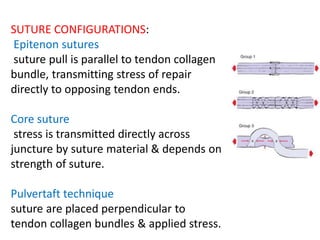
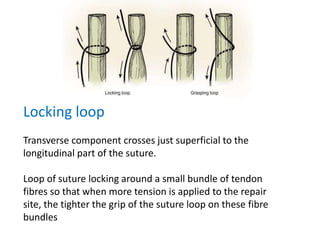
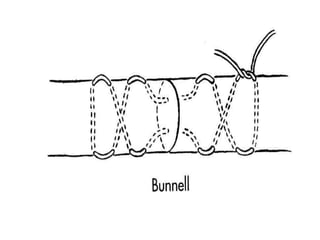
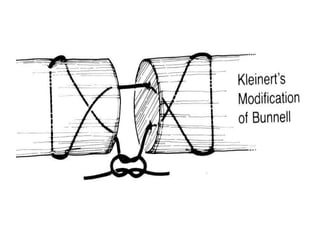
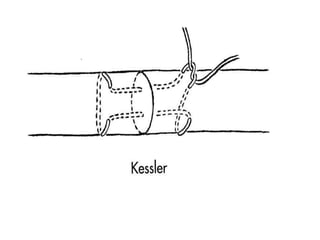
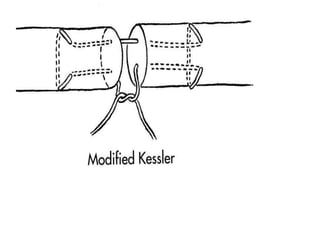
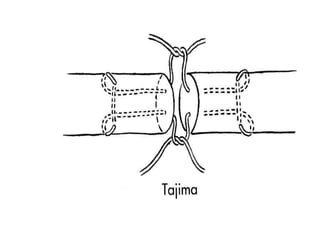
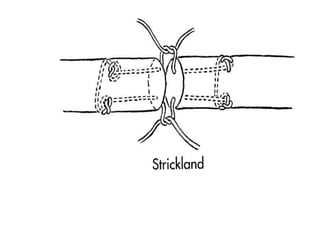
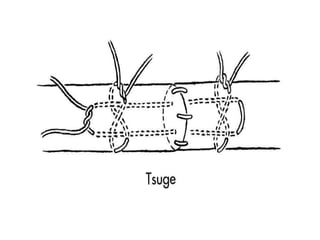
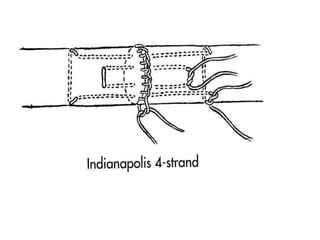
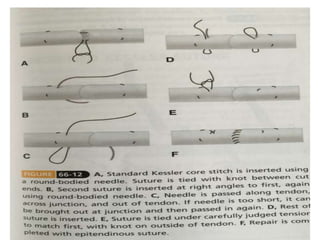
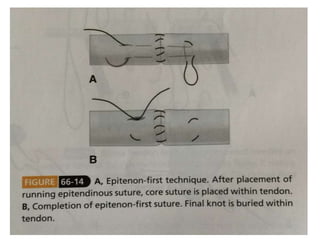
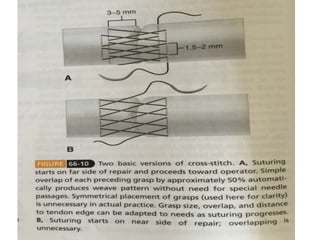
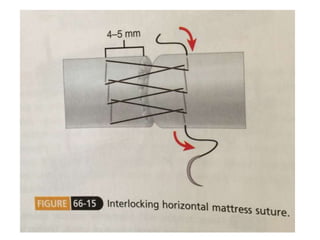
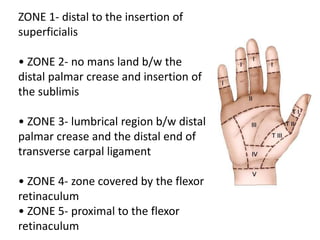
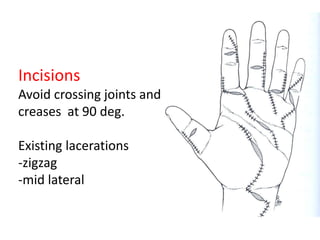
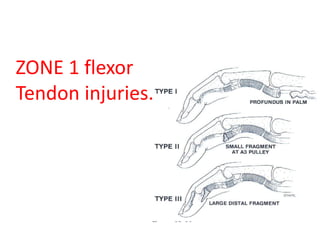
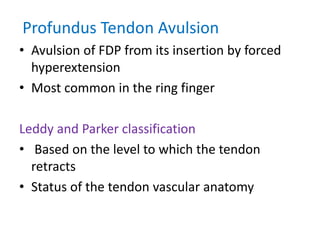
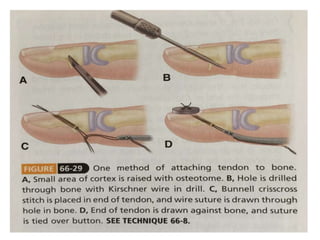
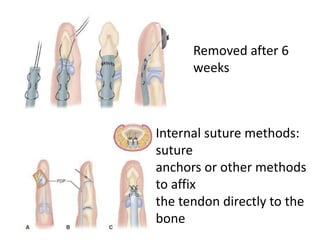
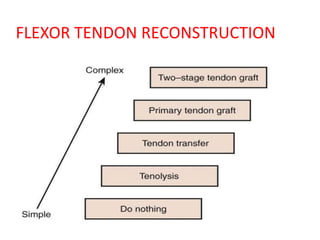
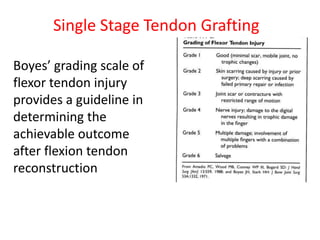
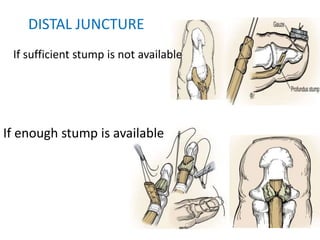
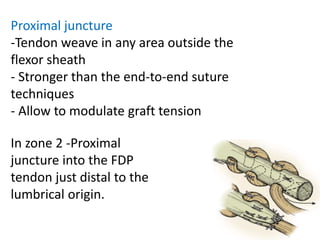
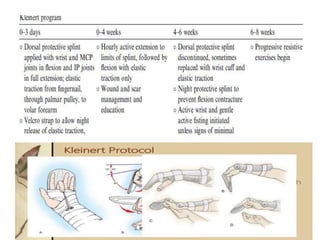
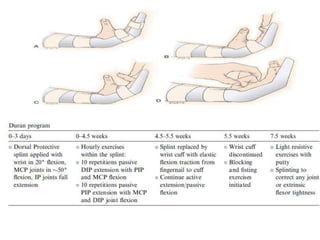
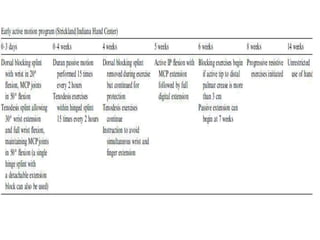
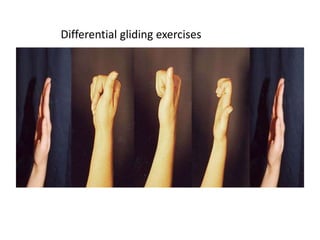
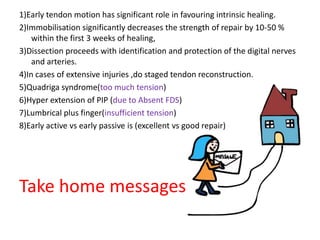
The document discusses the complexities of flexor tendon repair, including repair techniques, healing phases, and rehabilitation protocols. It outlines the critical considerations for tendon repair, the importance of suture techniques, and the classification of tendon injuries by zones. Additionally, it highlights complications, grafting principles, and suggestions for postoperative rehabilitation to enhance recovery outcomes.