This document discusses linked spatial data and spatial data infrastructures. It provides examples of using URIs to represent spatial things and linking spatial datasets. Key points discussed include:
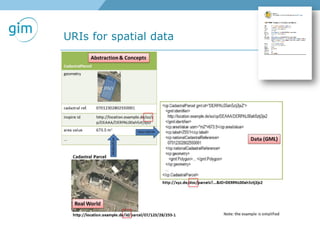
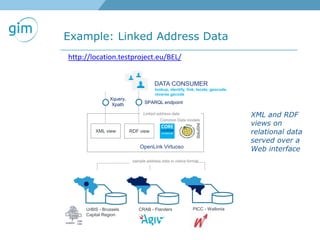
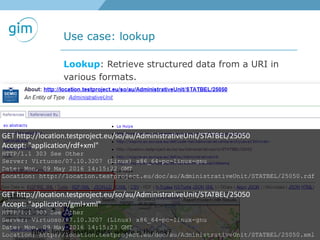
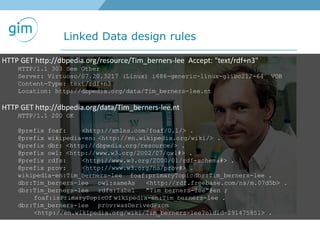
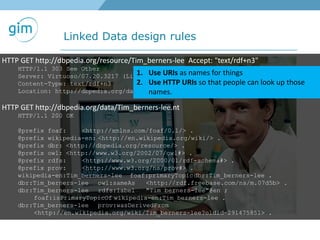
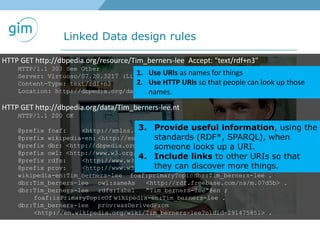
1. Using URIs and HTTP to identify spatial things like locations and allowing information about those things to be retrieved in different formats like RDF and GML.
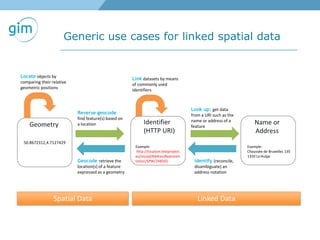
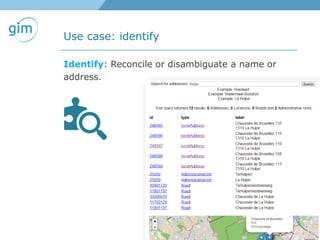
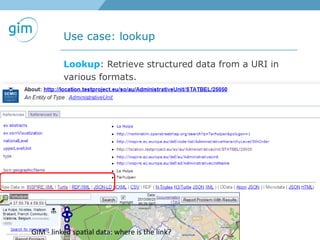
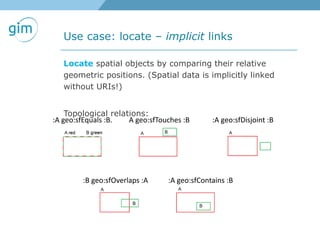
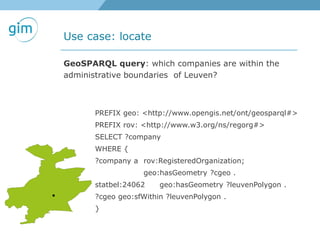
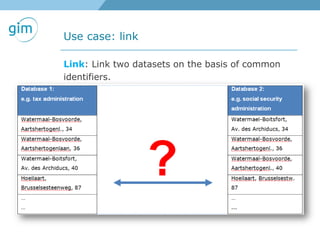
2. Examples of using linked spatial data for tasks like looking up information, identifying locations, linking datasets, and querying spatial relationships between objects.
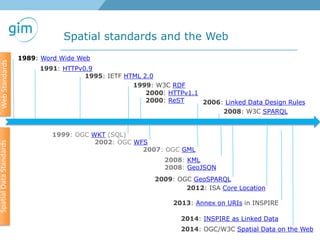
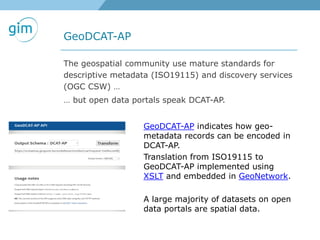
3. Initiatives to link spatial metadata standards like ISO19115 to open data schemas like DCAT-AP to make spatial data more accessible on the web.
4. Revenue models for linked data providers including public funding, advertisements, and


![Not all Linked Data is Open Data…
Open data is data available under an open licence (open
data and content can be freely used, modified, and
shared by anyone for any purpose e.g. CC0)
[OpenDefinition]
There is also Linked Closed Data, e.g. for privacy or
commercial reasons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flagislinkedopendatastijngoedertier-160517112630/85/Flagis-linked-open_data_stijn_goedertier-6-320.jpg)