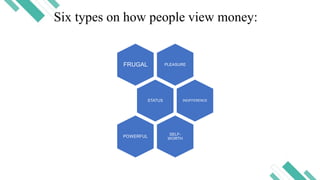
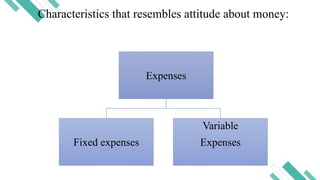
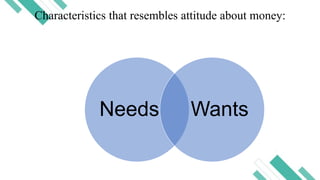
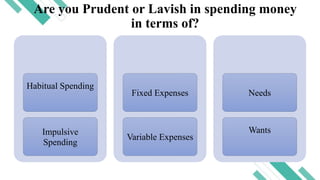
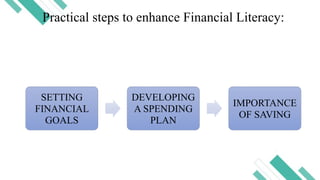
Financial literacy is defined as the ability to use knowledge and skills to manage financial resources for long-term security, encompassing understanding financial products, concepts, budgeting, and savings. In the Philippines, a significant portion of the population lacks financial literacy, with studies revealing low rates of bank account ownership and awareness of key financial concepts. The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas has initiated efforts to promote financial education, including stakeholder expos and national strategies for financial inclusion.