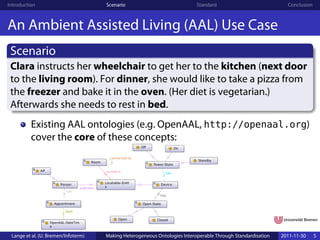
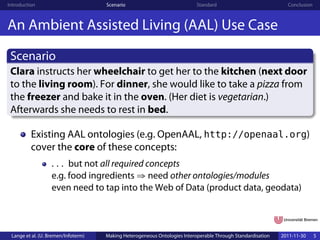
The document discusses making heterogeneous ontologies interoperable through standardization, presenting a scenario of an assisted living environment where different devices like a wheelchair and freezer need to communicate but use different ontologies. It argues for developing a standardized meta ontology language to facilitate integration and interoperability between these diverse ontologies used by different devices with varying knowledge needs.



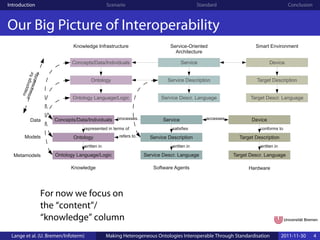

![Introduction Scenario Standard Conclusion
What do Devices Need to Know?
Some of the devices involved:
kitchen light switch
freezer (aware of its contents)
wheelchair (with navigation)
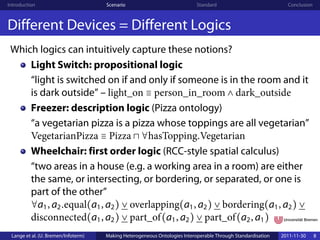
Different Services and Devices need to understand different
aspects of the real world at different levels of complexity.
Quote from the “Hitchhiker”
“Suddenly [the door] slid open. ‘Thank you,’
it said, ‘for making a simple door very
happy.’”
Lange et al. (U. Bremen/Infoterm) Making Heterogeneous Ontologies Interoperable Through Standardisation 2011-11-30 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/foo-111130111808-phpapp02/85/Making-Heterogeneous-Ontologies-Interoperable-Through-Standardisation-9-320.jpg)