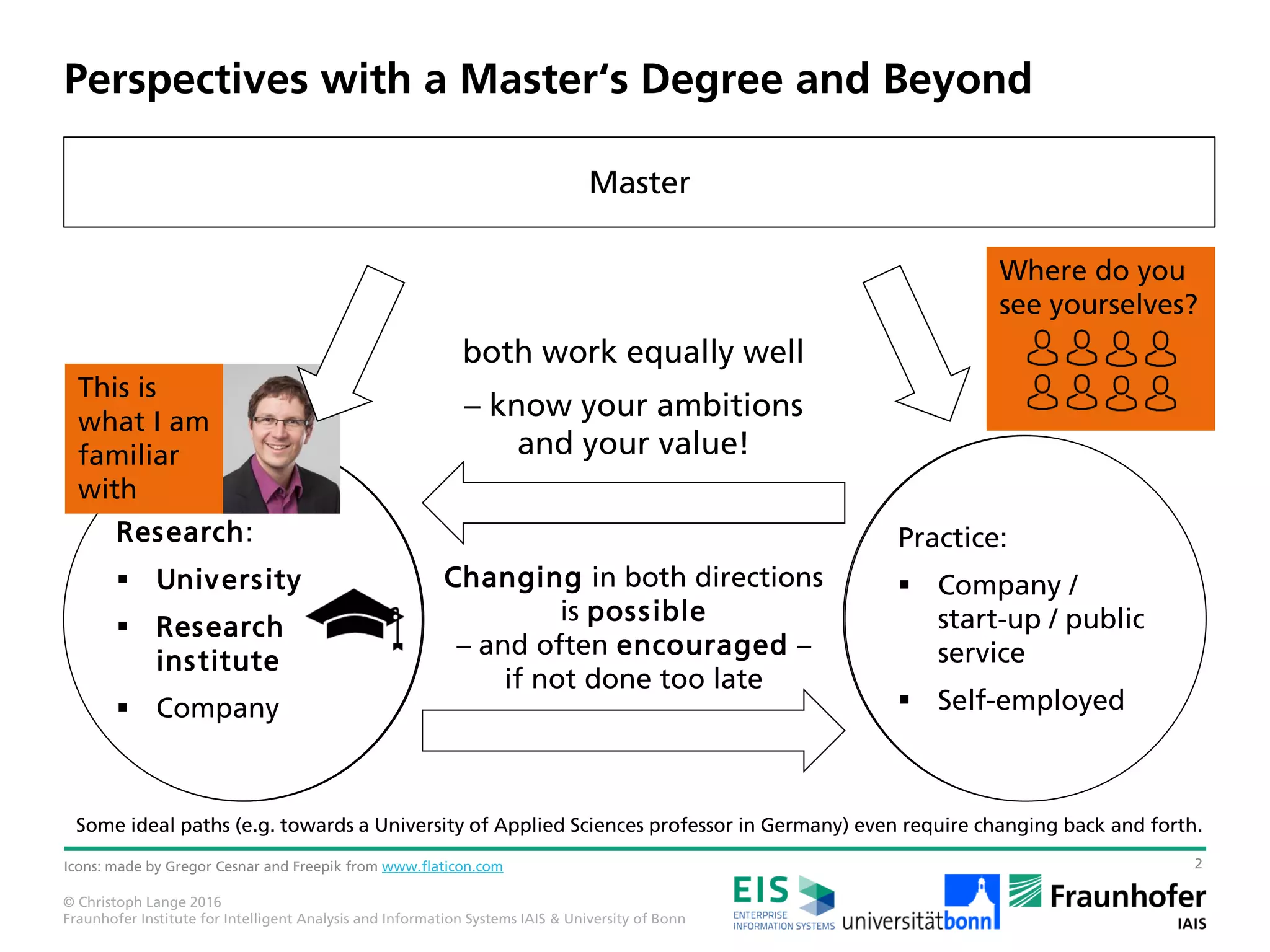
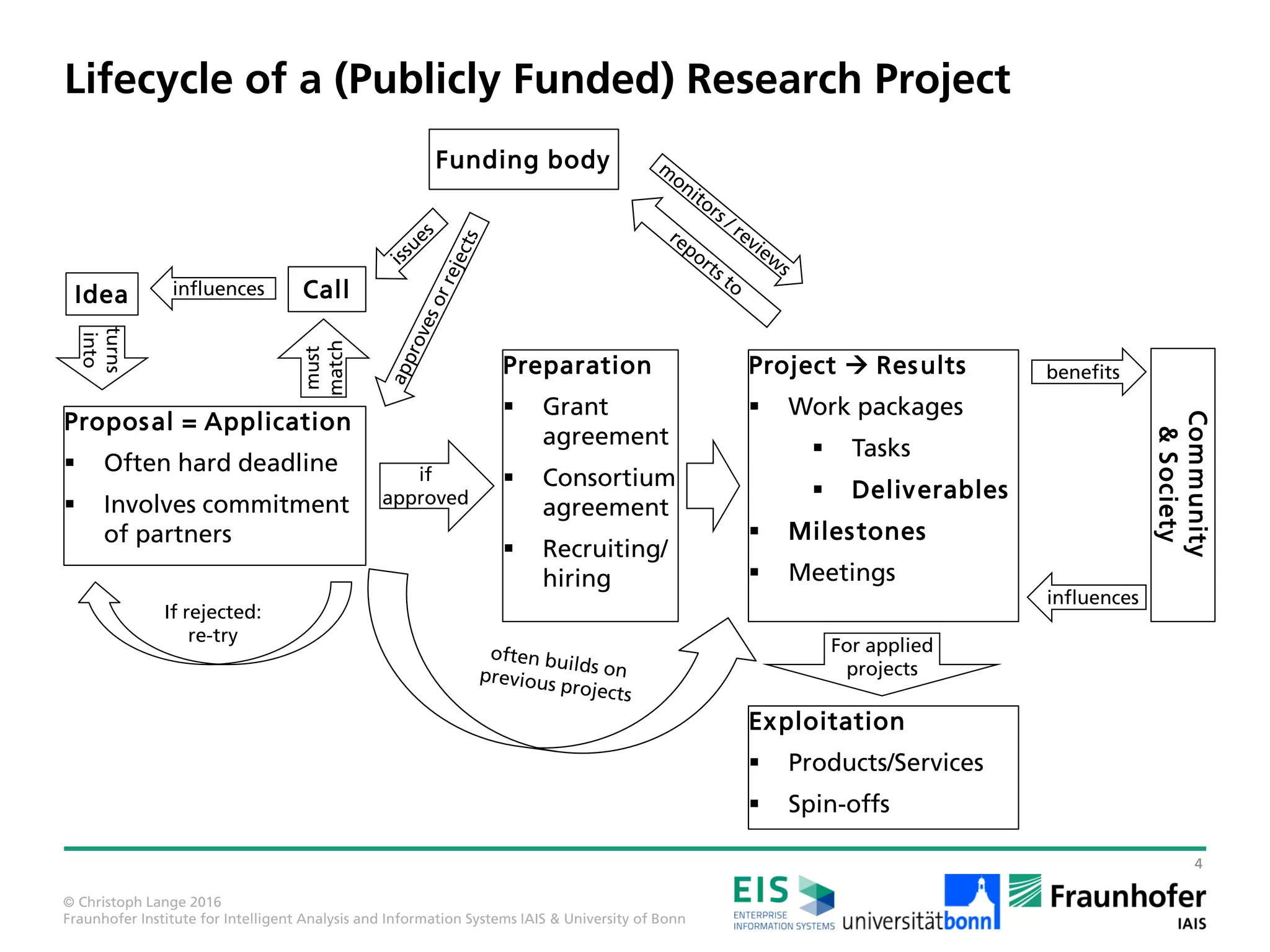
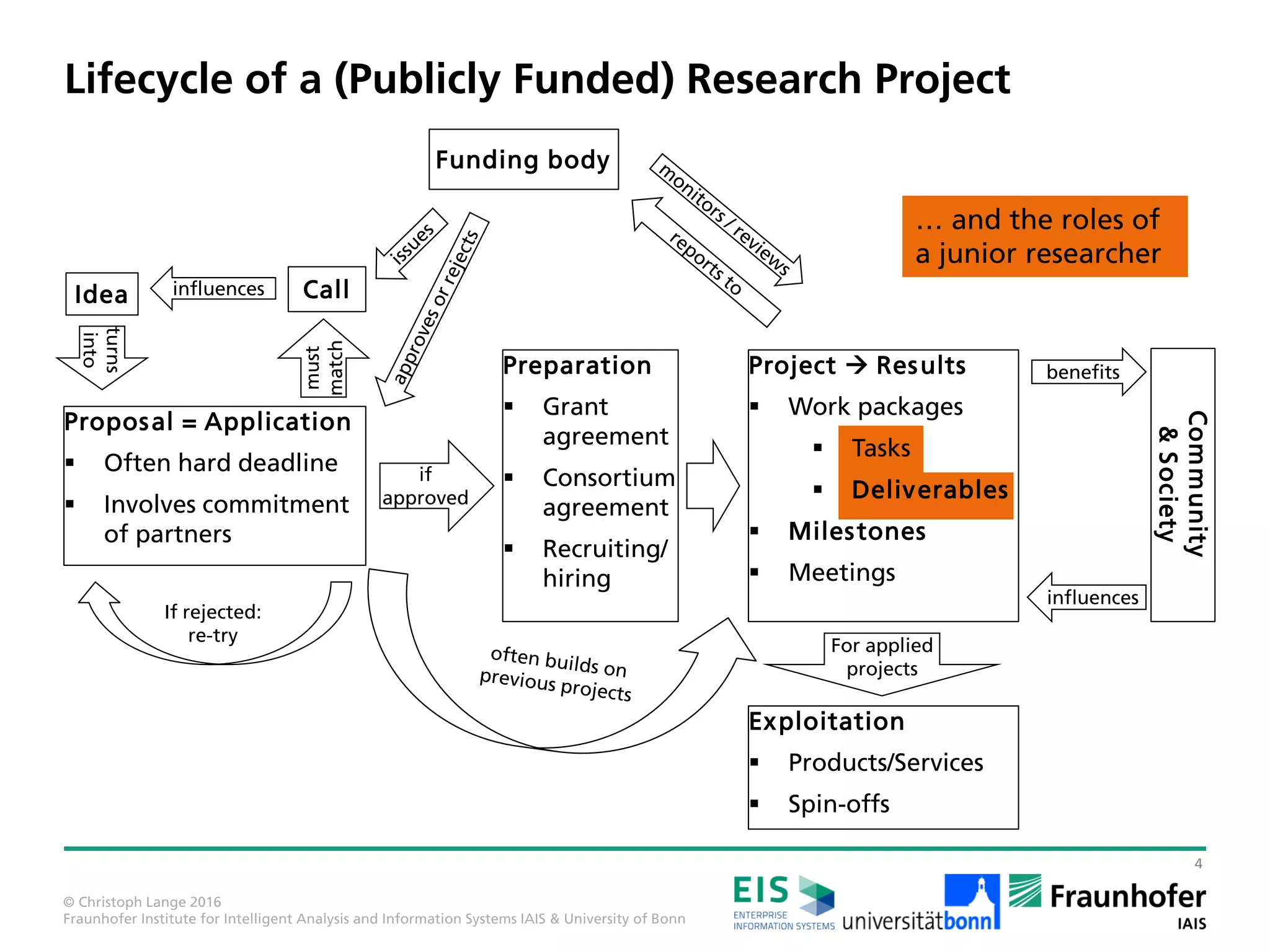
The document outlines various career paths available for individuals with a master's degree in applied computer science, emphasizing the options of practice (industry, startups, and public service) and research (universities and research institutes). It discusses the lifecycle of publicly funded research projects, detailing the process from idea proposal to project results and the importance of effective communication and collaboration among partners. Additionally, it highlights the skills PhD students should acquire, including project management, proposal writing, and teaching experiences, emphasizing the development of both technical and soft skills.