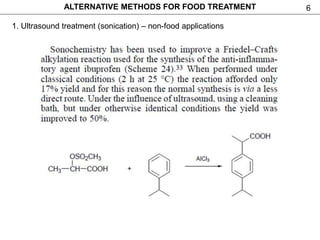
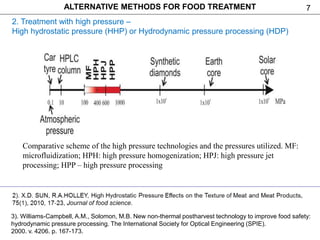
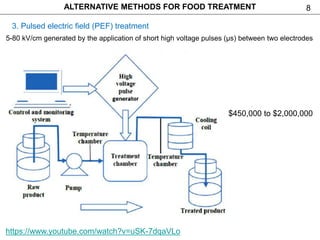
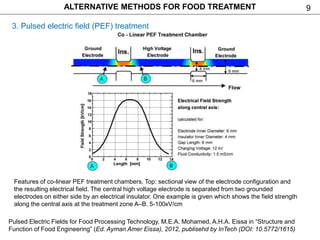
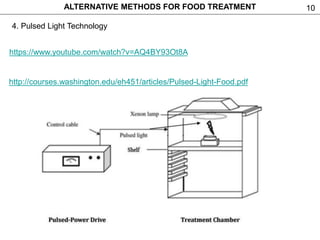
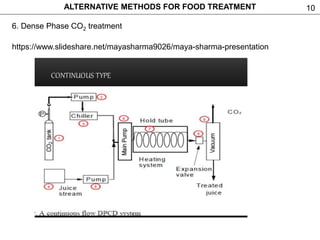
This document discusses alternative methods for food treatment, including ultrasound treatment (sonication), high pressure processing, pulsed electric fields, pulsed light technology, cold plasma treatment, and dense phase CO2 treatment. It provides details on the mechanisms, equipment, and applications of ultrasound treatment for food processing. High pressure processing is described as using pressures from 100-1000 MPa to reduce spoilage microorganisms. Pulsed electric fields apply short high voltage pulses between electrodes at 5-80 kV/cm to treat foods. Videos and additional resources are provided for pulsed light technology, cold plasma treatment, and dense phase CO2 treatment.