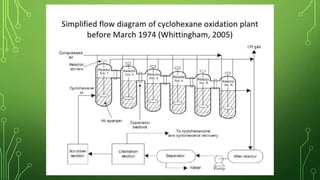
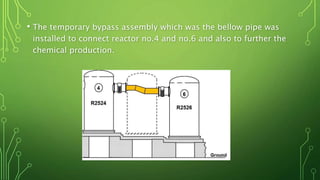
The Flixborough disaster occurred on June 1, 1974, caused by an explosion at the Nypro chemical plant resulting from a ruptured temporary bypass system leaking cyclohexane, which ignited and led to a massive vapor explosion. The document explains the mechanisms behind stress corrosion cracking (SCC) that contributed to the failure, detailing the stages of crack initiation, propagation, and brittle fracture, alongside the environmental factors and worker negligence involved. Recommendations for preventing similar incidents include careful steel selection, fabrication practices, surface treatments, stress design considerations, and protective coatings.