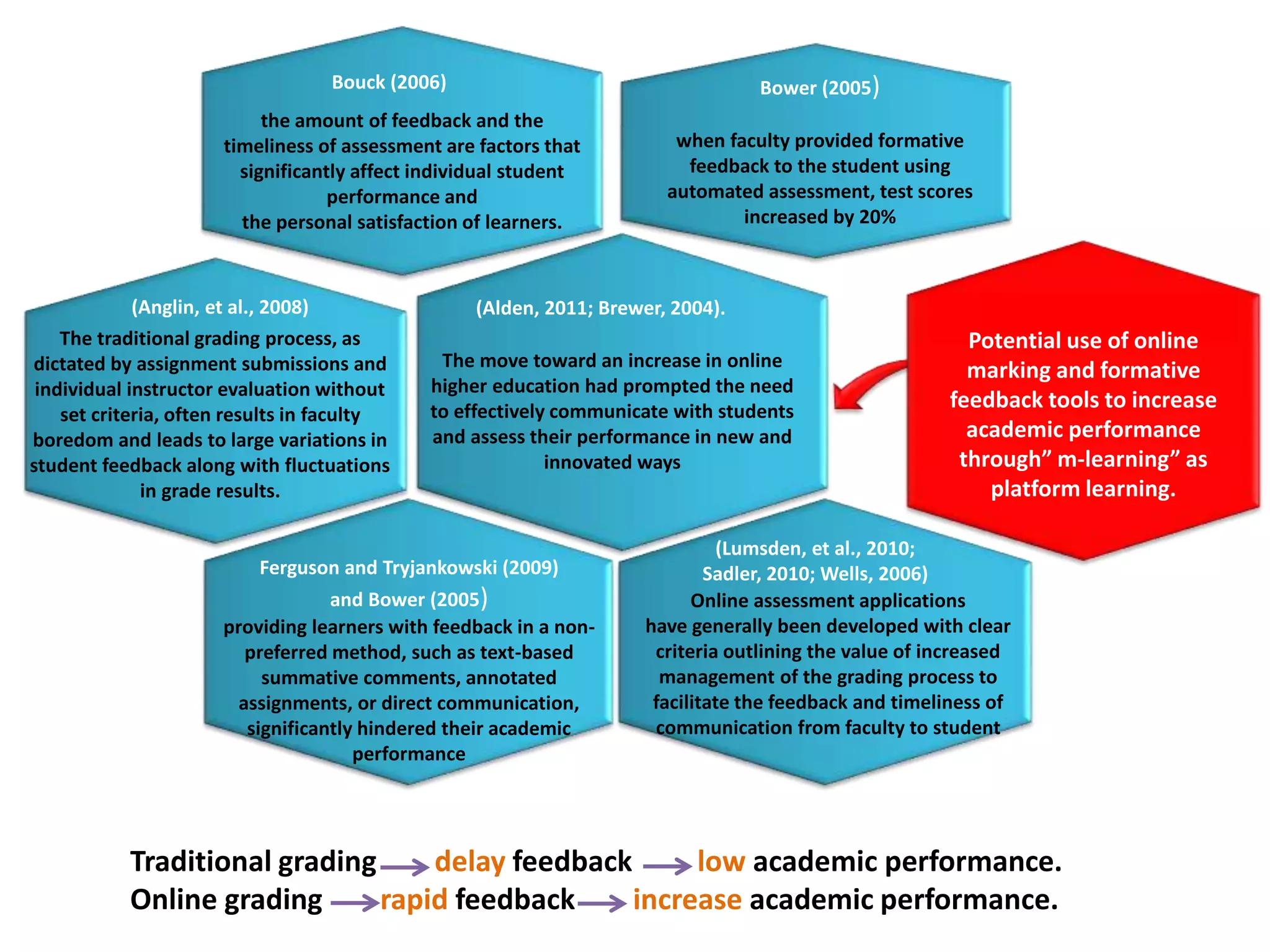
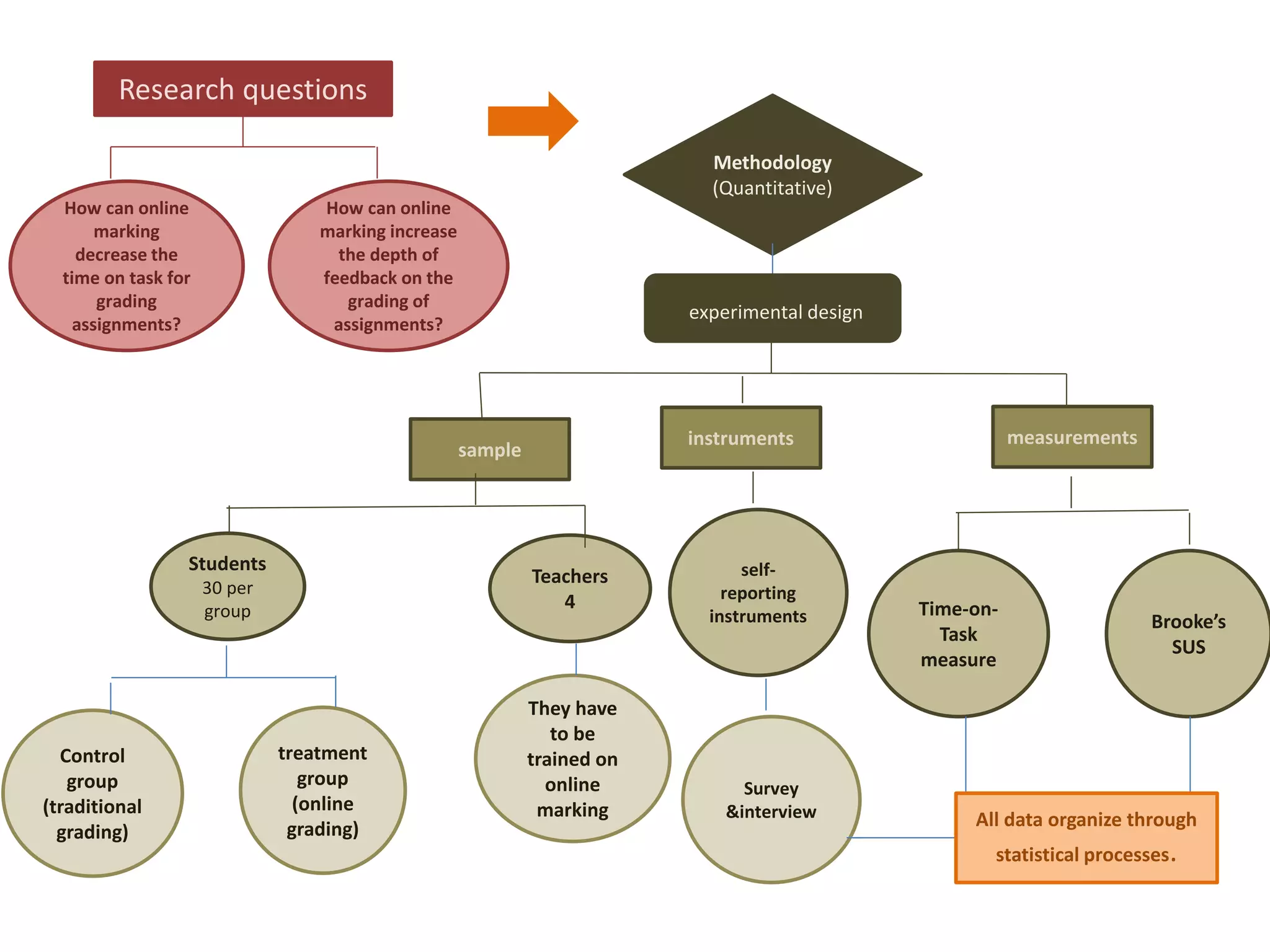
Traditional grading methods often result in delayed feedback and variation in student scores due to lack of set criteria. Research shows providing timely formative feedback through automated online assessment increases student test scores by 20%. Online grading tools may standardize feedback and assessment, increasing academic performance while reducing faculty grading time. This study aims to determine if online marking decreases faculty grading time and increases depth of feedback compared to traditional grading methods.