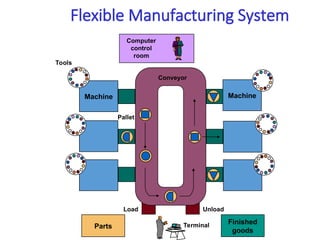
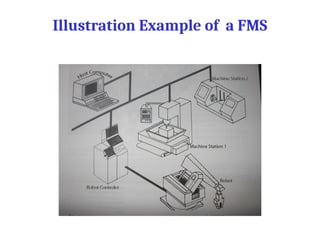
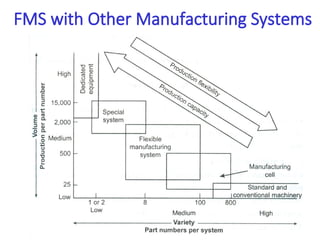
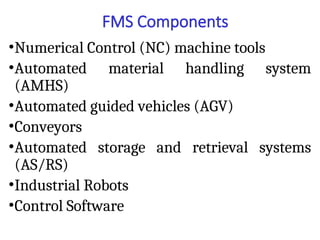
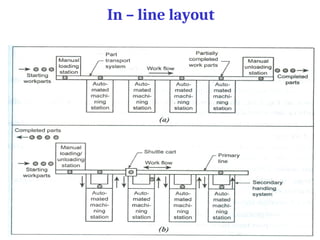
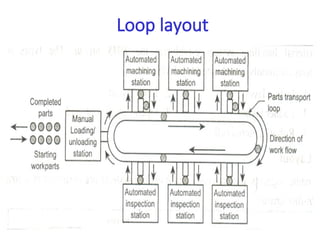
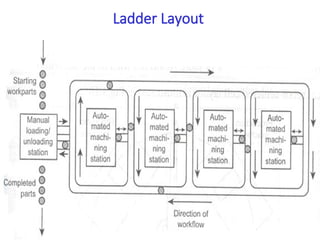
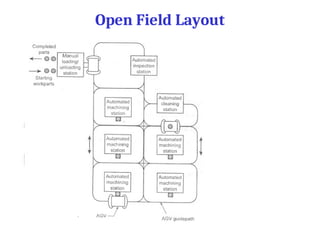
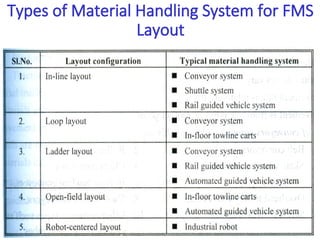
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a production system using numerically controlled machines connected by automated transportation, managed by dedicated computers. It offers flexibility in adapting to engineering changes, improves efficiency, and supports a variety of products through various layouts and components. FMS applications include processes like machining, assembly, and inspection, delivering advantages such as reduced setup times and improved product quality.