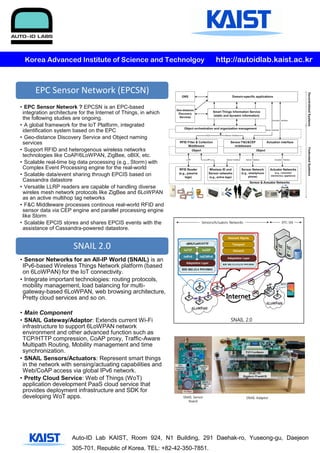
The Auto-ID Lab at KAIST conducts research on Internet of Things connectivity and applications. It consists of 6 professors and over 50 researchers working on projects involving EPC sensor networks, RFID/IoT technologies, big data analytics, and open source implementations of EPC network standards. The lab's research includes an EPC-based framework for IoT integration, heterogeneous wireless sensor networks, real-time big data processing, and scalable data sharing platforms.