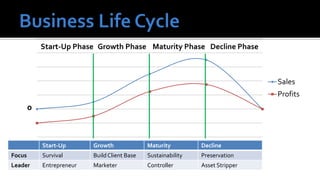
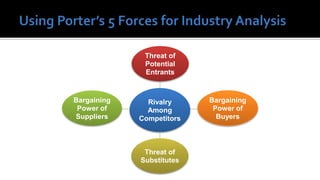
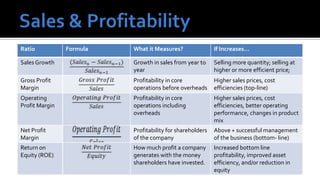
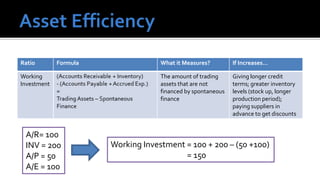
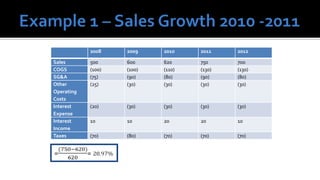
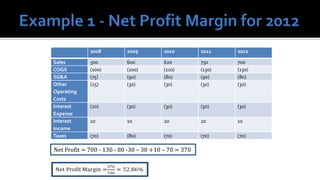
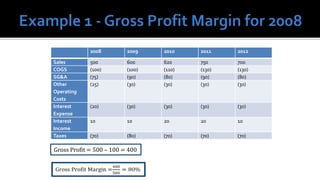
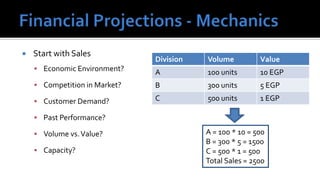
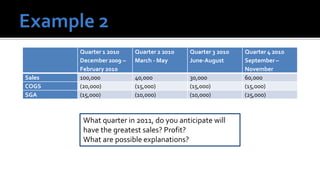
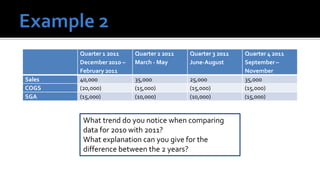
The document outlines key financial concepts for businesses, including sales profitability, asset efficiency, liquidity, and solvency while emphasizing the importance of setting targets and measuring progress against industry peers. It discusses various financial ratios and their implications for business performance across different phases of the business life cycle and highlights the necessity of feasibility studies and market research. Additionally, it addresses cost management strategies and the influence of macroeconomic factors on business operations.