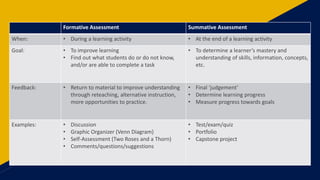
This document discusses strategies for providing effective and efficient feedback to students. It suggests evaluating multiple aspects of feedback in order to improve it while reducing the time spent on feedback. Some strategies discussed include focusing feedback on the most important points, decreasing unnecessary feedback, increasing engagement with feedback, and using tools like rubrics, feedback banks, and micro-rewrites to make feedback more targeted and useful for students.